Epidemiology
Etiology
- Malnutrition
- Heavy drinking
- Chronic renal failure
- Chronic hepatitis
- Drug interactions
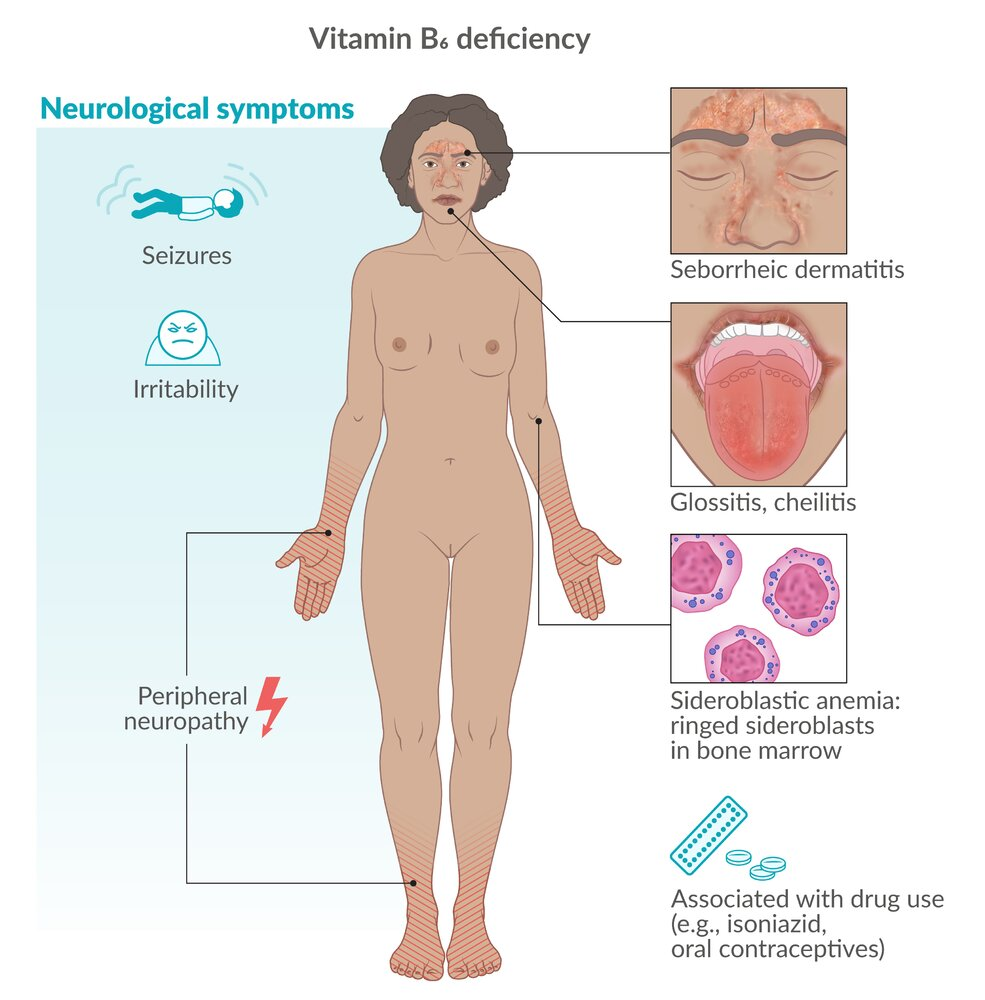
- Isoniazid
- Oral contraceptives
Pathophysiology
Active form: pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)
Vitamin B6 functions
- PLP is a coenzyme for the following reactions:
- Transamination (e.g., AST and ALT)
- Decarboxylation
- Amino acid metabolism
- Glycogenolysis (glycogen phosphorylase)
- Involved in the synthesis of:
- Heme, see Heme synthesis
- Histamine
- Niacin
- Gluthathione
- Cystathionine
- Neurotransmitters, including:
- Serotonin
- Dopamine
- Epinephrine
- Norepinephrine
- GABA
Clinical features
- Cheilosis, glossitis, stomatitis
- Sideroblastic anemia: Vitamin B6 deficiency causes heme synthesis dysfunction with impaired transfer of iron to hemoglobin, which ultimately leads to iron accumulation in RBCs.
- Irritability, seizures, peripheral neuropathy
- Because involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters
- Seborrheic dermatitis