Epidemiology
Etiology
- Microvascular damage (diabetes, hypertension, arteriosclerosis)
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis
Pathophysiology
The inferior oblique becomes unopposed, making the eye deviates upward and outward (extorted).
Clinical features
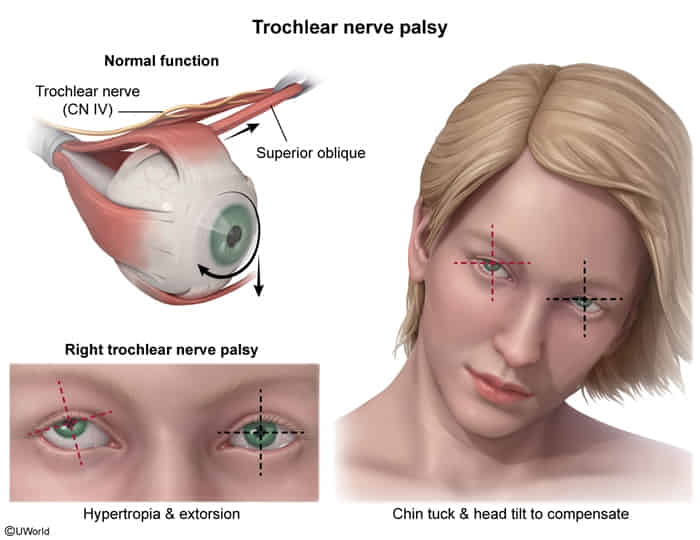
- Vertical or oblique diplopia
- Exacerbated on downgaze (e.g., reading, walking downstairs) away from side of affected muscle
- Worsens when patient turns the head towards the paralyzed muscle → compensatory head tilt to the opposite side of the lesion
Mnemonic
With damage to the CN IV, you cannot look at the floor.