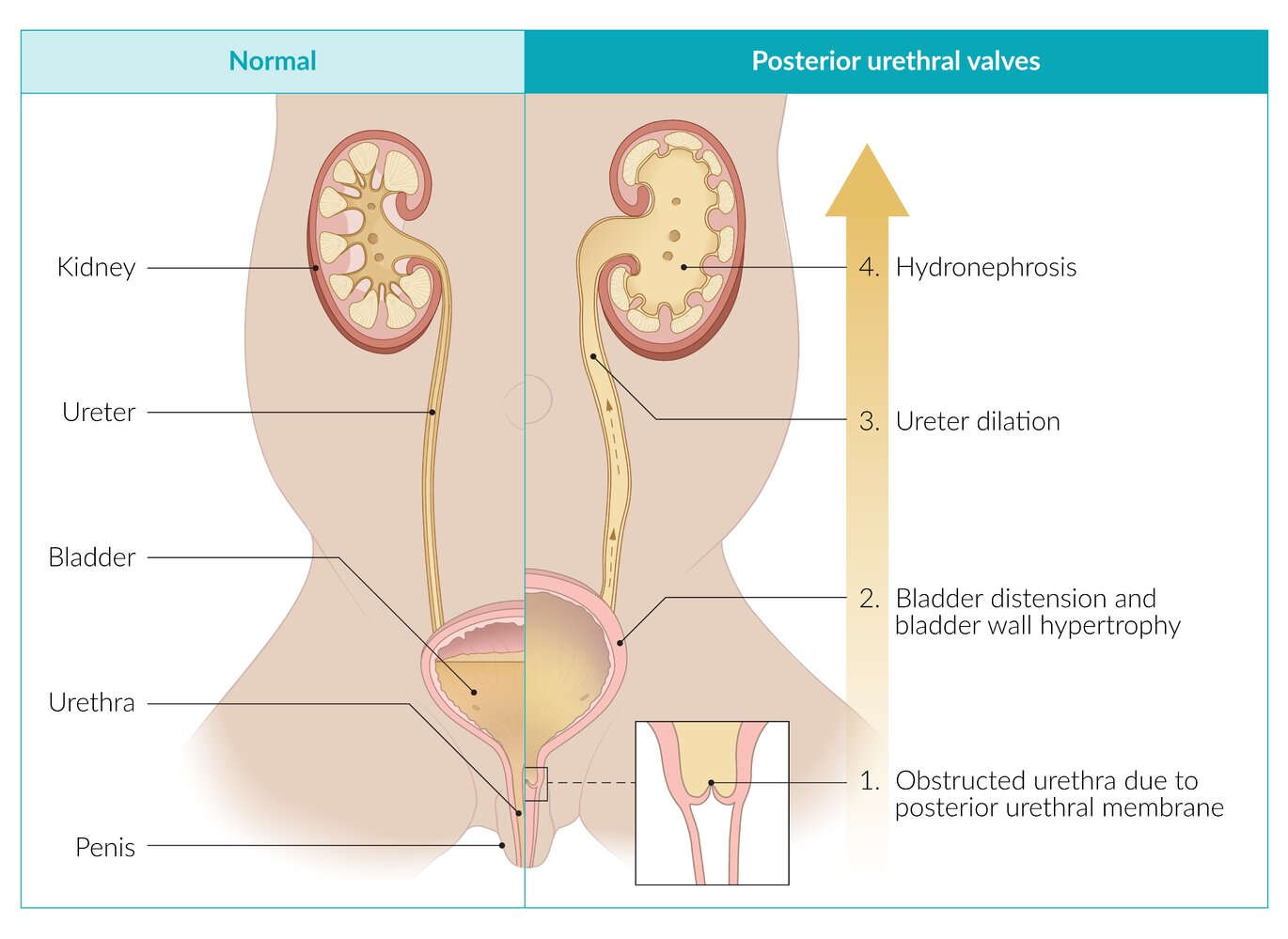
- Definition: congenital malformation in males where membranous folds of the urogenital membrane obstruct the membranous and prostatic urethra (posterior urethra) (aka incomplete canalization)
- Clinical features
- Most common cause of urinary tract obstruction in newborn males
- Respiratory distress secondary to pulmonary hypoplasia in cases with severe obstruction (see “Potter sequence”)
- Abdominal distention due to bladder distention
- Late manifestations:
- Difficulty voiding, poor urinary stream
- UTIs → urosepsis
- Diurnal enuresis
- Failure to thrive
- Diagnostics
- Voiding cystourethrogram (diagnostic study of choice) demonstrates
- Prenatal ultrasound of the upper urinary tract may demonstrate:
- Distended and/or thick-walled bladder, due to increased force to overcome pressure
- Bilateral hydroureters
- Bilateral hydronephrosis
