Core Concepts
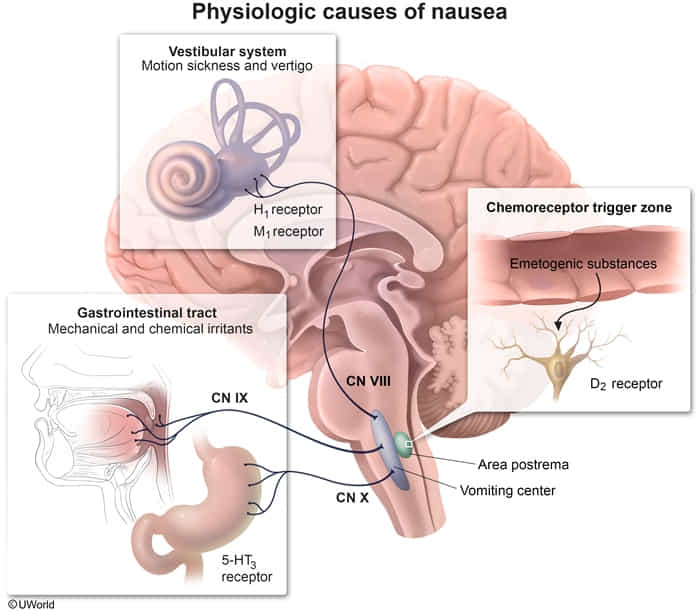
Nausea and vomiting are controlled by the vomiting center (nucleus tractus solitarius, NTS) in the medulla, which receives input from the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ or area postrema), GI tract (via vagus nerve), cerebral cortex, and vestibular system. Antiemetic drugs target specific receptors in these pathways.
| Class | MoA | Drug | Primary Use | Top Side Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT3 Antagonist | Blocks 5-HT3 receptors in CTZ & periphery | Ondansetron | Chemo & Post-Op N/V | QT Prolongation |
| D2 Antagonist | Blocks D2 receptors in Chemoreceptor Trigger Zone (CTZ) | Metoclopramide | Gastroparesis, CINV | Extrapyramidal Sx |
| NK1 Antagonist | Blocks NK1 receptors (for Substance P) in brainstem | Aprepitant | Delayed CINV | Fatigue, Hiccups |
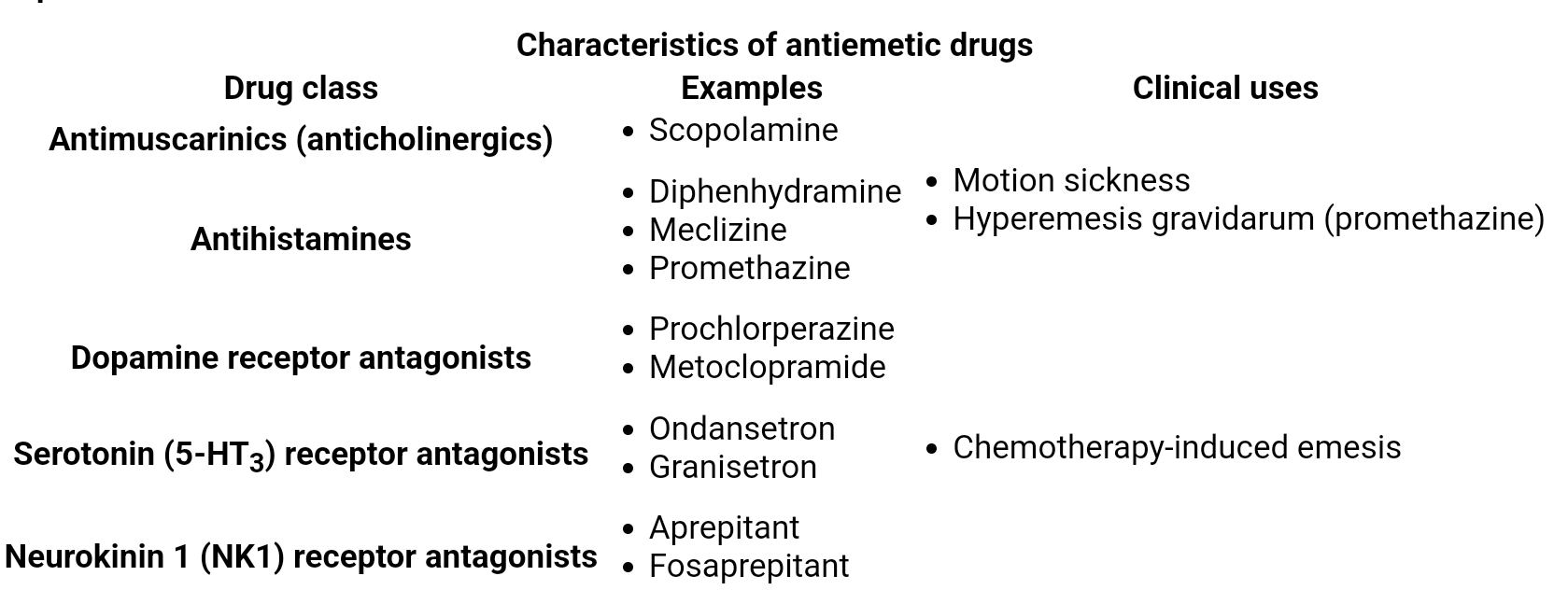
| H1/M1 Antagonist | Blocks H1 & M1 receptors in vestibular system | Meclizine, Scopolamine | Motion Sickness/Vertigo | Sedation, Anticholinergic |
5-HT3 Receptor Antagonists
- Drugs: Ondansetron, Granisetron, Palonosetron.
- Mechanism: Block 5-HT3 receptors in the CTZ and on vagal afferent nerves in the GI tract. This is particularly effective for emesis caused by GI irritants like chemotherapy, which triggers serotonin release from enterochromaffin cells.
- Clinical Use:
- Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV), especially acute phase.
- Postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV).
- Radiation-induced nausea and vomiting.
- Adverse Effects:
- Headache, constipation, dizziness.
- QT prolongation (risk of Torsades de Pointes); a dose-dependent effect.
- Potential for Serotonin Syndrome if used with other serotonergic agents.
D2 Receptor Antagonists
- Drugs:
- Phenothiazines: Prochlorperazine, Promethazine.
- Butyrophenones: Haloperidol, Droperidol.
- Benzamides: Metoclopramide.
- Mechanism: Block D2 receptors in the CTZ. Metoclopramide also has 5-HT3 antagonist effects at higher doses and prokinetic effects by increasing GI motility. Promethazine also blocks H1 receptors.
- Clinical Use:
- General purpose antiemetic (e.g., gastroenteritis).
- Migraine-associated nausea (Prochlorperazine).
- Gastroparesis (Metoclopramide).
- Adverse Effects:
- Extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) such as dystonia, akathisia, and parkinsonism, due to central dopamine blockade.
- Sedation, orthostatic hypotension.
- QT prolongation (especially Droperidol and Haloperidol).
- Metoclopramide has a black box warning for tardive dyskinesia with long-term use.
NK-1 Receptor Antagonists
- Drugs: Aprepitant, Fosaprepitant.
- Mechanism: Block neurokinin-1 (NK-1) receptors in the CNS, inhibiting substance P, a key mediator in the emetic pathway.
- Clinical Use:
- Primarily for delayed CINV (Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea & Vomiting).
- Often used in combination with a 5-HT3 antagonist and a corticosteroid (e.g., dexamethasone) for highly emetogenic chemotherapy.
- Adverse Effects:
- Fatigue, dizziness, hiccups.
- Can have significant drug-drug interactions via CYP3A4 metabolism.
H1 Receptor Antagonists & Anticholinergics
- Drugs:
- H1 Antagonists: Diphenhydramine, Meclizine, Promethazine.
- Anticholinergics (Muscarinic M1 antagonists): Scopolamine.
- Mechanism: Act on H1 and M1 receptors in the vestibular nuclei and NTS. Effective for emesis originating from the vestibular system.
- Clinical Use:
- Motion sickness.
- Vertigo.
- Adverse Effects:
- Sedation, especially with first-generation antihistamines.
- Anticholinergic effects: dry mouth, blurred vision, urinary retention, constipation, confusion (especially in the elderly).
Other Antiemetic Classes
- Corticosteroids (e.g., Dexamethasone):
- Mechanism: Not fully understood, but may involve inhibition of prostaglandins and enhancing the efficacy of other antiemetics.
- Use: Commonly used as an adjunct for CINV and PONV.
- Benzodiazepines (e.g., Lorazepam):
- Mechanism: Provide anxiolysis and sedation, which is useful for anticipatory nausea and vomiting before chemotherapy.
- Cannabinoids (e.g., Dronabinol, Nabilone):
- Mechanism: Agonists at cannabinoid receptors in the CNS.
- Use: Refractory CINV.
- Adverse Effects: Altered perception, dizziness, euphoria, drowsiness.