- Impaired copper excretion causes copper to accumulate in the body.
- Early-stage Wilson disease is characterized by the presence of copper deposits in the liver.
- As the disease progresses, copper accumulates in other organs as well, most importantly in the brain and cornea.
Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
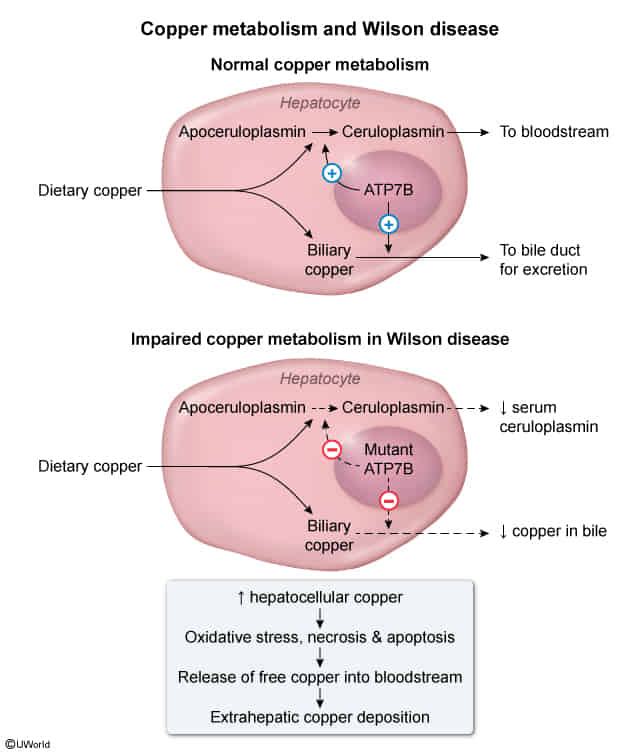
- Autosomal recessive mutations in the ATP7B gene (Wilson gene) on chromosome 13, which encodes for a membrane-bound, copper-transporting ATPase → defective ATP7B protein
- Reduced incorporation of copper into apoceruloplasmin → ↓ serum ceruloplasmin (The major carrier of copper in the blood and an important enzyme with ferroxidase activity.)
- Reduced biliary copper excretion
- Results in ↑ free serum copper → accumulation in the liver, cornea, CNS (basal ganglia, brain stem, cerebellum), kidneys, and enterocytes
Tip
Don’t mess up with Hemochromatosis
Clinical features
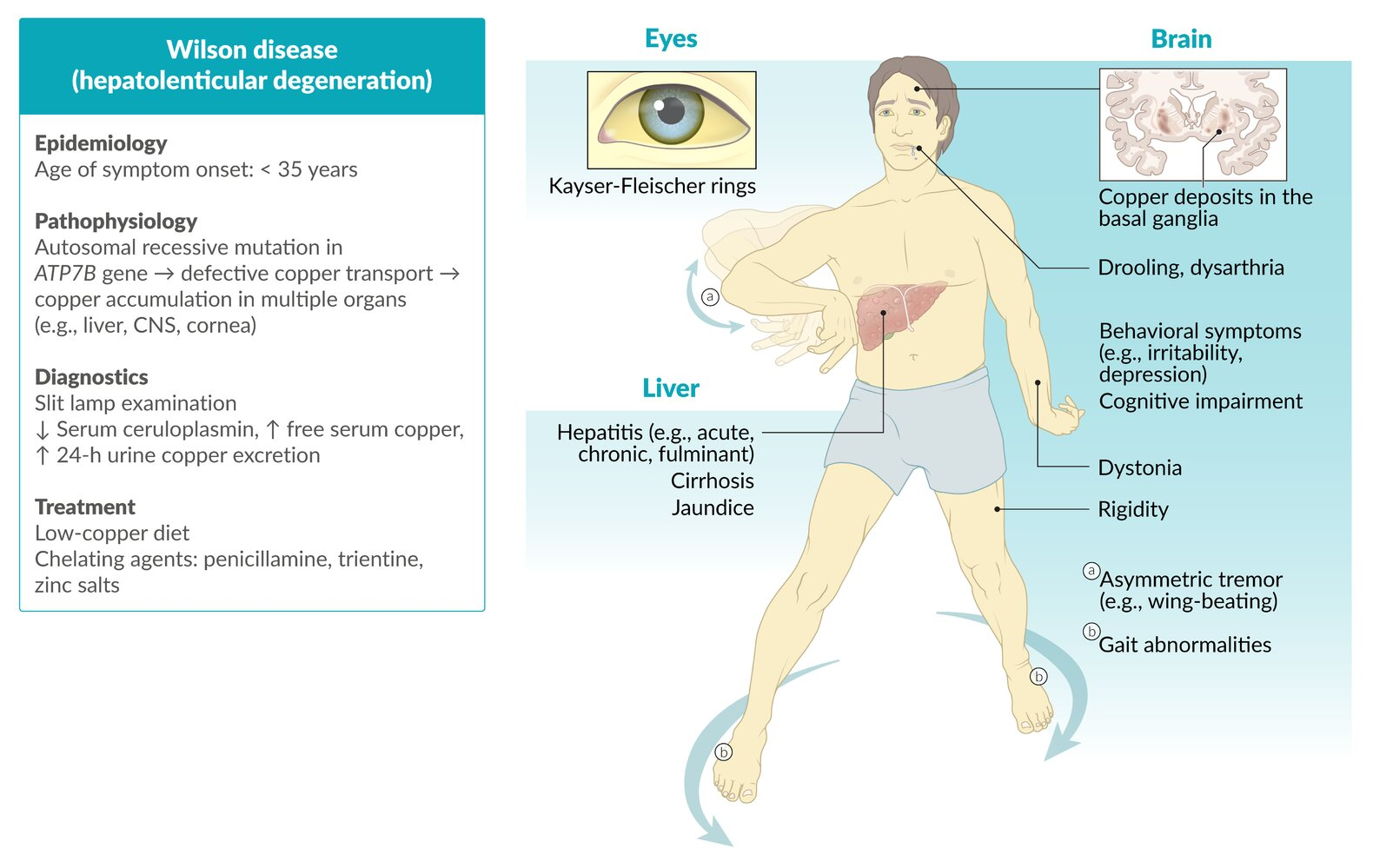
- Neurological
- Cerebellar symptoms, e.g.:
- Dysarthria (most common)
- Extrapyramidal symptoms, e.g.:
- Dystonia
- Parkinsonism
- Tremor (usually asymmetric, affecting the hands), which may be any combination of:
- Resting tremor
- Intention tremor
- Wing-beating tremor: a low frequency, high amplitude tremor that is most prominent when the arms are outstretched anteriorly or laterally
- Drooling (caused by oropharyngeal dysphagia)
- Cognitive impairment
- Cerebellar symptoms, e.g.:
Wilson disease vs hemochromatosis
- Wilson disease has neurologic symptoms but hemochromatosis doesn’t have
- Think about Wilson from Don’t Starve, the mad scientist
Diagnostics
Treatment
General principles
- Encourage a low-copper diet (e.g., avoidance of organ meats, shellfish, nuts, chocolate, copper-containing dietary supplements).
- Refer patients with refractory decompensated cirrhosis or acute liver failure for liver transplantation.
Pharmacological therapy
- First line: chelating agents, e.g., penicillamine (preferred) or trientine
- Chelating agents facilitate renal excretion of copper by forming water-soluble compounds.
- Adverse effect: Membranous nephropathy
- Maintenance therapy: reduced-dose zinc salts or a chelating agent
