Epidemiology
- Peak incidence: 60–70 years
Classification
- Classical trigeminal neuralgia (CTN): caused by neurovascular compression, most often by an aberrant loop of a neighboring artery (usually the superior cerebellar artery)
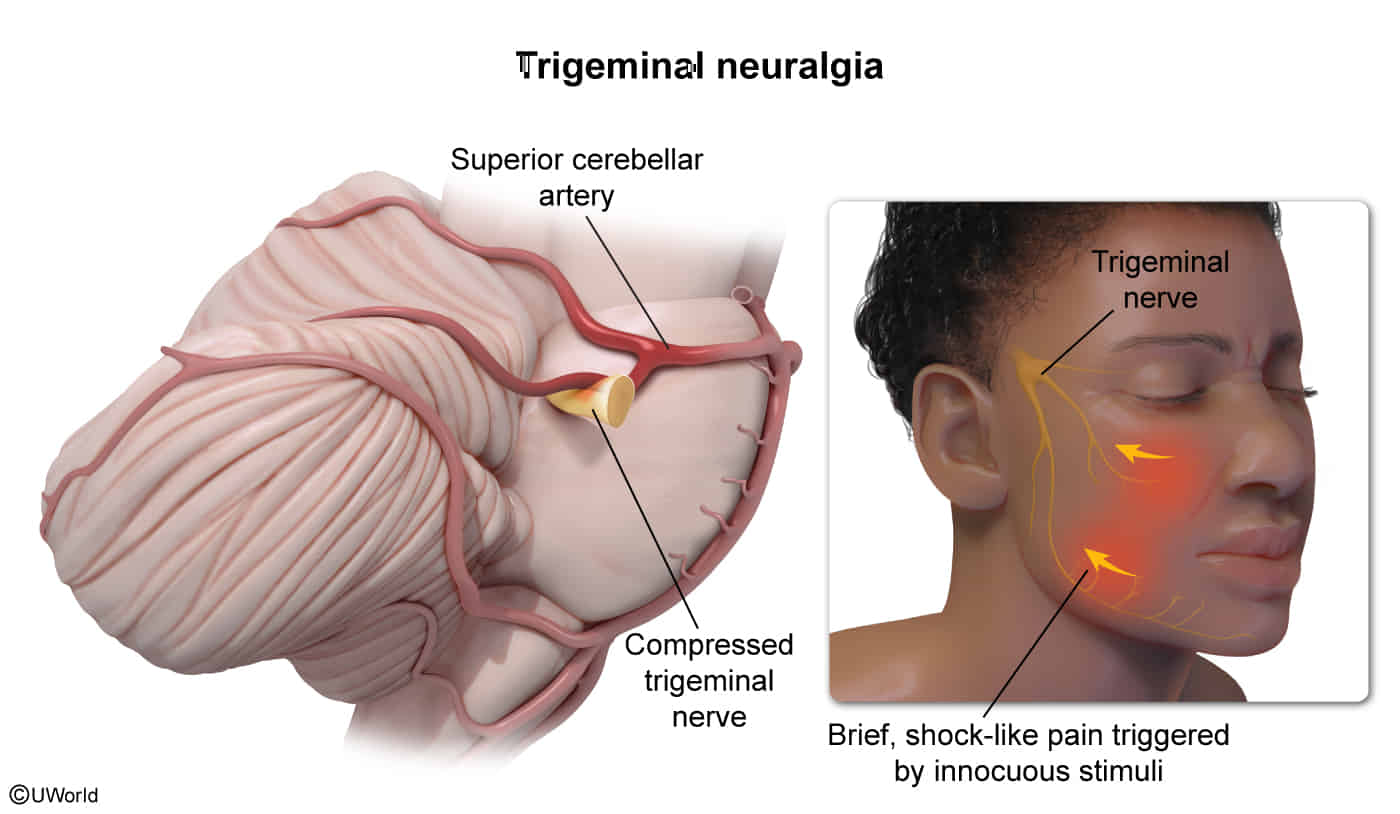
- Secondary trigeminal neuralgia (STN): caused by a major underlying neurological disease, most frequently multiple sclerosis, a tumor at the cerebellopontine angle, or arteriovenous malformation.
- Idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia (ITN): no identifiable cause (unremarkable findings on MRI and electrophysiological tests)
Clinical features
- Unilateral facial pain: paroxysmal, severe shooting or stabbing (like an electric shock), followed by a burning ache
- Lasts several seconds (in rare cases, several minutes) and may occur up to 100 times per day
- Typically shoots from mouth to the angle of the jaw on the affected side
- Occurs either at rest or is triggered by movements such as chewing, talking, or touch (e.g., brushing teeth, washing face); becomes worse with stimulation
Diagnostics
Treatment
<% tp.file.cursor() %>