Epidemiology
- ♀ > ♂ (∼ 5:1)
- Peak incidence: 30–50 years
Etiology
Pathophysiology
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by vasculopathy and fibrosis of the skin and other organs.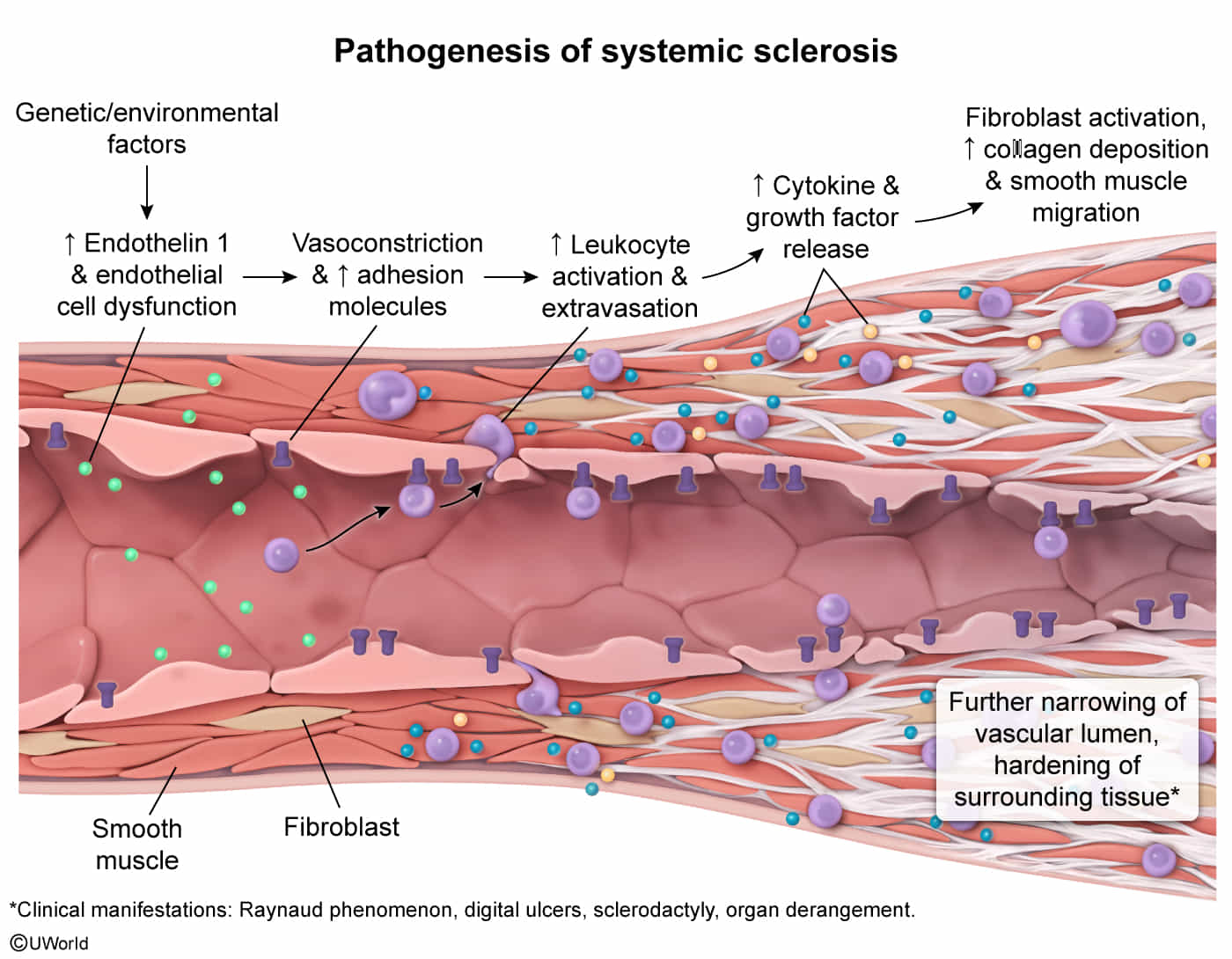
Clinical features
| Category | Limited Cutaneous | Diffuse Cutaneous |
|---|---|---|
| Manifestations | Distal sclerosis (most prominent in the fingers), CREST syndrome | Proximal sclerosis (involves the trunk & proximal extremities) |
| Serology | Anticentromere | Anti–Scl-70 |
| Complications | Pulmonary hypertension, Scleroderma renal crisis | Interstitial lung disease |
CREST syndrome
CREST syndrome refers to a constellation of symptoms traditionally associated with limited SSc (can also be seen in diffuse SSc).
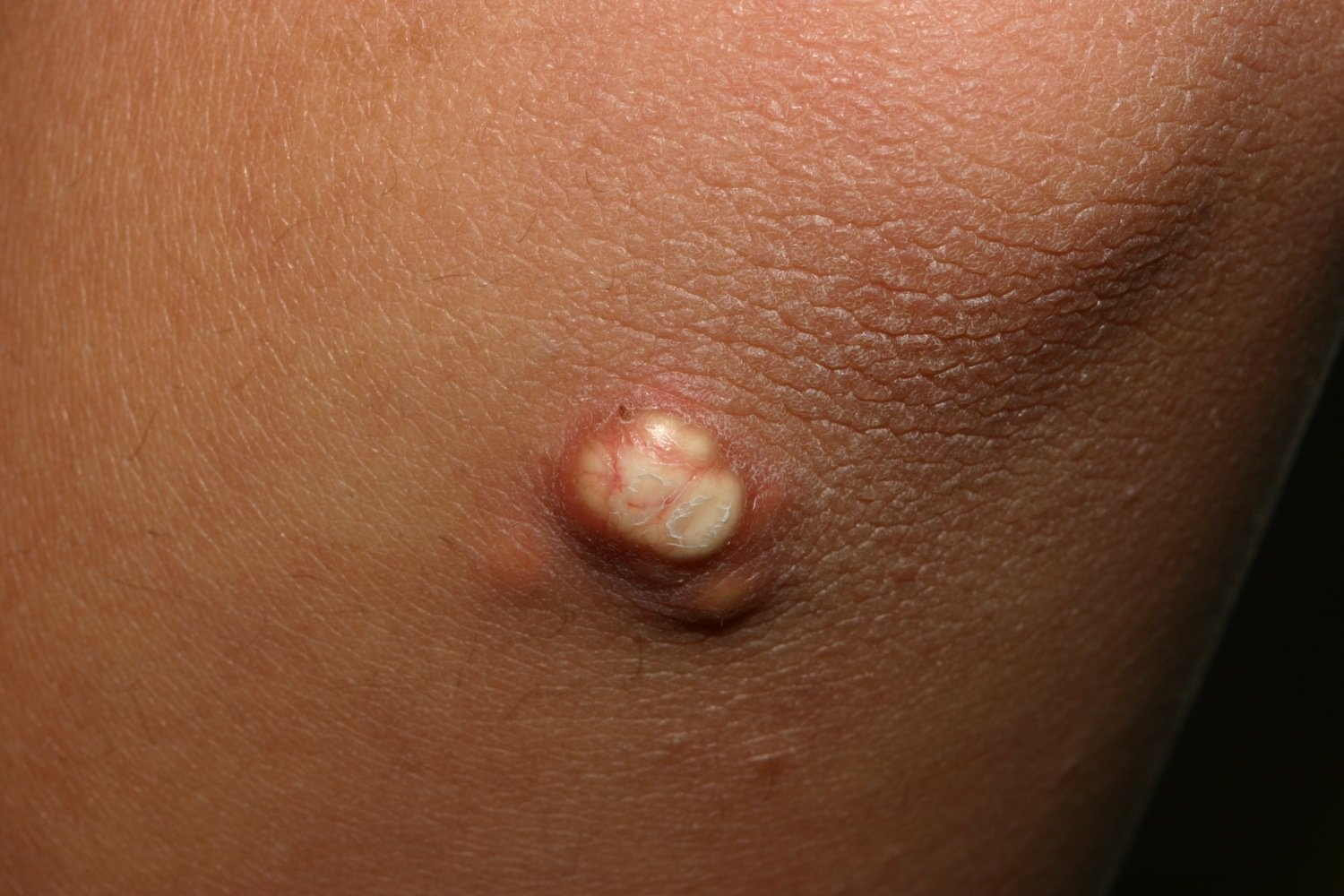
- C: Calcinosis cutis: small white calcium deposits on the pressure points of the extremities (e.g., elbows, knees, fingertips)
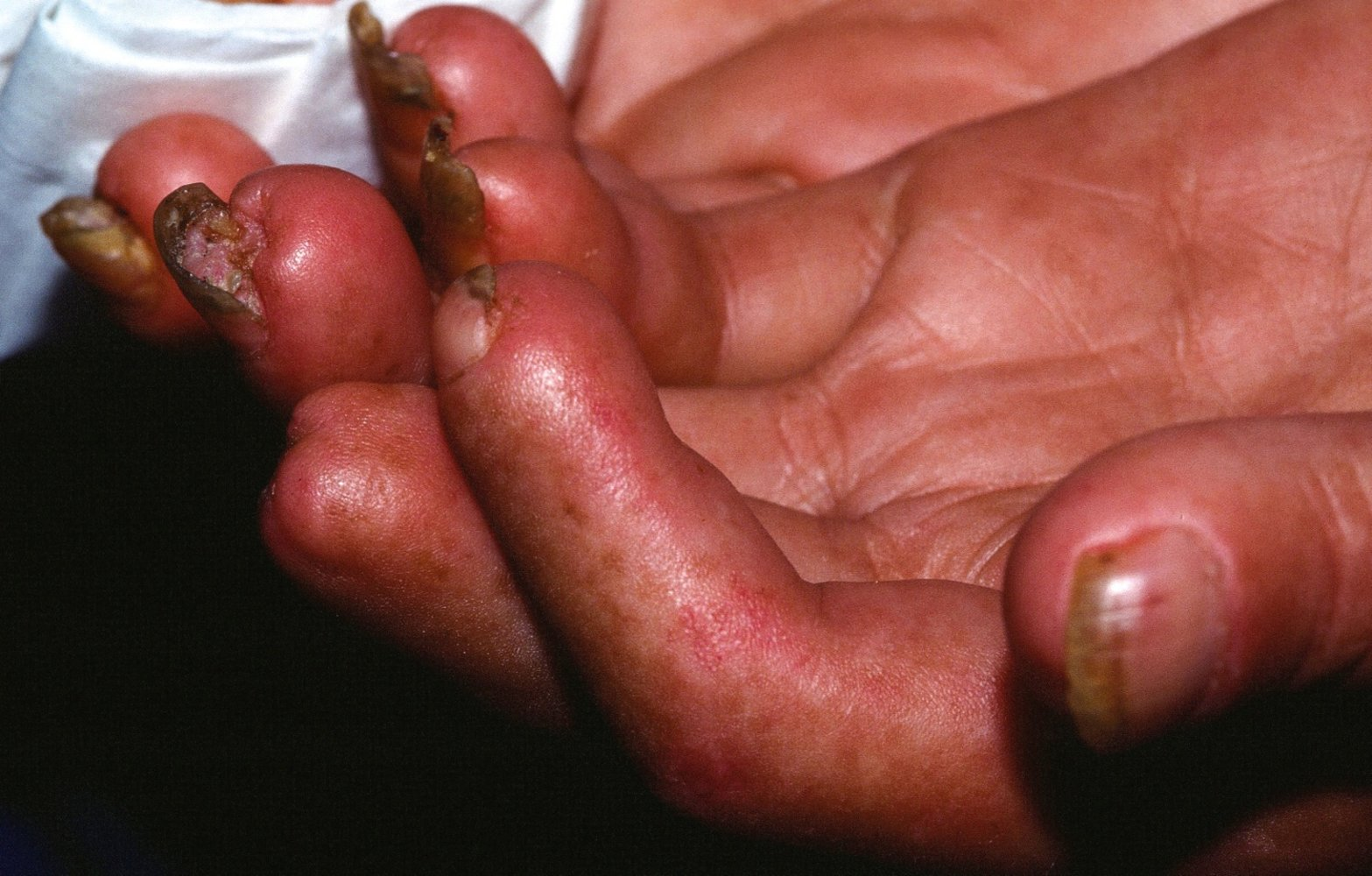
- R: Raynaud phenomenon
- E: Esophageal hypomotility (systemic sclerosis): smooth muscle atrophy and fibrosis → esophageal dysmotility and decreased lower esophageal sphincter pressure → dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux, heartburn → aspiration, Barrett esophagus, stricture. See Esophageal motility disorders
- S: Sclerodactyly
- T: Telangiectasia
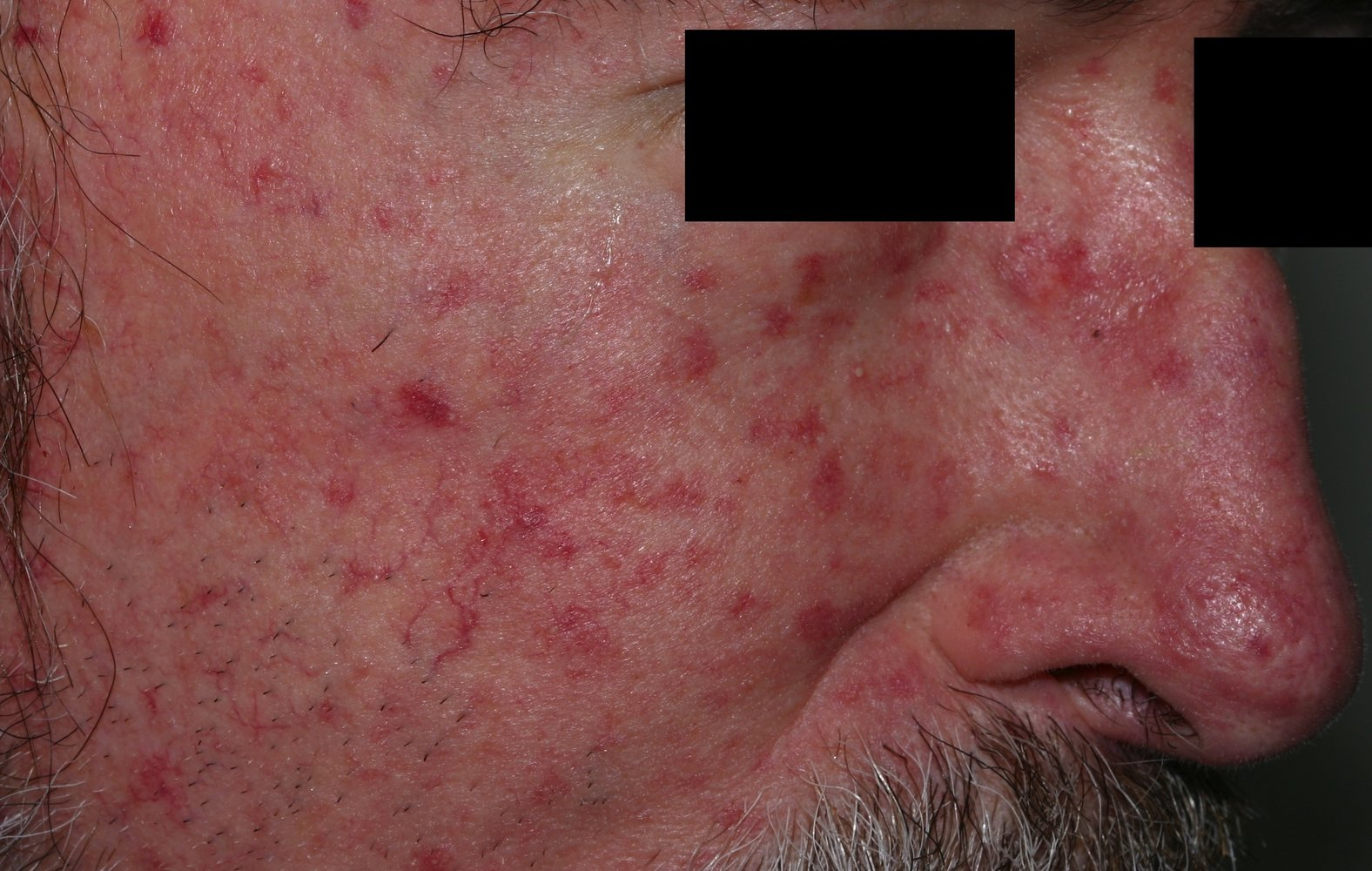
Cutaneous
- Thickening and hardening of the skin, which appears smooth, shiny, and puffy
- Sclerodactyly: fibrotic thickening and tightening of the skin on the fingers and hands
- Edema followed by fibrosis that results in a waxy appearance of the skin
- Limited range of motion and possibly flexure contractures and clawing of the digits
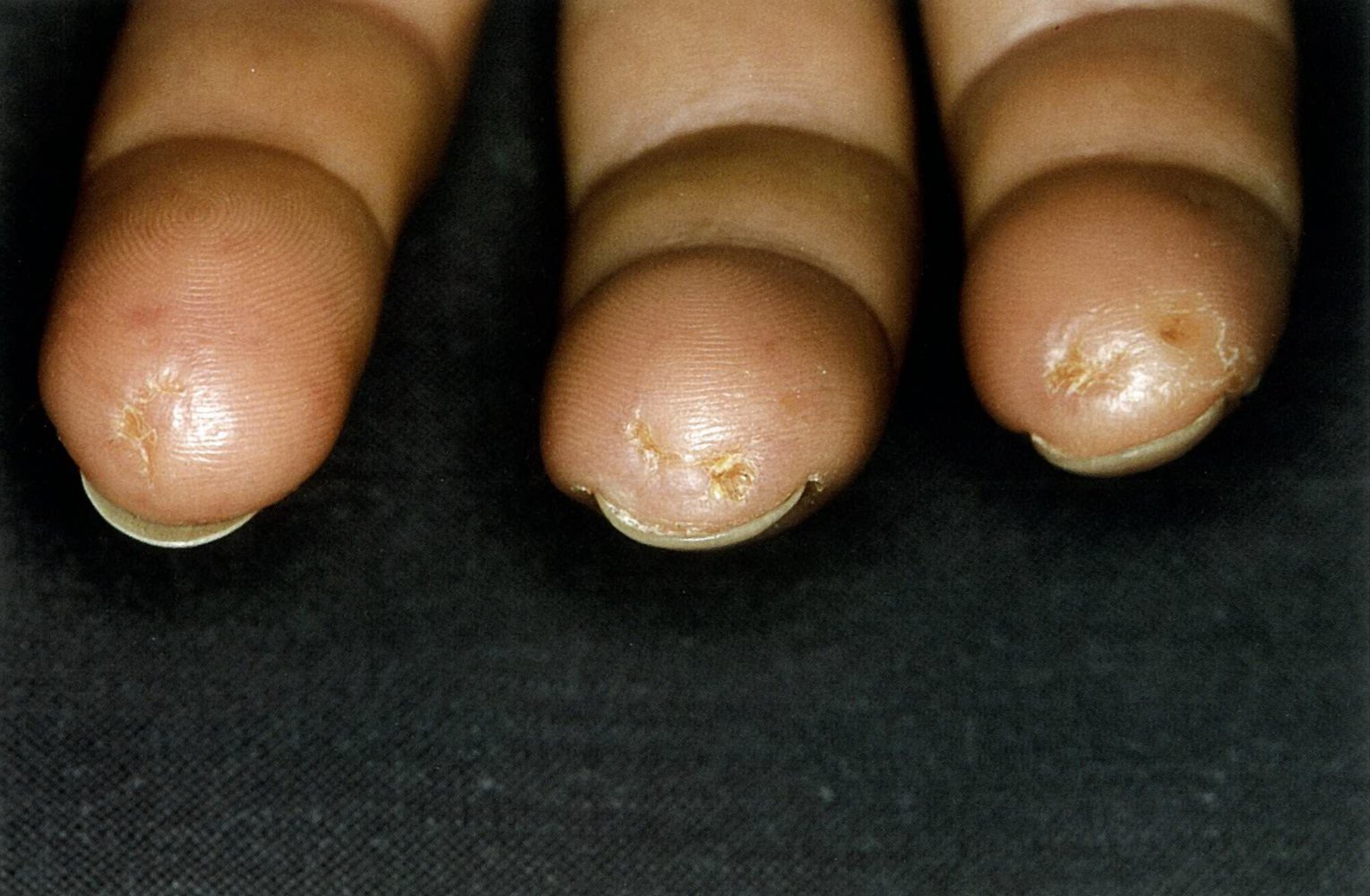
- Multiple, painful ischemic digital ulcers with atrophy and necrotic spots
- Digital pitting: hyperkeratotic scarring that most commonly affects the fingertips
- Face changes
- Loss of expression (mask-like facies)
- Smoothing of deep wrinkles
- Microstomia (a disproportionately small mouth) accompanied by characteristic perioral wrinkles
Renal
- Scleroderma renal crisis (SRC)
- Abrupt onset, life threatening
- SRC is caused by immune-mediated injury to small renal vessels that typically spares the glomerular capillaries
- Clinical features of SRC
- Oliguric acute kidney injury, proteinuria, hematuria
- Hypertension with or without symptoms of hypertensive emergency
- Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA) and thrombocytopenia
- Treatment: ACE inhibitors
- Chronic kidney disease: reduced kidney function due to abnormal collagen deposition → thickening of renal arteriolar walls → decreased renal blood flow
Pulmonary
- Interstitial lung disease
- Pulmonary artery hypertension
Other extracutaneous
- Gastrointestinal tract
- Esophageal dysmotility → dysphagia and reflux
- Small bowel dysmotility → bloating, gas, constipation, and cramping
- Dysmotility creates an ideal environment for bacterial overgrowth.
- Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth
- Vascular disease
- Raynaud phenomenon
- Thromboembolism
Diagnostics
Warning
Scleroderma renal crisis is a medical emergency with a high mortality rate. Promptly evaluate serum creatinine and urine protein in individuals with SSc who present with an acute rise in blood pressure and start management of SRC.
-
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA): present in ∼ 90% of patients
-
SSc-specific autoantibodies
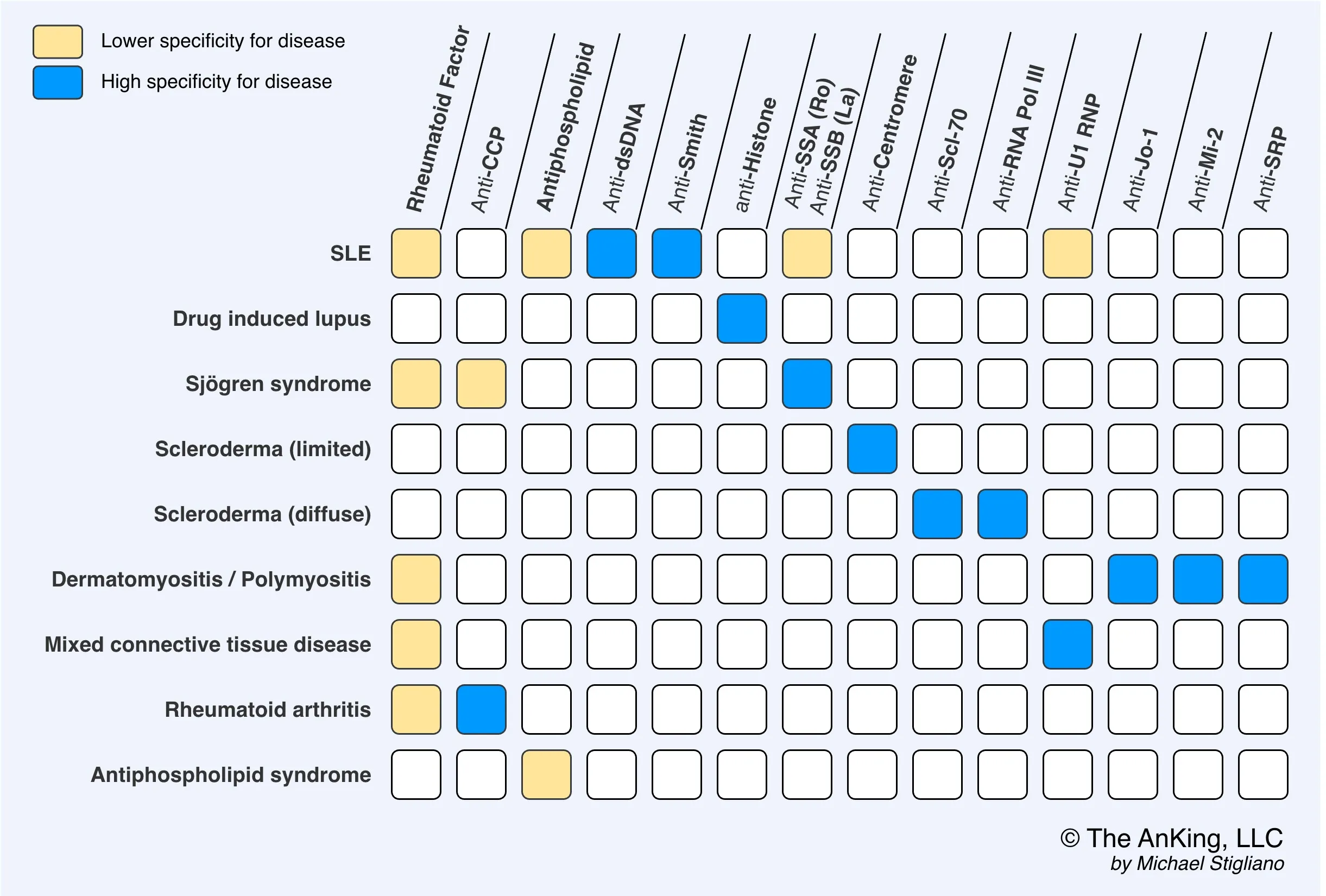
- Anticentromere antibodies: associated with limited SSc, increased risk for vascular complications (e.g., PAH)
- Anti-SCl-70 (anti-topoisomerase I antibody): associated with severe and rapidly progressive diffuse SSc, limited SSc, ILD, digital ulcers
- Anti-RNA polymerase III: associated with diffuse SSc, scleroderma renal crisis
-
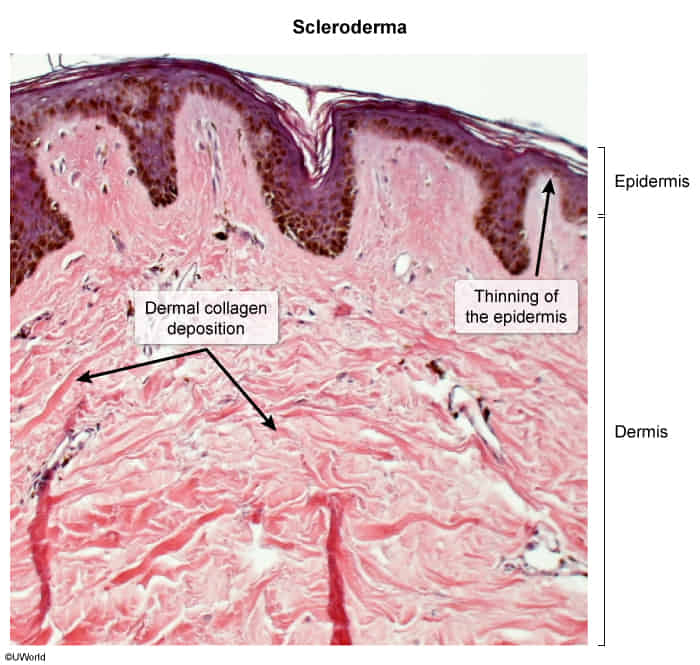
A characteristic skin biopsy finding is dermal layer expansion due to diffuse deposition of collagen (eosinophilic connective tissue), resulting in atrophy of the intradermal adipose tissue and dermal appendages (ie, hair follicles, glands).