Epidemiology
- Peak incidence: 30–50 years
- Most common cause of bloody or serous nipple discharge
Etiology
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
- Solitary papilloma (also known as central papilloma)
- Multiple papillomas (also known as peripheral papillomas)
- May be asymptomatic
- Can present as a peripherally located palpable breast mass
- Nipple discharge is uncommon.
Diagnostics
Core needle biopsy
- Indication: all patients with suspected intraductal papilloma
- Findings
- Papillary structure with fibrovascular core covered by both epithelial and myoepithelial cells
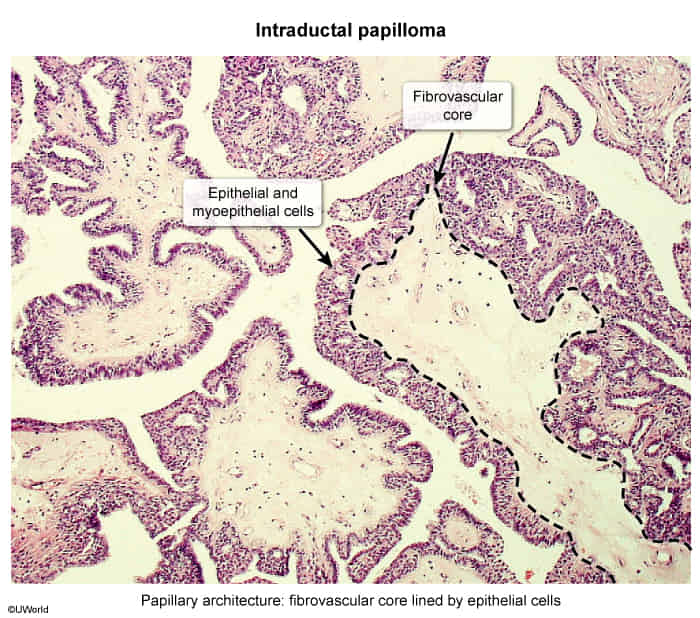
- Peripheral papillomas may be associated with cellular atypia, DCIS, or invasive breast cancer.
Treatment
