Etiology
Classifications
Tip
Squamous and small cell carcinomas are sentral (central) and often caused by tobacco smoking.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Adenocarcinoma
- Location: Peripheral
- Characteristics
- Most common type of primary lung cancer
- More common in women and nonsmokers
- Associated with mutations in:
- EGFR gene
- ALK gene
- KRAS gene
- Common finding: hypertrophic osteoarthropathy (digital clubbing)
- Most common type of lung cancer that originates in pulmonary scars
- Prognosis is usually better than in other types of lung cancer
Adenocarcinoma of Lung Kinase”: Cancer (adenocarcinoma of lung) and the gene product (tyrosine kinase) are associated with ALK mutations.
“
Lung neuroendocrine tumors
Histology
- Neuroendocrine Kulchitsky cells
- Rapid growth pattern
- Expressed tumor markers
- Chromogranin A
- Synaptophysin
- Neuron-specific enolase
Large cell carcinoma
- Location: Peripheral
- Characteristics
- Strong association with smoking
- Poor response to chemotherapy
- Early metastases
- Poor prognosis
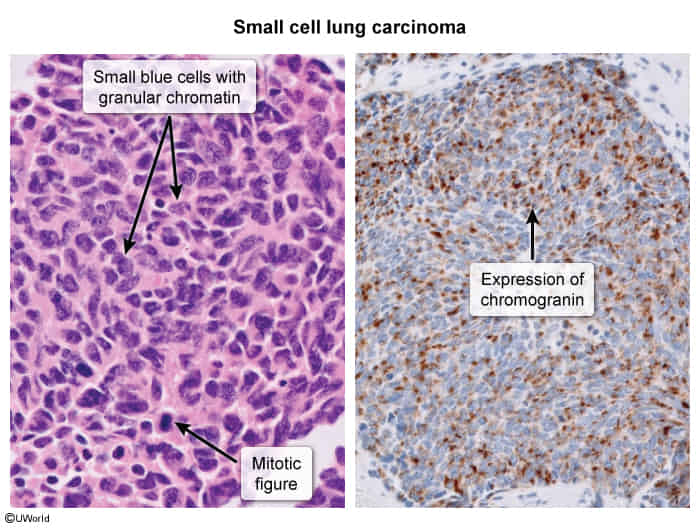
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
- Location: Peripheral
- Characteristics
- Strong association with smoking
Bronchial carcinoid tumor
- Location: Central or peripheral
- A rare type of neuroendocrine lung tumor that consists predominantly of neuroendocrine Kulchitsky cells
- Neuroendocrine Kulchitsky cells
- Rapid growth pattern
- Expressed tumor markers
- Chromogranin A
- Synaptophysin
- Neuron-specific enolase
Variants of lung cancer
Pancoast tumor
- An apical lung carcinoma
- Located in the superior sulcus of the lung (superior sulcus tumor)
- Predominantly NSCLC
- May lead to the development of Pancoast syndrome
- Cervical sympathetic ganglion (stellate ganglion): Horner syndrome (ipsilateral miosis, ptosis, and anhidrosis)
- Brachial plexus
- Localized pain in the axilla and shoulder (plexus neuralgia)
- Upper limb motor and sensory deficits (e.g., hand muscle weakness and atrophy)
- Recurrent laryngeal nerve: hoarseness
- Brachiocephalic vein
- Unilateral edema of the arm
- Facial swelling
- Phrenic nerve: paralysis of the hemidiaphragm (visible as elevated hemidiaphragm on chest x-ray)
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Paraneoplastic syndromes
Shared paraneoplastic features and syndromes
NSCLC
Squamous cell carcinoma
- Hypercalcemia of malignancy (increased risk with squamous cell carcinoma)
- Secrete PTHrP
Adenocarcinoma
- Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy
- Clubbing of the fingers and toes (Hippocratic fingers)
- Dermatomyositis or polymyositis
- Migratory thrombophlebitis (Trousseau syndrome)
SCLC (Secretion caused problems, except for PTHrP)
- Cushing syndrome
- Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)
- Lambert-Eaton syndrome, see Myasthenia gravis > Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS)
- Cerebellar ataxia
Diagnostics
Microscopic
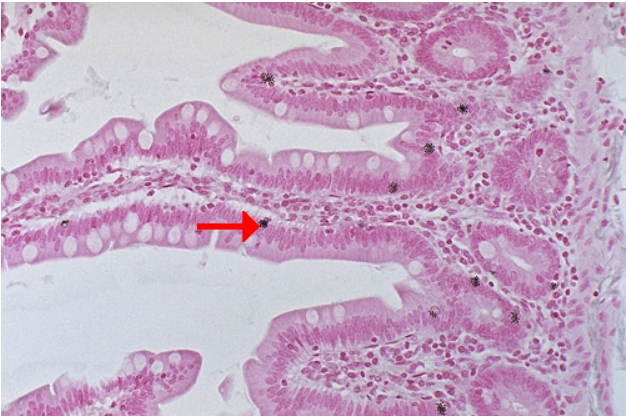
Adenocarcinoma
 composed of columnar cells that proliferate along the framework of alveolar septae, a so-called “lepidic” growth pattern.
composed of columnar cells that proliferate along the framework of alveolar septae, a so-called “lepidic” growth pattern.
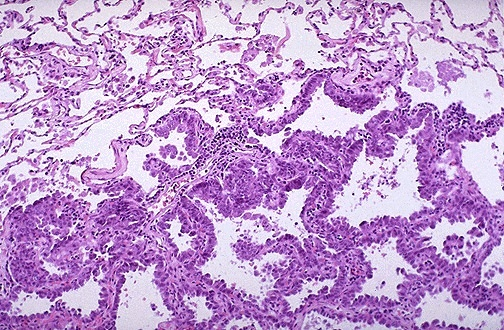
Squamous cell carcinoma
- pink cytoplasm
- keratin pearls
- distinct cell border
Large cell carcinoma
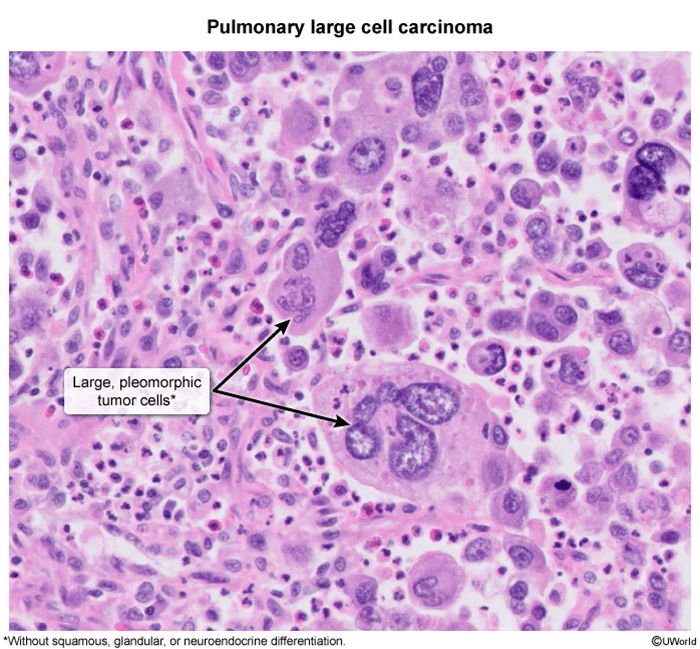
- Undifferentiated
- Large tumor cells
Small cell carcinoma
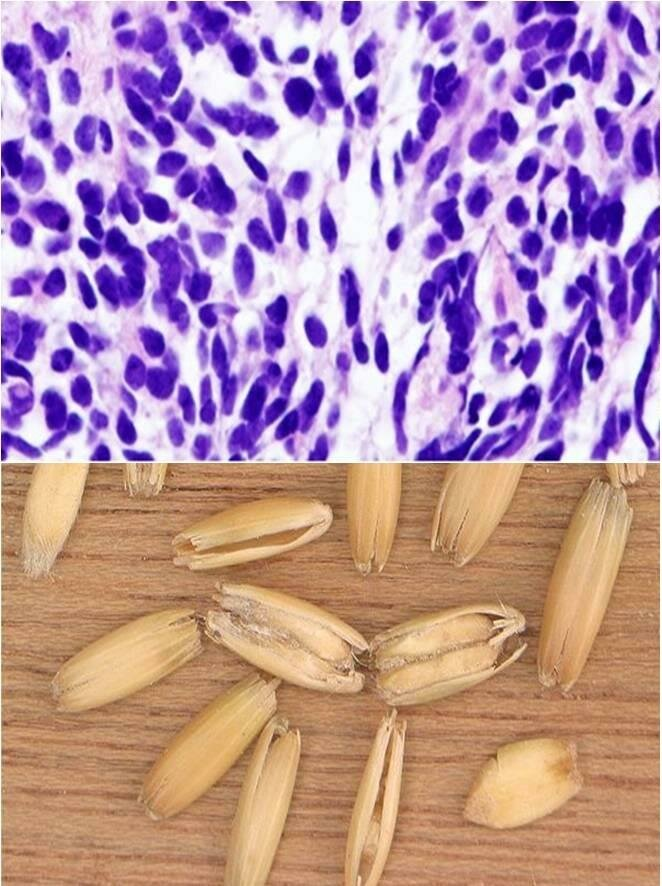
 This is the microscopic pattern of a small cell anaplastic (oat cell) carcinoma in which small dark blue cells with minimal cytoplasm are packed together in sheets.
This is the microscopic pattern of a small cell anaplastic (oat cell) carcinoma in which small dark blue cells with minimal cytoplasm are packed together in sheets.
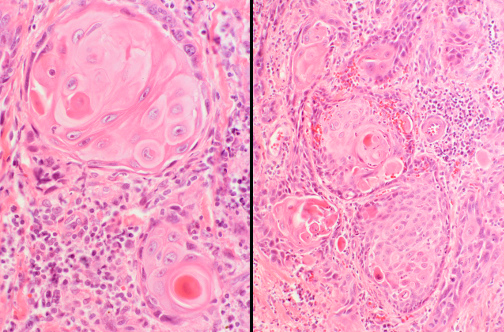
Hamartoma
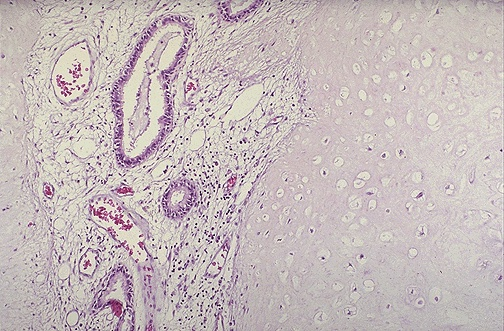 composed mostly of benign cartilage on the right that is jumbled with a fibrovascular stroma and scattered bronchial glands on the left. A hamartoma is a neoplasm in an organ that is composed of tissue elements normally found at that site, but growing in a haphazard mass.
composed mostly of benign cartilage on the right that is jumbled with a fibrovascular stroma and scattered bronchial glands on the left. A hamartoma is a neoplasm in an organ that is composed of tissue elements normally found at that site, but growing in a haphazard mass.