Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
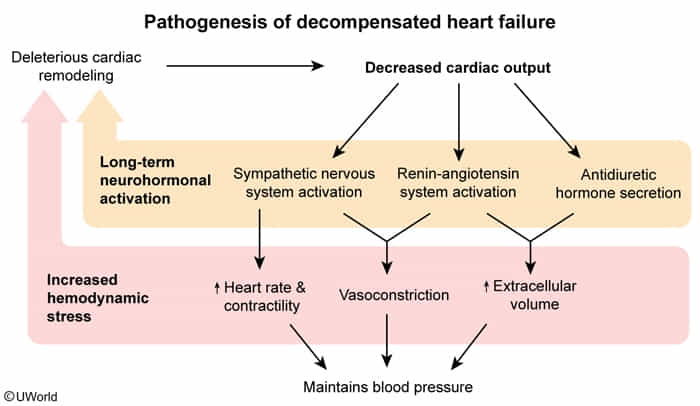
- Pressure Overload (e.g., chronic hypertension, aortic stenosis) → Concentric Hypertrophy (sarcomeres in parallel) → initially HFpEF → decompensates to HFrEF.
- Volume Overload (e.g., aortic/mitral regurgitation, Ischemic Cardiomyopathy) → Eccentric Hypertrophy (sarcomeres in series) → HFrEF.
Clinical features
Diagnostics
Pathology
- Sputum analysis in patients with pulmonary edema may show heart failure cells (hemosiderin-containing cells).
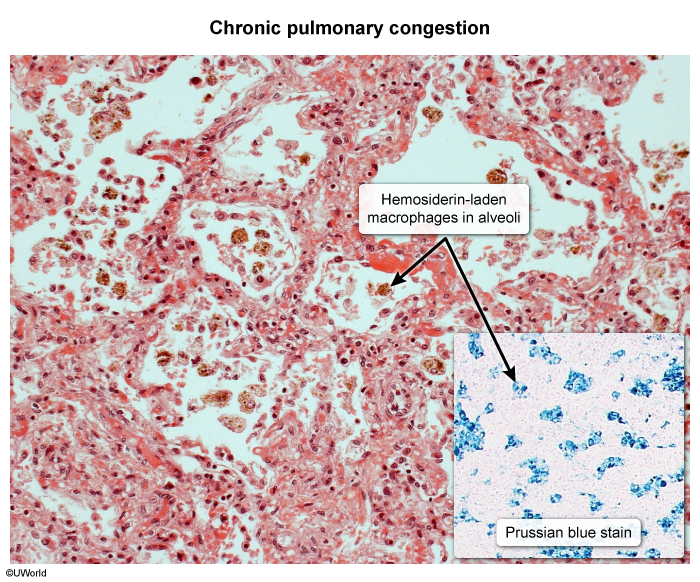
- Pulmonary venous congestion may result in intra-alveolar bleeding. Macrophages that subsequently phagocytose the erythrocytes are called “heart failure cells.” These cells may also be detected in the sputum of patients with pulmonary infarction, vasculitis, or aspiration of blood.
- Their color is most likely due to hemosiderin from ingested erythrocytes.
ECG
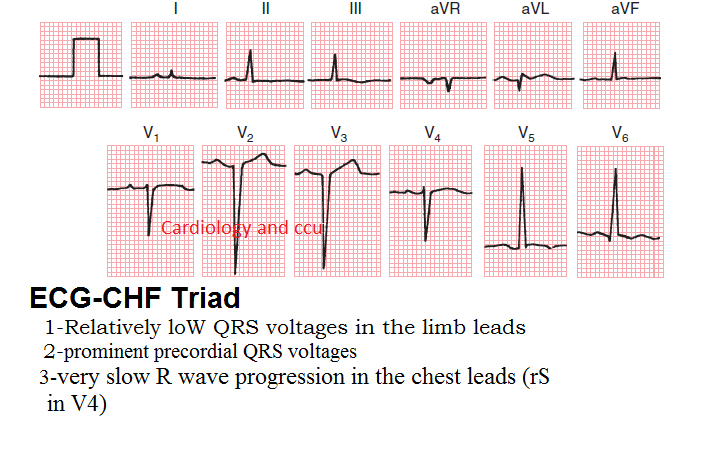
- ECG-CHF triad
- Low QRS voltages in the limb leads (caused by peripheral edema in CHF patients)
- Left ventricular hypertrophy (prominent precordial QRS voltages)
- Very slow R wave progression in chest leads (rS in V4)
Treatment
| Agent | Mortality Benefit |
|---|---|
| Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (e.g., sacubitril-valsartan) OR ACE inhibitor (e.g., lisinopril) OR Angiotensin II receptor blocker (e.g., losartan) | Yes |
| Beta blocker (e.g., metoprolol, carvedilol) | Yes |
| Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (e.g., spironolactone, eplerenone) | Yes |
| Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor (e.g., dapagliflozin, empagliflozin) | Yes |
| Diuretic (e.g., furosemide, metolazone) | No, only improves symptoms & reduces hospitalization. |
| Digoxin | No, only reduces hospitalization. |
Explanation
The primary role of MRAs (Spironolactone, Eplerenone) in HFrEF is neurohormonal blockade, not diuresis.
- Primary Mechanism (Mortality Benefit):
- In heart failure, the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) is chronically activated.
- Persistently high aldosterone levels are directly harmful to the heart, causing:
- Myocardial Fibrosis: Promotes collagen deposition, leading to stiffening of the ventricle.
- Adverse Cardiac Remodeling: Contributes to the progressive enlargement and dysfunction of the heart.
- Endothelial Dysfunction & Inflammation: Worsens vascular health.
- MRAs directly block the aldosterone receptor, preventing these cardiotoxic effects. This slows disease progression and improves survival.
- Secondary Mechanism (Diuresis):
- MRAs have a mild diuretic effect by promoting sodium/water excretion and potassium retention in the collecting ducts.
- This effect is weak and is not the reason they are a cornerstone of therapy.
HFrEF (EF ≤40%): Chronic Management
- Goal: Mortality reduction via “Quadruple Therapy” or the “4 Pillars”.
- 1. ARNI (Sacubitril/Valsartan): Preferred over ACEi/ARB. A 36-hour washout period is required when switching from an ACE inhibitor.
- 2. β-Blockers: Only use evidence-based ones (Carvedilol, Metoprolol Succinate, Bisoprolol). Do not start or increase during acute decompensation.
- 3. MRAs (Spironolactone, Eplerenone): Block aldosterone-mediated fibrosis. Monitor for hyperkalemia.
- 4. SGLT2 Inhibitors (-flozins): Reduce mortality and hospitalizations, even in non-diabetics.
- Symptom & Add-On Therapy:
- Loop Diuretics (e.g., Furosemide): For congestion relief (dyspnea, edema). No mortality benefit.
- Hydralazine + Isosorbide Dinitrate: Provides mortality benefit in African American patients (NYHA III-IV) on optimal therapy, or as an alternative for those intolerant to ACEi/ARB/ARNI.
- MOA: Hydralazine (arterial vasodilator) reduces afterload; Isosorbide dinitrate (venodilator) reduces preload.
- Ivabradine: Reduces hospitalizations. Use in stable patients on max βB dose with sinus rhythm & HR ≥70 bpm.
- MOA: Selectively inhibits the If (“funny”) current in the SA node to slow heart rate.
HFpEF (EF ≥50%): Chronic Management
- Goal: Control symptoms and comorbidities (especially HTN).
- Key Therapies:
- SGLT2 Inhibitors (-flozins): Proven to reduce HF hospitalizations.
- Diuretics: For fluid overload symptoms.
- Manage comorbidities aggressively (HTN, AFib, obesity, diabetes).
Acute Decompensated HF (ADHF)
- Goal: Relieve congestion (“wet”) and improve perfusion (“warm”).
- Mnemonic “LMNOP” for initial management:
- Lasix (IV Loop Diuretics): Mainstay for volume removal.
- Morphine: Historically used for anxiolysis and venodilation (rarely used now).
- Nitrates (e.g., Nitroglycerin): IV vasodilators to reduce preload and afterload if BP is adequate.
- Oxygen: If patient is hypoxic (SpO2 <90%).
- Position: Have the patient sit upright to decrease venous return.
- “Warm & Wet” (Congested but well-perfused):
- Tx: IV Loop Diuretics + IV Vasodilators (Nitroglycerin).
- “Cold & Wet” (Congested and poorly perfused/hypotensive):
- Tx: IV Loop Diuretics + Inotropes (Dobutamine, Milrinone) to improve cardiac output. May require vasopressors if in shock.
Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs)
- Drug names: sacubitril/valsartan
- Sacubitril inhibits neprilysin, increasing beneficial ANP/BNP, while valsartan blocks the AT1 receptor (RAAS inhibition).
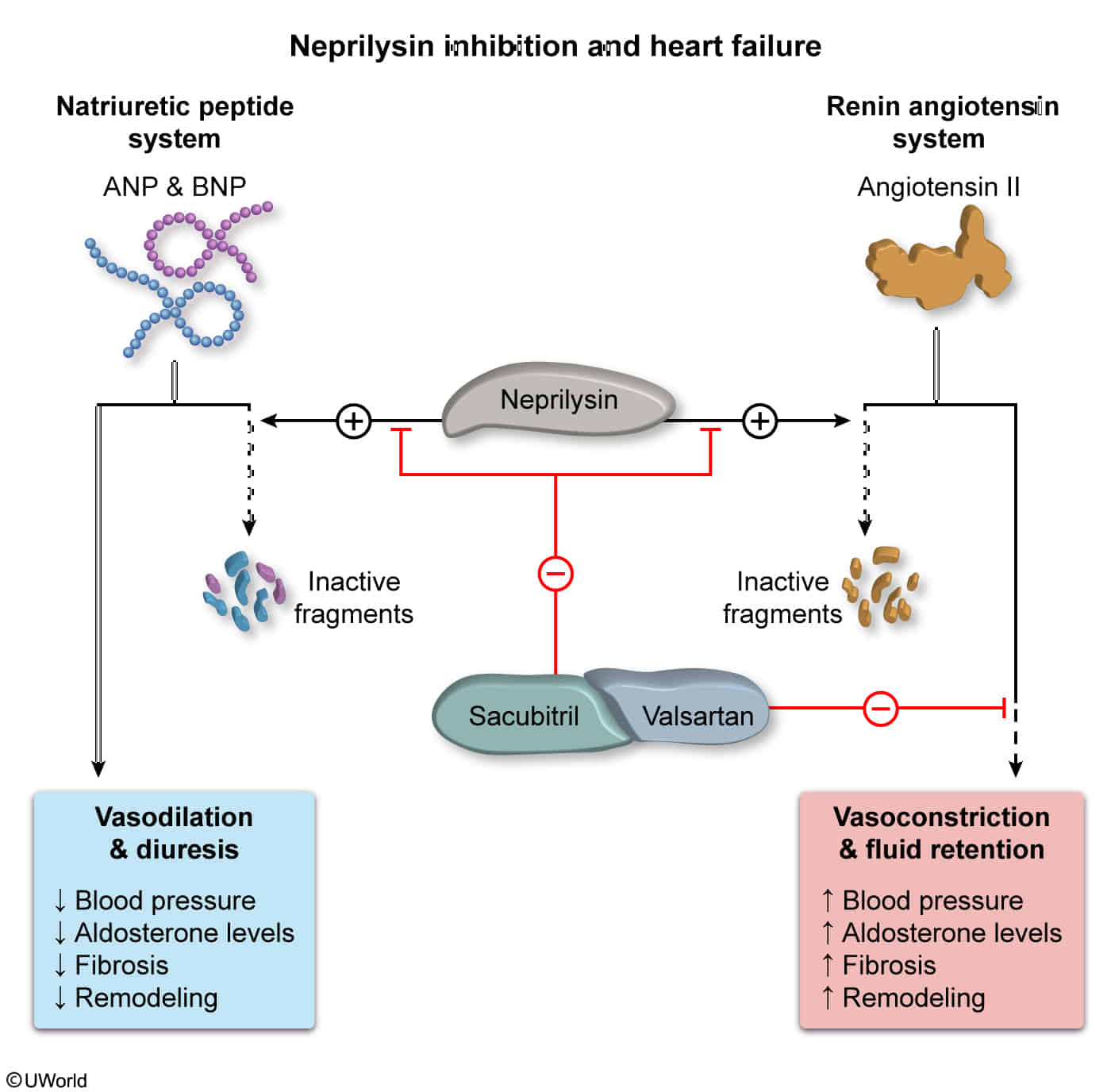
- Neprilysin is a zinc-dependent metalloprotease that cleaves peptides at the amino side of hydrophobic residues and inactivates several peptide hormones including glucagon, enkephalins, substance P, neurotensin, oxytocin, and bradykinin.
- Sacubitril inhibits neprilysin, increasing beneficial ANP/BNP, while valsartan blocks the AT1 receptor (RAAS inhibition).
- Indication: Stage C or D HFrEF (preferred initial agent for RAAS inhibition)