- Definition: an injury of the thoracic aorta resulting from blunt trauma; most commonly occurs distal to the left subclavian artery in the aortic isthmus (between Aortic arch and descending aorta)
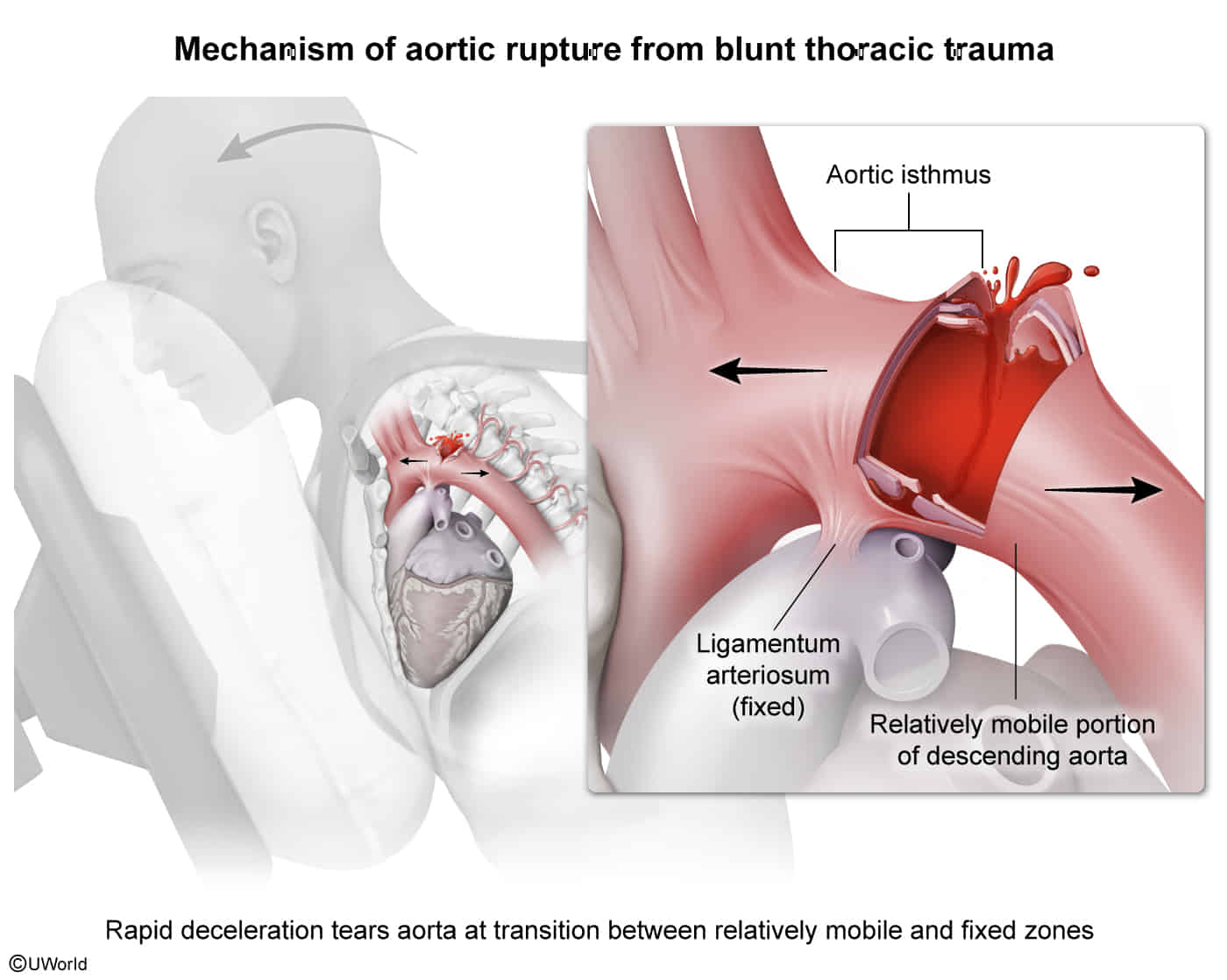
- Etiology: rapid deceleration from blunt trauma (e.g., MVC, fall from height)
- Clinical features: Severity ranges from intimal lesions (e.g., aortic pseudocoarctation) to thoracic aortic rupture.
- Chest pain
- Upper back pain
- Dyspnea, hoarseness and/or stridor
- Dysphagia
- Chest wall instability and/or ecchymoses
- New interscapular murmur
- Thoracic aortic rupture: signs of hemorrhagic shock (e.g., tachycardia, hypotension) and tearing pain
- Imaging
- CXR (initial imaging); potential findings include:
- Left main bronchus depression
- Tracheal deviation
- Apical pleural cap
- Left pleural effusion (hemothorax)
- Obscuration of the aortic knob
- Mediastinal widening
- Definitive imaging
- CTA chest in hemodynamically stable patients
- Transesophageal echocardiography
