| Feature | Asbestosis | Coal Worker’s | Silicosis | Berylliosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposure | Shipbuilding, roofing, pipes | Coal mining | Sandblasting, rock mining | Aerospace, electronics |
| Lung Zone | Lower Lobes | Upper Lobes | Upper Lobes | Upper Lobes |
| CXR Buzzword | Pleural plaques | Nodular opacities | Eggshell calcification | Hilar adenopathy |
| Pathology | Asbestos bodies | Anthracosis | Fibrotic nodules | Non-caseating granulomas |
| High-Yield Association | Mesothelioma, Bronchogenic CA | Caplan Syndrome (rheumatoid arthritis and pneumoconiotic nodules) | ↑↑ Risk of Tuberculosis | Mimics Sarcoidosis |
Mnemonic
- Asbestos is from the roof (was common in insulation), but affects the base (lower lobes).
- Silica, coal, and berries are from the base (earth), but affect the roof (upper lobes).
Mnemonics
“Silly Sandy rocks! She builds tunnels”
Silicosis:
-
Sanblasting
-
Rock mining
-
Tunneling
“Beto insults that ship’s pipes”
Asbestosis
-
Insulators
-
Shipyard workers
-
Pipe fitting
“Busy cotton”
Byssinosis:
- Cotton
“Very electronic”
Berylliosis:
- Electronic manufacture
“Sugar makes me vaga” (vaga is Spanish for lazy)
Bagassosis:
- Moldy sugar cane
Pathophysiology
Classifications
Asbestosis
- Etiology: Airborne asbestos fibers
- Population at risk:
- Asbestos miners and millers
- Brake linings and insulation manufactures
- Ship construction workers
- Demolishers
- Clinical features:
- Symptoms typically develop 15–20 years after initial exposure.
- Exertional dyspnea
- Dry cough that transforms into productive cough
- Digital clubbing
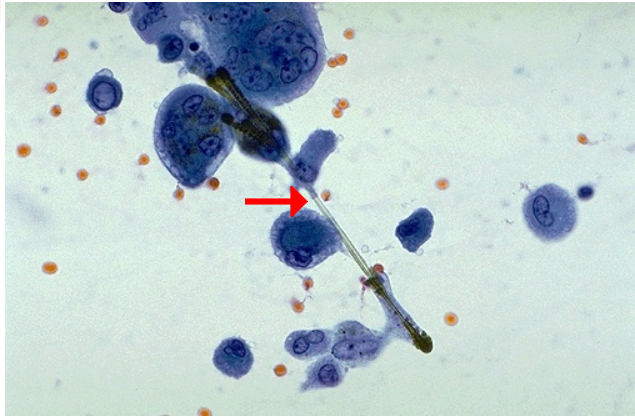
- Ferruginous bodies in alveolar septa on histology
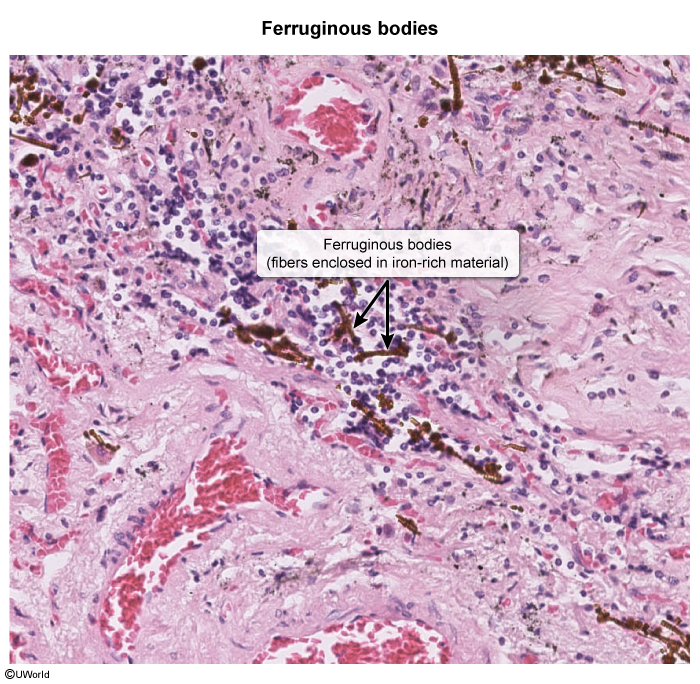
- Complications
- Lung cancer (smoking increases the risk):bronchogenic carcinoma is most common
- Mesothelioma: rarely occurs without a history of asbestos exposure
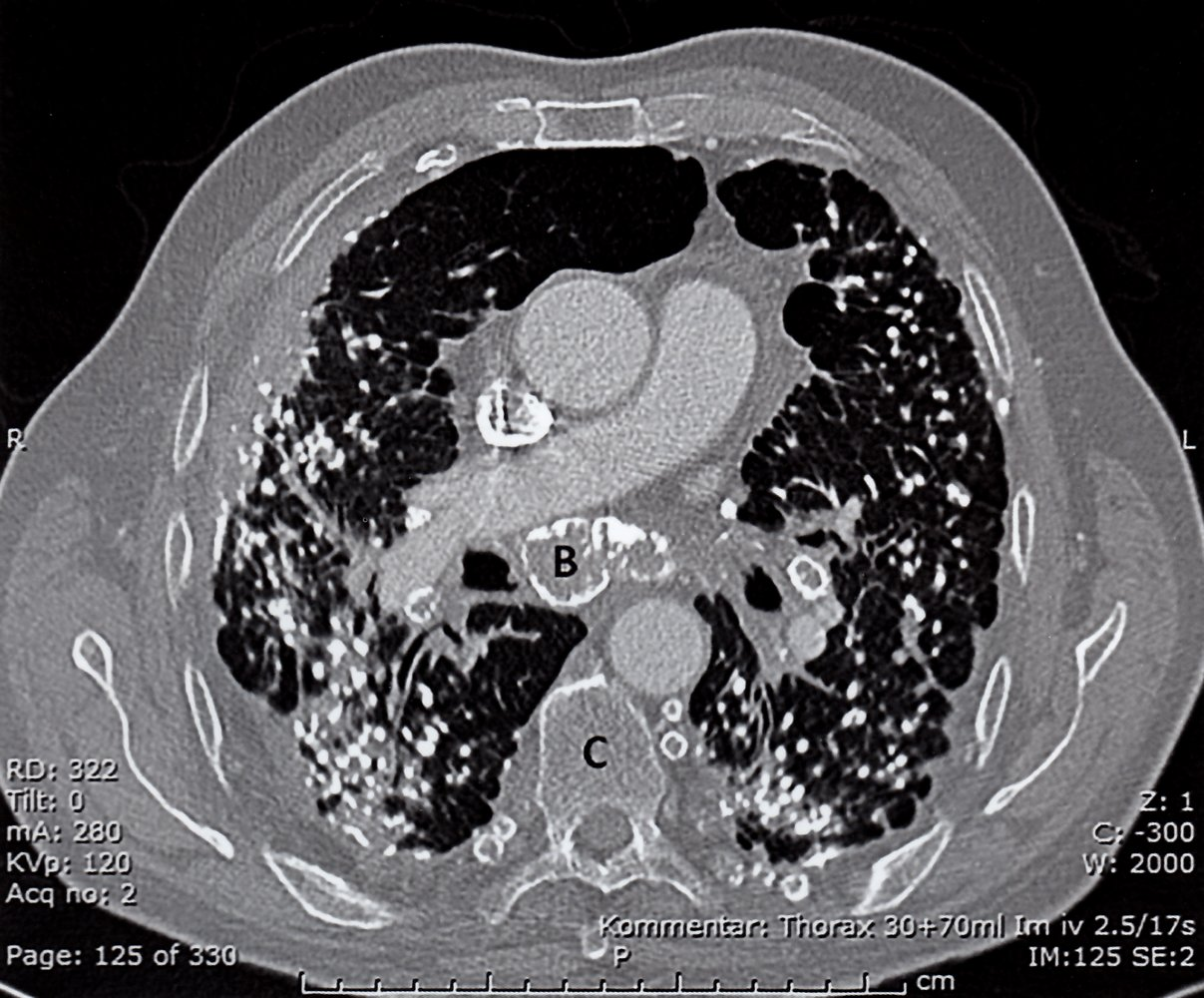
- Chest x-ray:
- Diffuse bilateral infiltrates predominantly in the lower lobes
- Interstitial fibrosis
- Calcified pleural plaques (usually indicate benign pleural disease)
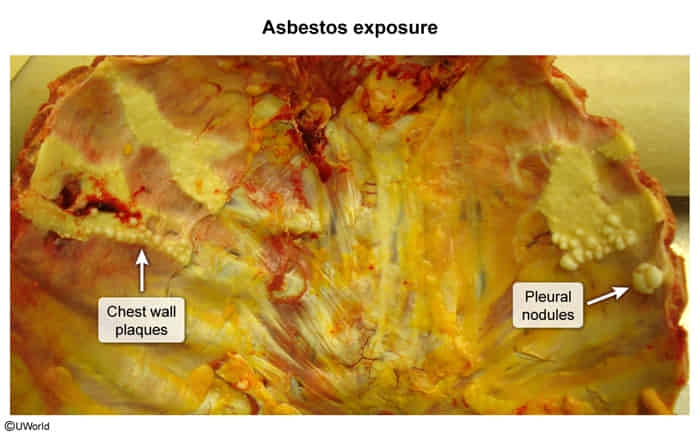
- Microscopic
This is the causative agent for asbestosis, a long, thin asbestos fiber. Some houses, business locations, and ships still contain building products with asbestos, particularly insulation materials, so care must be taken when doing remodelling or reconstruction.
Silicosis
- Etiology
- Inhalation of crystalline silica, most commonly as dust
- High-risk occupations for the development of silicosis include sandblasting, mining, and working in foundries
Mnemonic
The silly egg sandwich I found is mine!
- Clinical features
- Chronic cough (often with sputum) and exertional dyspnea
- Caplan syndrome: pneumoconiosis in combination with rheumatoid arthritis; characterized by rapid development of basilar nodules and mild obstruction of ventilation
- Chest x-ray
- Eggshell calcification: well-defined sickle-shaped calcification of the rims of hilar lymph nodes
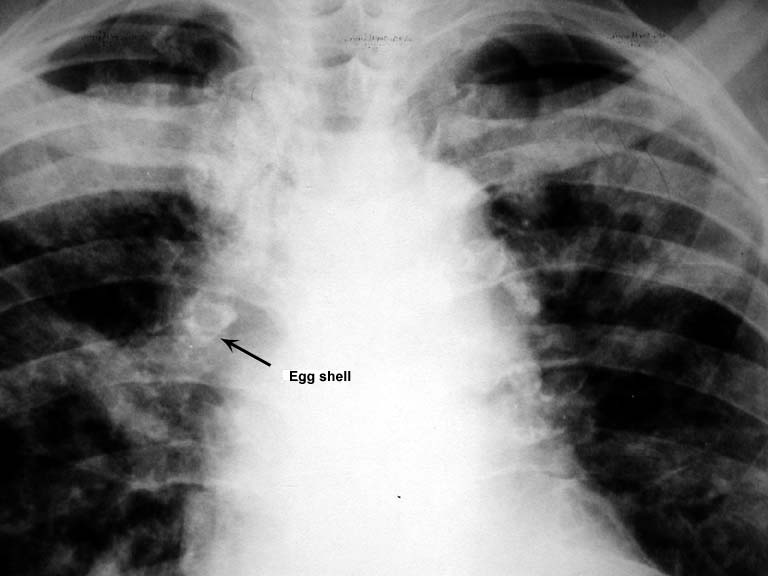
- Bilateral diffuse ground glass opacities
- Large number of rounded, solitary, small (≤ 1 cm in diameter) opacities particularly in the upper lobe of the lungs
- Eggshell calcification: well-defined sickle-shaped calcification of the rims of hilar lymph nodes
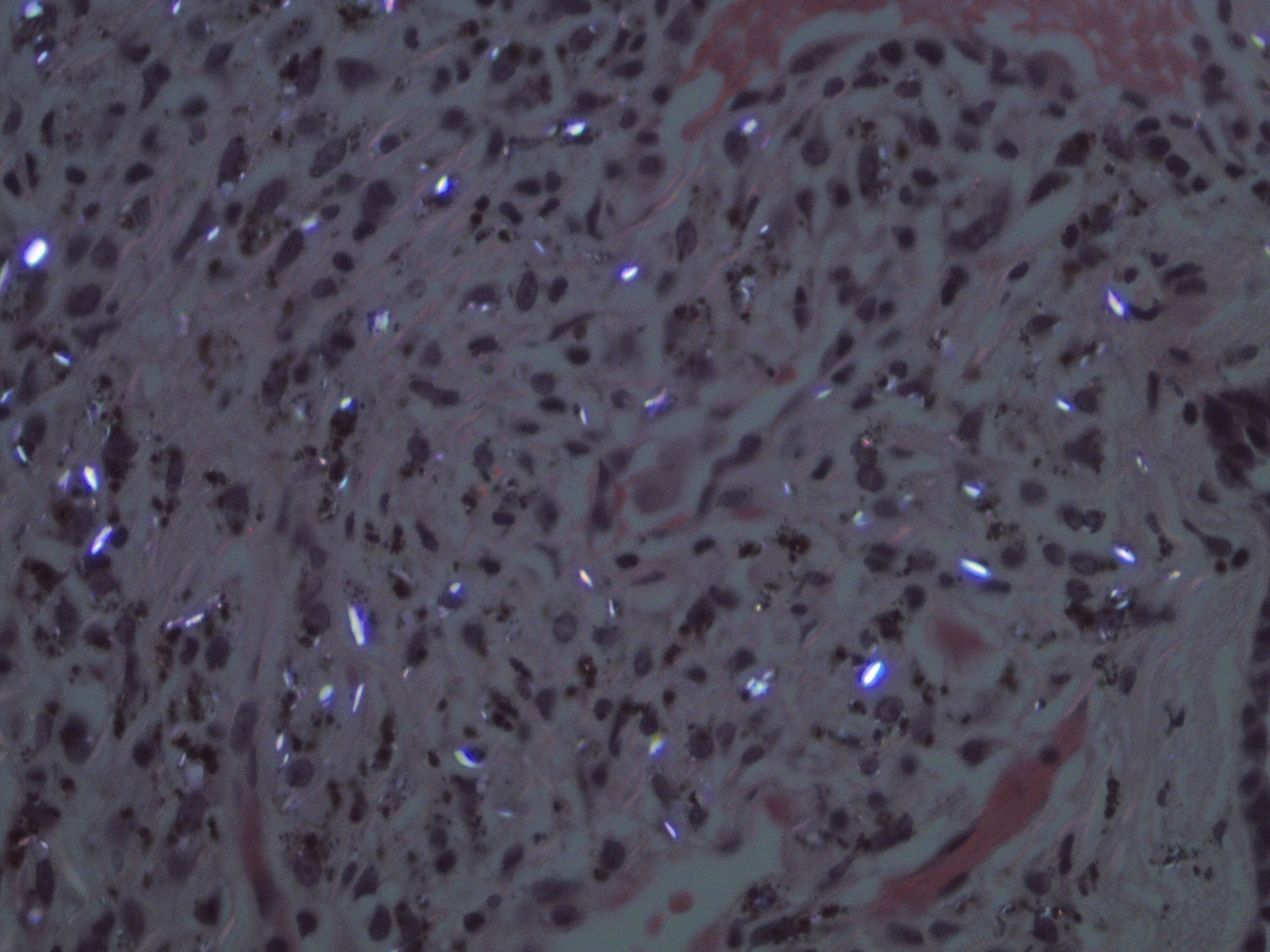
- Biopsy: silicotic nodules, characterized by weakly birefringent silica particles in a central hyalinized region surrounded by concentric “onion-skin” collagen fibers
- Etiology:
- Population at risk:
- Clinical features:
- Chest x-ray:
- Etiology:
- Population at risk:
- Clinical features:
- Chest x-ray:
- Etiology:
- Population at risk:
- Clinical features:
- Chest x-ray:
- Etiology:
- Population at risk:
- Clinical features:
- Chest x-ray:
- Etiology:
- Population at risk:
- Clinical features:
- Chest x-ray: