Cannabis intoxication
Substances
- Whole-plant cannabis (street names: marijuana, weed, grass, pot, ganja)
Mechanisms of action
- Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC): main psychoactive component
- Interacts with cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 → inhibition of adenylate cyclase
Clinical features
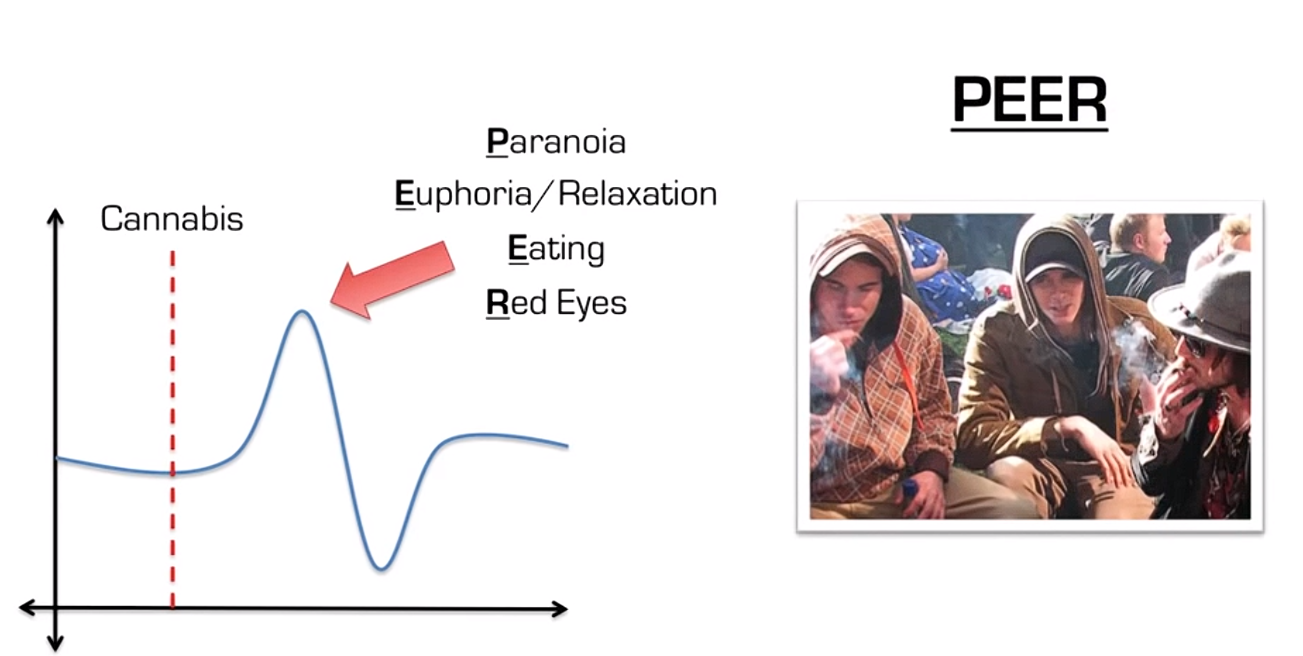
Neuropsychiatric effects of cannabis
- Positive neuropsychiatric effects
- Euphoric mood, joviality
- Calming and relaxation
- Increased awareness of the senses
- Negative neuropsychiatric effects
- Decreased attention, disorganized thought
- Distorted sense of time
- Impairments in concentration, reaction time, coordination, judgment, and/or memory
- Depression, anxiety, agitation, panic
- Perceptual disturbances and other psychotic symptoms
- Social detachment
Physiologic effects of cannabis
- Tachycardia, tachypnea, tremor, arrhythmia
- Increased or decreased blood pressure
- Conjunctival injection, mydriasis, nystagmus
- Increased appetite