Definition: head trauma through strong rotational and shearing force
Epidemiology
high mortality and a significant cause of death
Etiology
violent shaking of a child
Pathophysiology
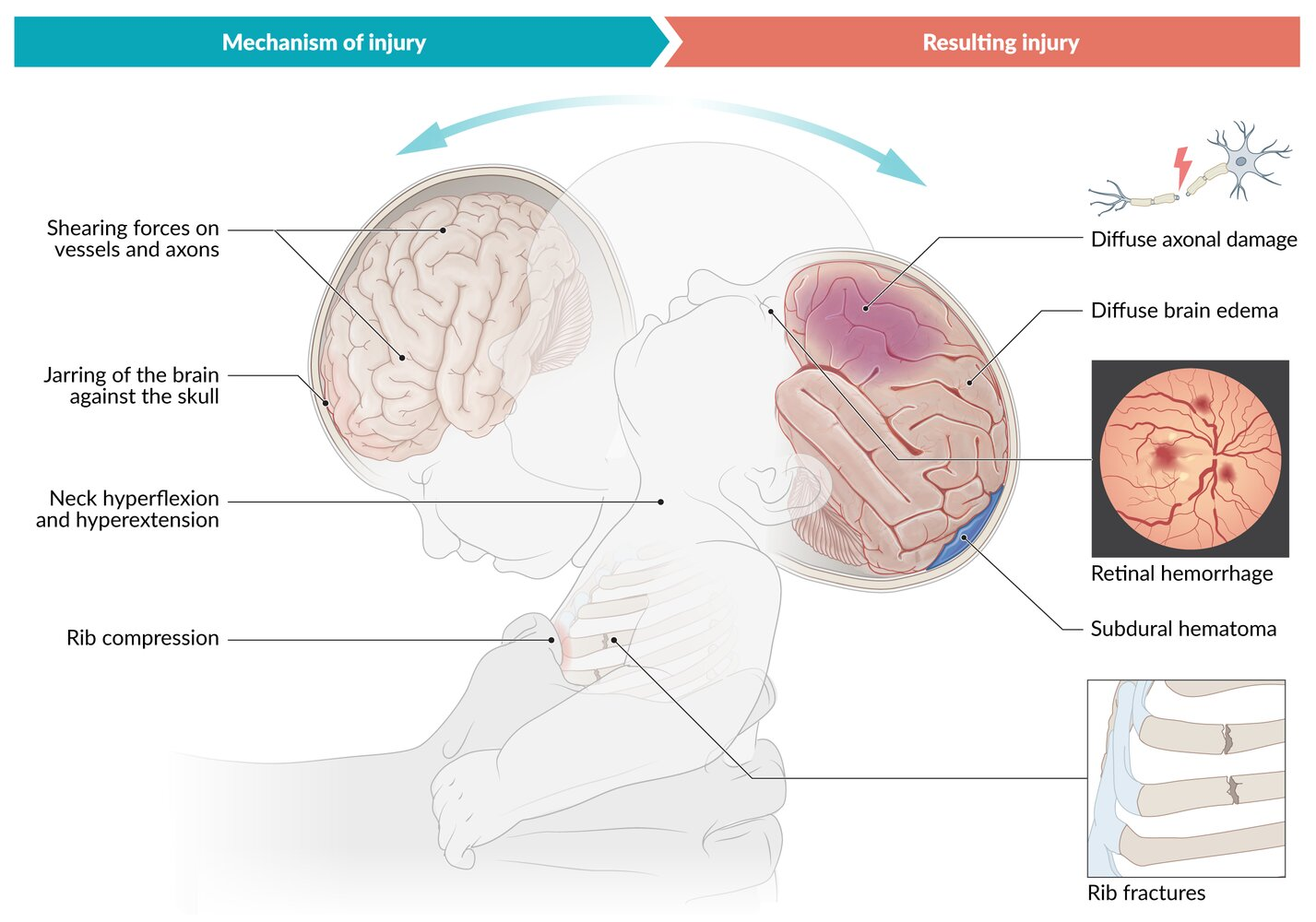
- Rotational and shearing forces → shearing off of bridging veins → subdural hematoma
- Shaking of the child with a weak neck support → respiratory problems and apnea → hypoxia → brain edema and ischemia → diffuse axonal damage
Clinical features
- Inconsistent or implausible history from caretakers
- Injuries are hardly evident or entirely absent on physical exam.
- Retinal hemorrhages
- Irritability or lethargy
- Seizures
- Vomiting
- Tense fontanelle
- Rib fractures
Diagnostics
- Non-contrast CT
- Subdural hematomas and/or subarachnoid hemorrhage of varying ages
- Reversal sign: diffuse blurring of the grey-white matter interface
- Diffuse punctate hemorrhages
Treatment
- Always notify Child Protective Services.
- Medical practitioners are obligated to report child abuse even if that means breaking patient-physician confidentiality.
- Reasonable suspicion is sufficient; confirmation of abuse or neglect is not required for reporting purposes.
- Interview child and parent/caregiver separately if possible.
- Keep verbatim record.