A genetic disorder characterized by impaired osteogenesis that results in skeletal deformities and brittle bones that fracture easily
Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
- The most common cause (>90% of cases) is an autosomal dominant mutation in the COL1A1 or COL1A2 genes.
- These genetic defects lead to deficient or abnormal synthesis of Type I collagen, the primary structural protein in bone, skin, and sclera.
- Defective Type I collagen results in impaired bone matrix formation, leading to extreme skeletal fragility.
Clinical features
- The classic triad includes:
- Multiple recurrent fractures with minimal or no trauma. It is crucial to distinguish this from child abuse.
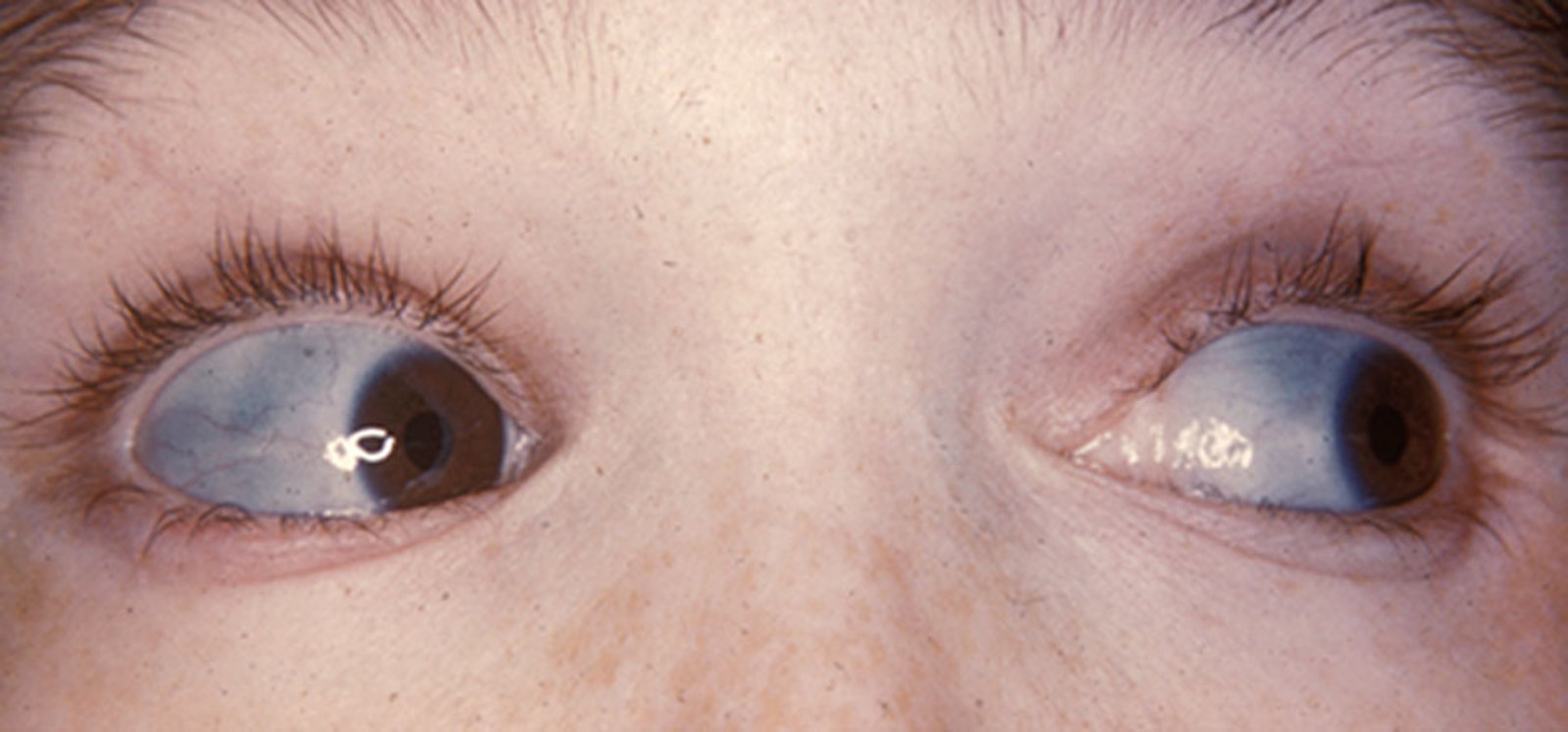
- Blue sclerae: The thin, translucent sclera reveals the underlying choroidal veins.
- Hearing loss: Often conductive, developing in early adulthood due to abnormalities or fracture of the auditory ossicles.
- Other common features:
- Dentinogenesis imperfecta: Opalescent, brittle teeth that wear down easily due to defective dentin.
- Short stature, bone deformities (bowing of long bones), and joint hypermobility.
- A curved spine (scoliosis) and barrel-shaped chest may also be present.
- Types (Sillence Classification)
- Type I: The most common and mildest form. Patients have a quantitative reduction in normal collagen. They present with blue sclerae and minimal bone deformity, with fractures often decreasing after puberty.
- Type II: The most severe and perinatally lethal form. It results from a qualitative defect (abnormal collagen structure). Severe fractures and deformities are present in utero, and survival beyond the neonatal period is rare.
- Type III: A severe, progressively deforming type. Patients produce abnormal collagen and suffer numerous fractures, significant bone deformities, and are often wheelchair-dependent.
- Type IV: Moderately severe, with a severity between Type I and Type III. Sclerae are often of normal color.