Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
All patients with Meniere disease have impaired endolymph resorption that results in endolymph hydrops.
- Endolymph hydrops: accumulation of fluid in the endolymphatic sac.
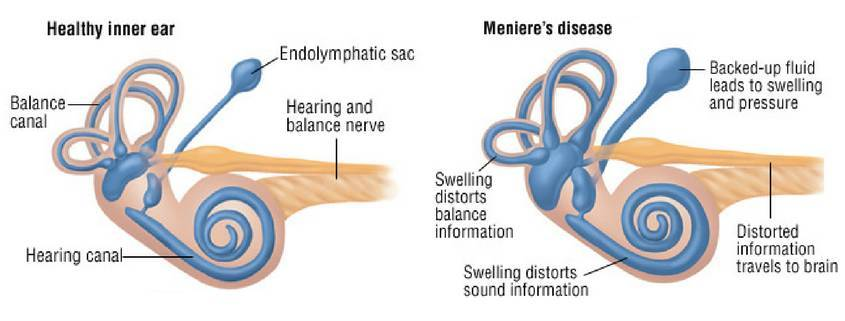
- Rupture theory: fluid accumulation in the endolymphatic sac → tear in the Reissner membrane → increased perilymphatic potassium → depolarization of the afferent acoustic nerve fibers → symptom onset
- Compression theory: impaired endolymph resorption → compression of the semicircular canals → symptom onset
Clinical features
Meniere disease characteristically manifests as recurrent episodes of acute, unilateral symptoms that last from minutes to hours.
Meniere triad
- Peripheral vertigo
- Tinnitus
- Asymmetric fluctuating sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL)
BPPV vs Ménière disease
- BPPV
- Recurrent, brief episodes (seconds)
- Positional, Dix-Hallpike (+)
- Only vertigo, without cochlear (e.g., hearing loss or tinnitus) or neurological symptoms.
- Ménière disease
- Recurrent episodes (minutes–hours)
- Vertigo, ear fullness/pain, unilateral hearing loss & tinnitus