Rate limiting enzyme
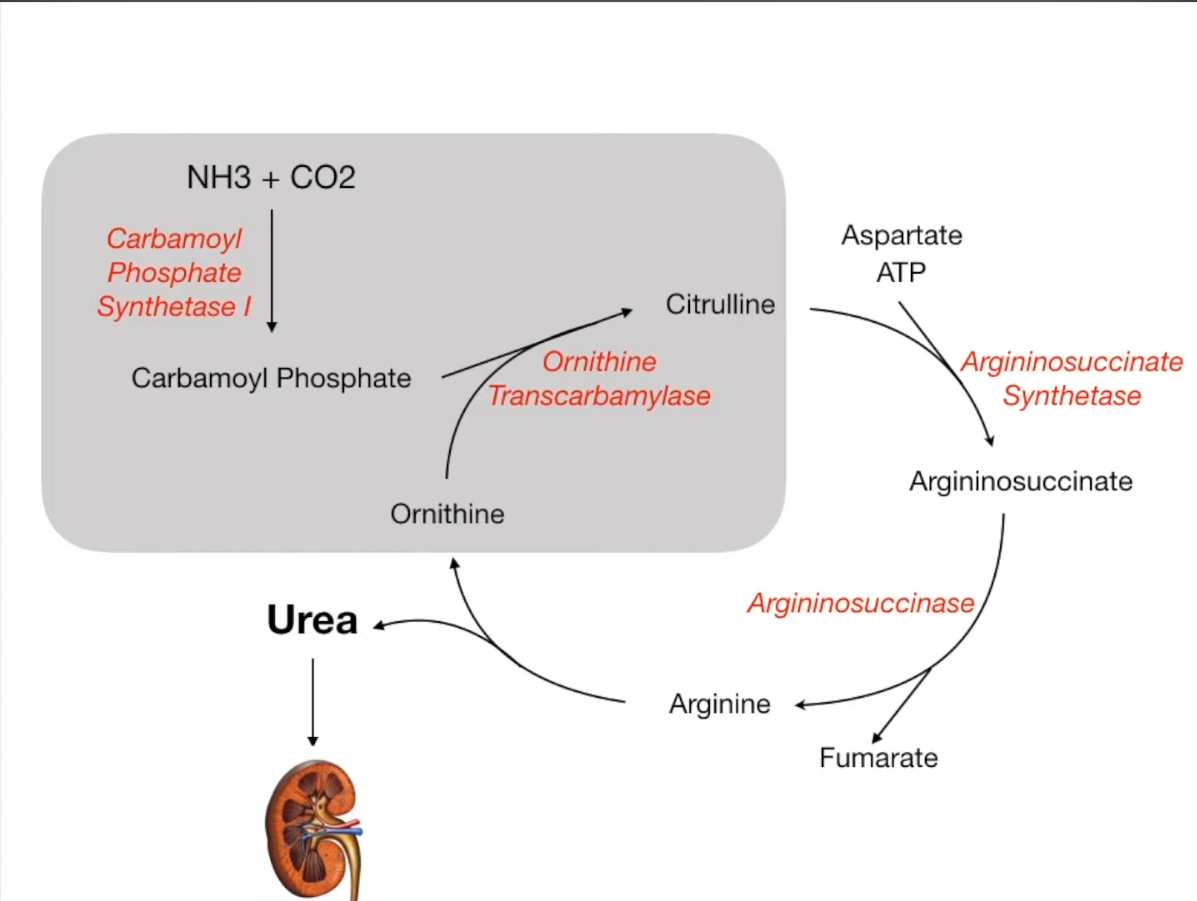

Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency

- Definition: inherited genetic disorder characterized by the inability to excrete ammonia
- Epidemiology: most common urea cycle defect
- Inheritance: X-linked recessive (in contrast to the rest of urea cycle enzyme deficiencies which are all autosomal recessive)
- Pathophysiology
- Defect in the enzyme ornithine transcarbamylase → impaired conversion of carbamoyl phosphate and ornithine to citrulline (and phosphate) → ammonia cannot be eliminated and accumulates
- Conversion of excess carbamoyl phosphate to orotic acid occurs as part of the pyrimidine synthesis pathway
- Clinical features
- Symptoms commonly manifest in the first days of life but can develop at any age.
- Nausea, vomiting, irritability, poor feeding
- Delayed growth and cognitive impairment
- In severe cases, metabolic encephalopathy with coma and death
- Does not cause megaloblastic anemia (as opposed to orotic aciduria)
- Diagnostics
- Hyperammonemia (usually > 100 μmol/L)
- ↑ Orotic acid in urine and blood
- ↓ BUN
- ↑ Carbamoyl phosphate and ↓ citrulline in the serum
- Normal ketone and glucose levels
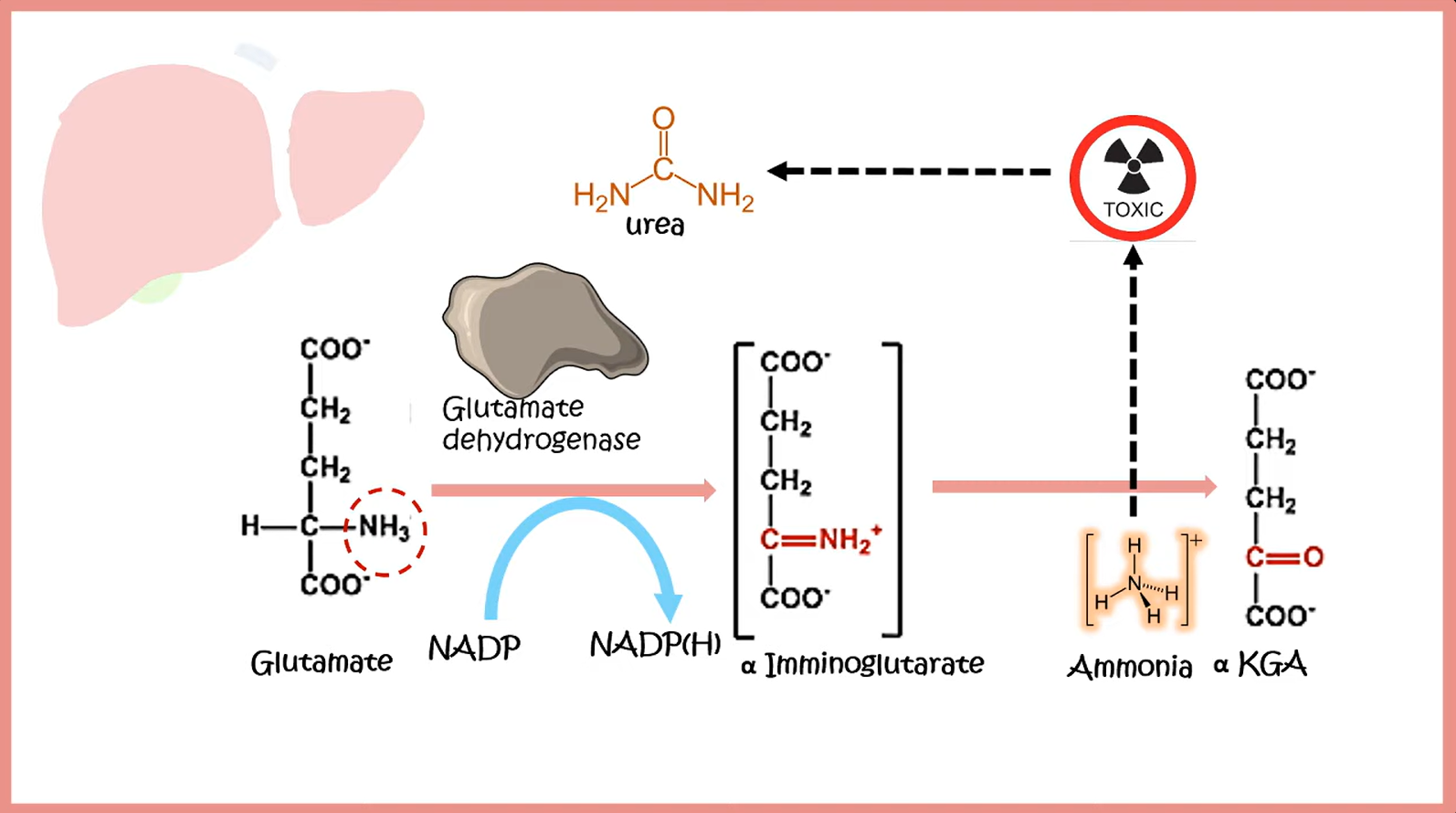
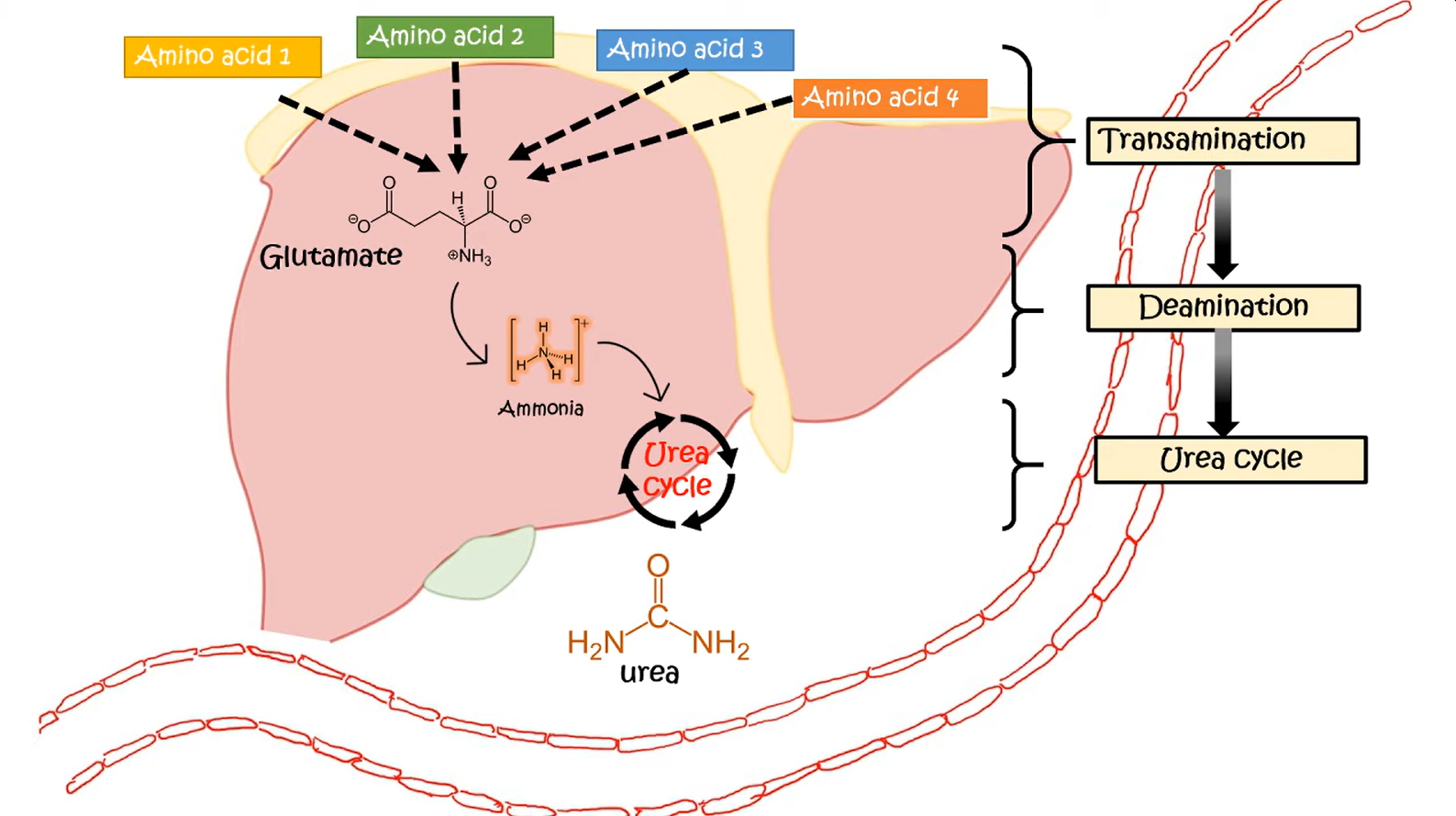
Transport of ammonia by alanine
- In the liver, alanine is transaminated by alanine aminotransferase to pyruvate with the amino group being transferred to α-ketoglutarate to form glutamate. Almost all aminotransferase enzymes use α-ketoglutarate as the amino group acceptor.
- Thus, amino groups are funneled into glutamate during protein catabolism.
- Glutamate is further metabolized by the enzyme glutamate dehydrogenase, which liberates free ammonia and regenerates α-ketoglutarate.
- Ammonia then enters the urea cycle to form urea, the primary disposal form of nitrogen in humans.
- Urea subsequently enters the blood and is excreted in the urine.
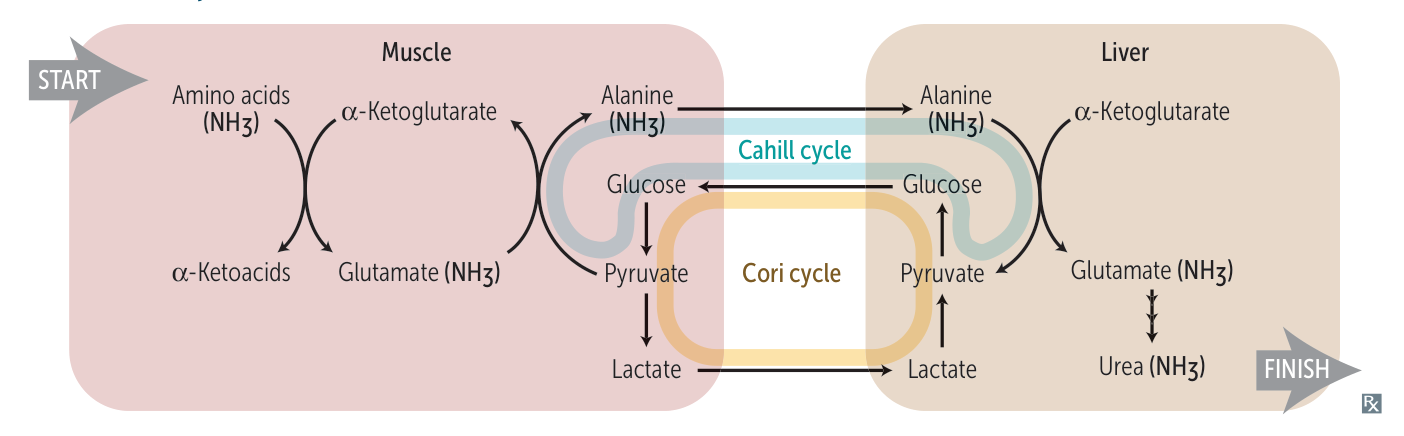
Cori cycle & Cahill cycle
Lactate/alanine is transported to the liver, where it is converted into glucose. It is then transported back to the muscles for energy production.
Catabolism of amino acids
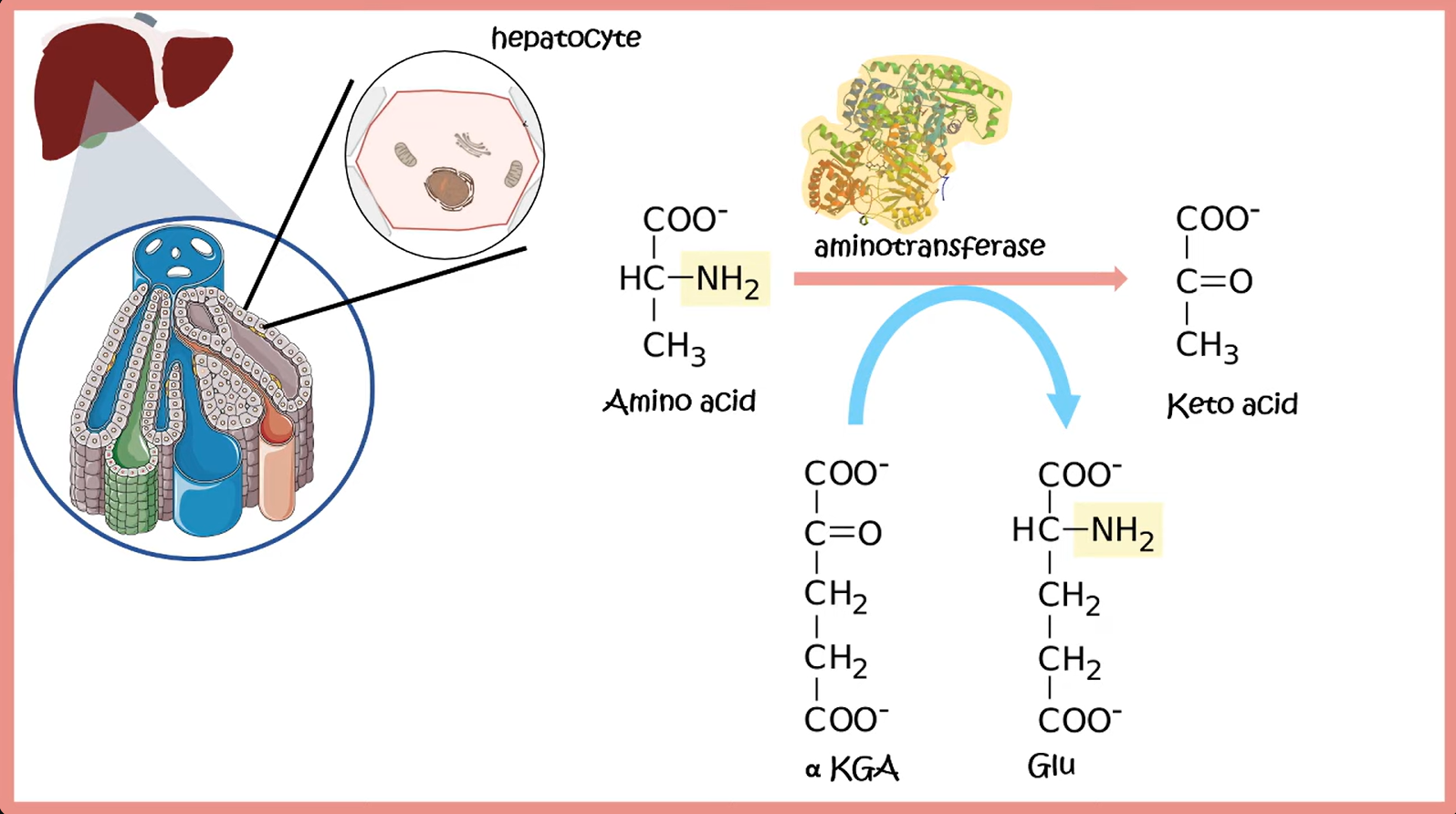
- Transamination: transfer of an amino group from an AA to an α-ketoacid for breakdown, or to an α-ketoacid to form a nonessential AA
- Decarboxylation: release of the α-carboxyl group of an AA via splitting of CO2
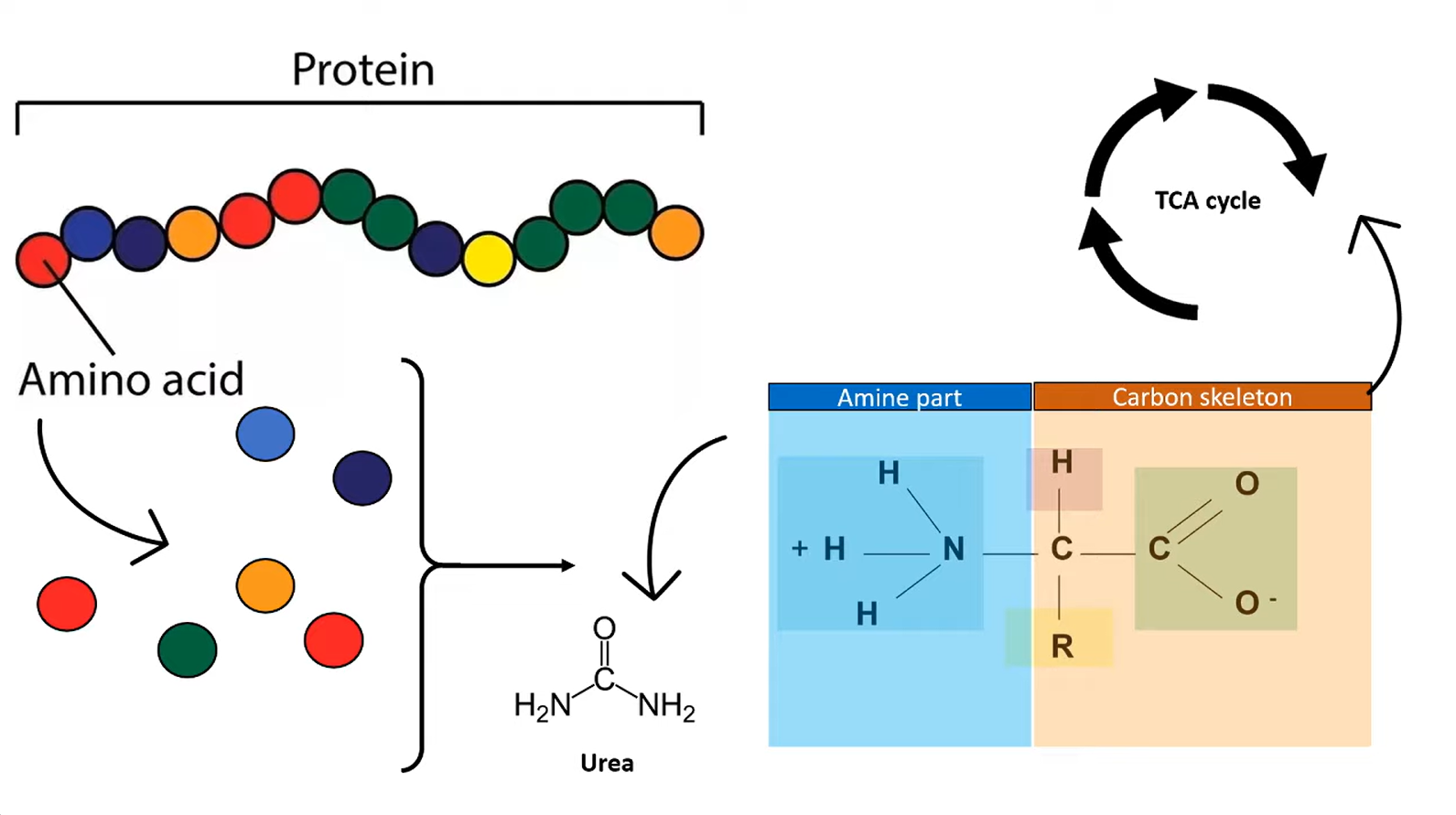
- ALT: alanine + α-ketoglutarate ⇄ pyruvate + glutamate
- AST: aspartate + α-ketoglutarate ⇄ oxalacetate + glutamate