Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
- Stage 1: Early Localized (days to 1 month)
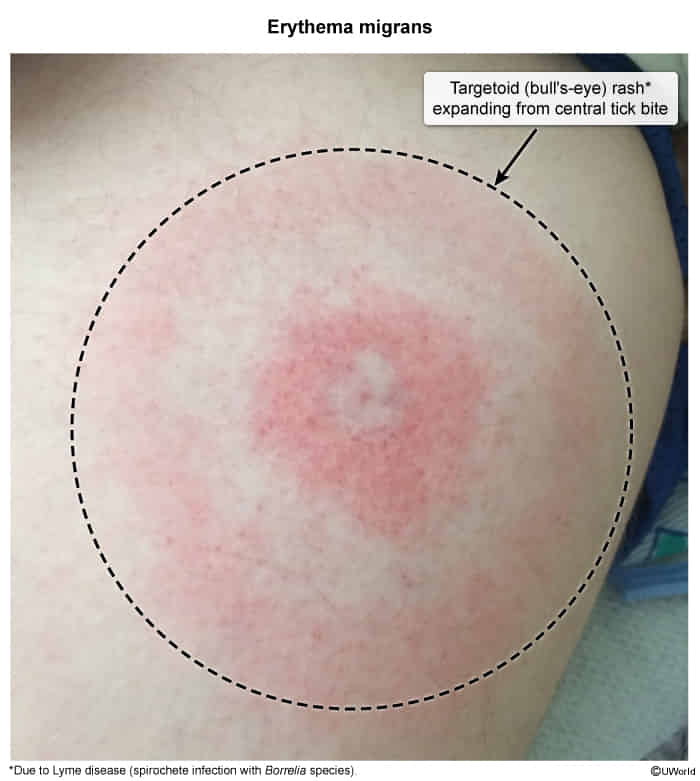
- Erythema migrans: Classic “bull’s-eye” rash. Often appears within 7-14 days. Not always present, painful, or pruritic.
- Flu-like symptoms: Fever, malaise, fatigue, myalgias, headache.
- Stage 2: Early Disseminated (weeks to months)
- Neurologic: Unilateral or bilateral facial nerve (CN VII) palsy is pathognomonic. Aseptic meningitis, radiculopathy.
- Cardiac: AV block (1st, 2nd, or 3rd degree), myocarditis.
- Musculoskeletal: Migratory arthralgias.
- Multiple smaller erythema migrans lesions.
- Stage 3: Late Disseminated (months to years)
- Musculoskeletal: Asymmetric oligoarthritis, typically affecting large joints like the knee.
- Neurologic: Encephalopathy (memory loss, mood changes), peripheral neuropathy.
Diagnostics
Treatment
