Epidemiology
- Most common cause of teratogenic damage in children (0.2–1.5 per 1,000 live births)
- Most common preventable cause of intellectual disability in the US
Etiology
Pathophysiology
Failed neuronal and glial cell migration
Clinical features
Dysmorphic features
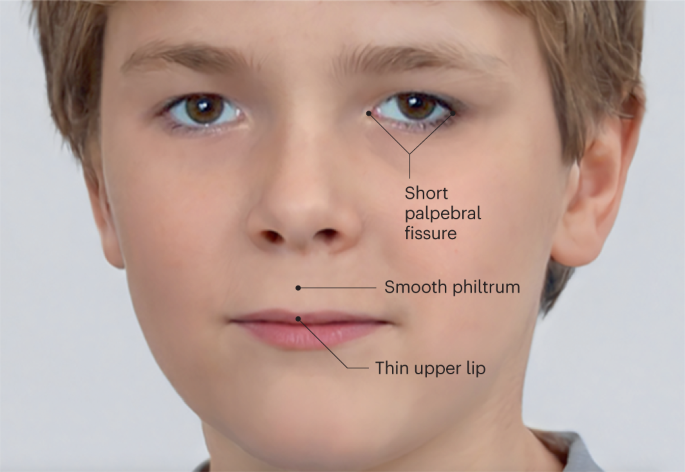
- Thin upper lip
- Smooth hypoplastic philtrum
- Down-slanting, short palpebral fissures
- Hypertelorism
- Microcephaly
Other
- Hyperactivity
- Intellectual disability (e.g., impaired language development, learning disabilities, memory deficits), and subsequent problems in social interactions and school performance