-
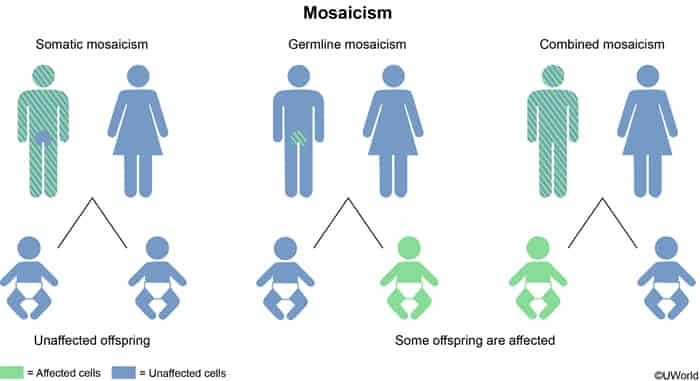
Mosaicism: the presence of two or more populations of cells within an organism, each with a different genetic composition
-
Somatic Mosaicism
- Mutation propagates through mitotic division to specific body tissues.
- Does not affect gametes; cannot be passed to offspring.
- Clinical Relevance:
- McCune-Albright Syndrome: Due to a mutation in the GNAS gene (G-protein activation). The mutation is lethal if it occurs before fertilization (affecting all cells), but survivable if present as somatic mosaicism.
- Classic Triad: Unilateral café-au-lait spots (“coast of Maine”), fibrous dysplasia, endocrine abnormalities (e.g., precocious puberty).
- Can result in milder phenotypes of chromosomal disorders (e.g., Mosaic Turner Syndrome [45,X/46,XX] or Mosaic Down Syndrome).
- McCune-Albright Syndrome: Due to a mutation in the GNAS gene (G-protein activation). The mutation is lethal if it occurs before fertilization (affecting all cells), but survivable if present as somatic mosaicism.
-
Gonadal (Germline) Mosaicism
- Mutation is present only in the egg or sperm cells.
- The parent is phenotypically healthy/asymptomatic (somatic cells are normal).
- Clinical Relevance:
- Suspect when phenotypically normal parents have multiple children affected by an autosomal dominant or X-linked disorder.
- Classic USMLE examples: Osteogenesis Imperfecta (Type I) and Tuberous Sclerosis.
- Note: If only one child is affected, it is likely a sporadic (de novo) mutation. If multiple are affected, suspect gonadal mosaicism.