- Definition: inherited genetic disorders characterized by impaired metabolism of fats and proteins
- Pathophysiology
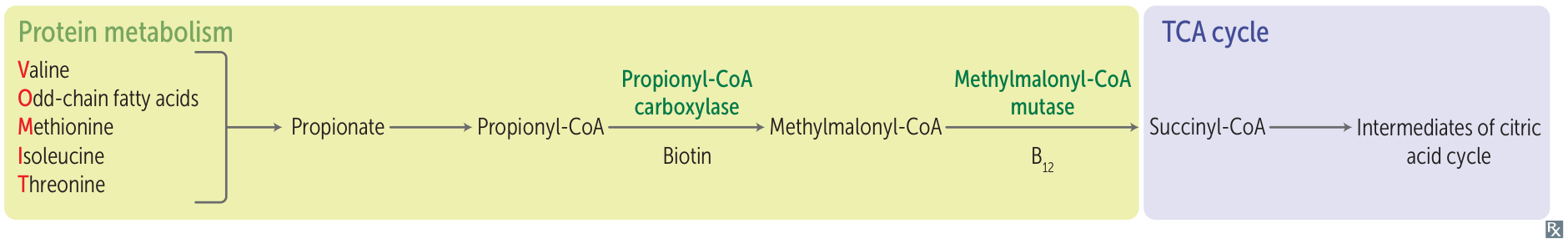
- Propionic acidemia: propionyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency → impaired conversion of propionyl-CoA to methylmalonyl-CoA → ↑ propionyl-CoA and ↓ methylmalonate → conversion into propionic acid, which accumulates in serum and urine
- Methylmalonic acidemia: methylmalonyl-CoA mutase deficiency or vitamin B12 deficiency → accumulation of methylmalonic acid
- Methylmalonyl-CoA is transformed into succinyl-CoA by the enzyme methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, which requires adenosylcobalamin, the active form of vitamin B12, as a cofactor.
- Accumulation of organic acids leads to
- Clinical features
- Most commonly present in infancy with poor feeding, vomiting, hypotonia, high anion gap metabolic acidosis, hepatomegaly, seizures.
