Epidemiology
Frequency: hepatic hemangioma (most common) > focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) > hepatocellular adenoma (rare)
Etiology
- Hepatic hemangioma: possible hormonal component; estrogen therapy associated with increased growth
- FNH
- Mostly unknown
- Suggested to be the result of a localized hyperplastic reaction by hepatocytes to an underlying arteriovenous malformations
- Hepatocellular adenoma: oral contraceptives and anabolic steroids
Diagnostics
- Ultrasonography: best initial test
- Biopsy
- Performed to confirm the diagnosis if imaging is inconclusive
- Contraindicated in hepatic hemangiomas, as it may cause bleeding
- Pathology
- Hepatic hemangioma
- Cavernous vascular spaces of variable size, lined by flat endothelial cells
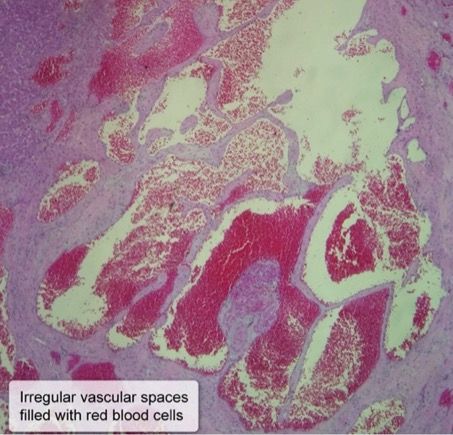
- Cavernous vascular spaces of variable size, lined by flat endothelial cells
- Hepatic hemangioma