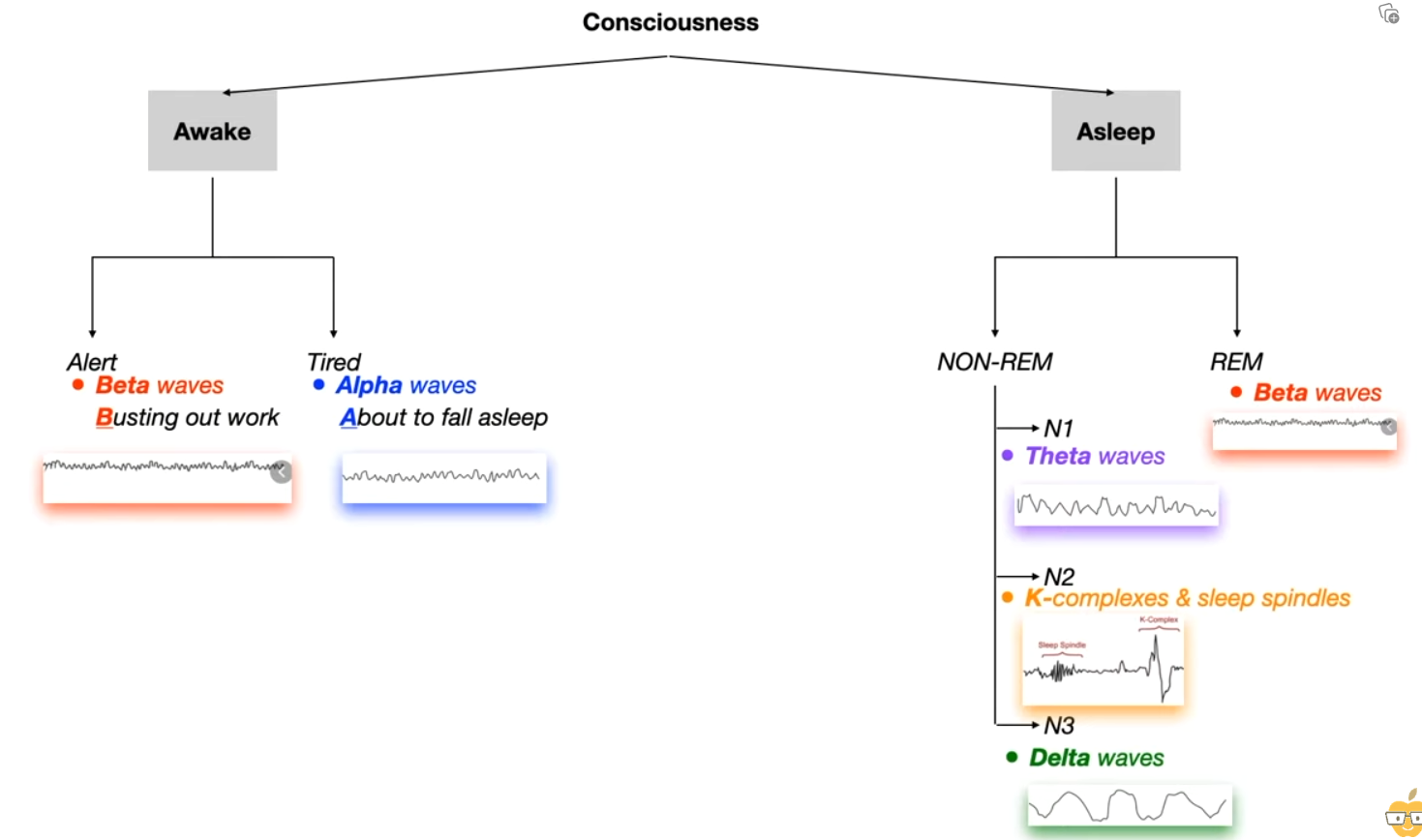
Sleep physiology
Tip
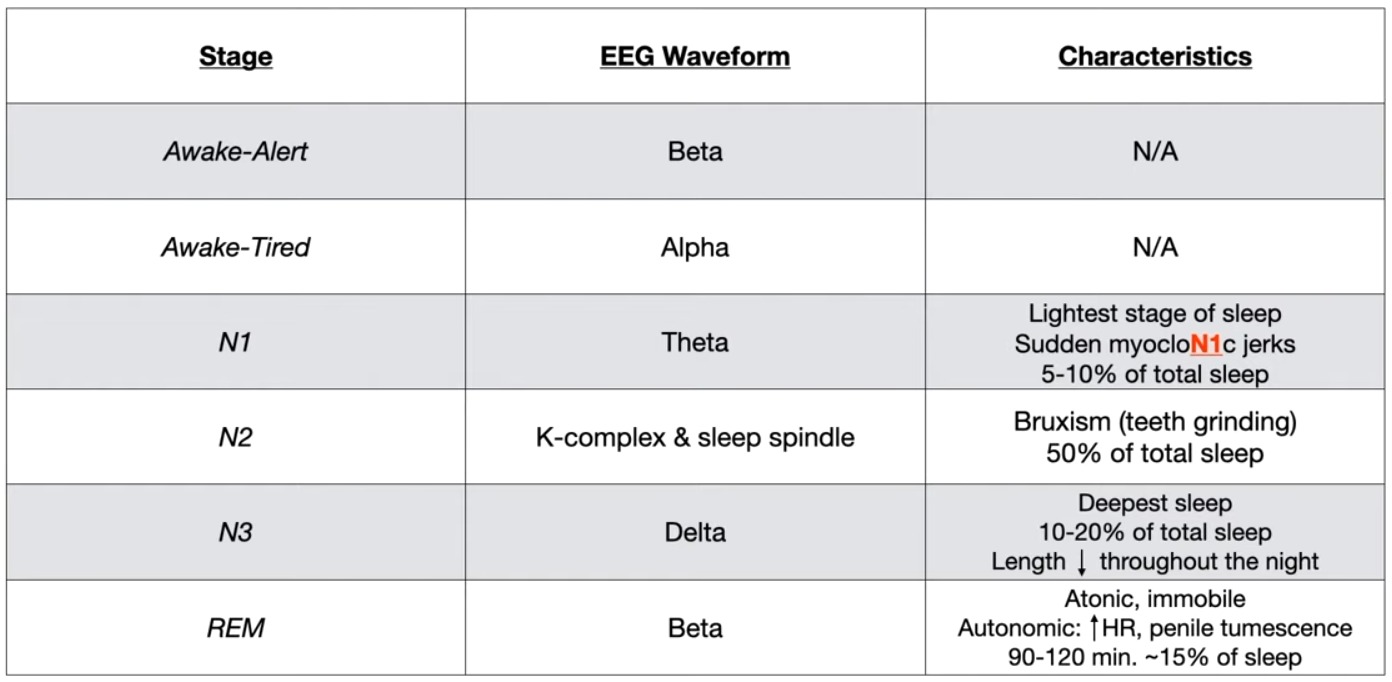
Alert and REM are both Beta waves.
Mnemonic
- In REM stage, B for Beta and Boner.
- REMember your dream
- REMain still (so you won’t act like in dreams)
- To remember K complex and Sleep Spindle is N2
- It takes ‘2’ to “KiSS” (also note that kissing involves mouth and hence teeth=Teeth grinding)
- Delta for Deepest sleep
Mnemonic
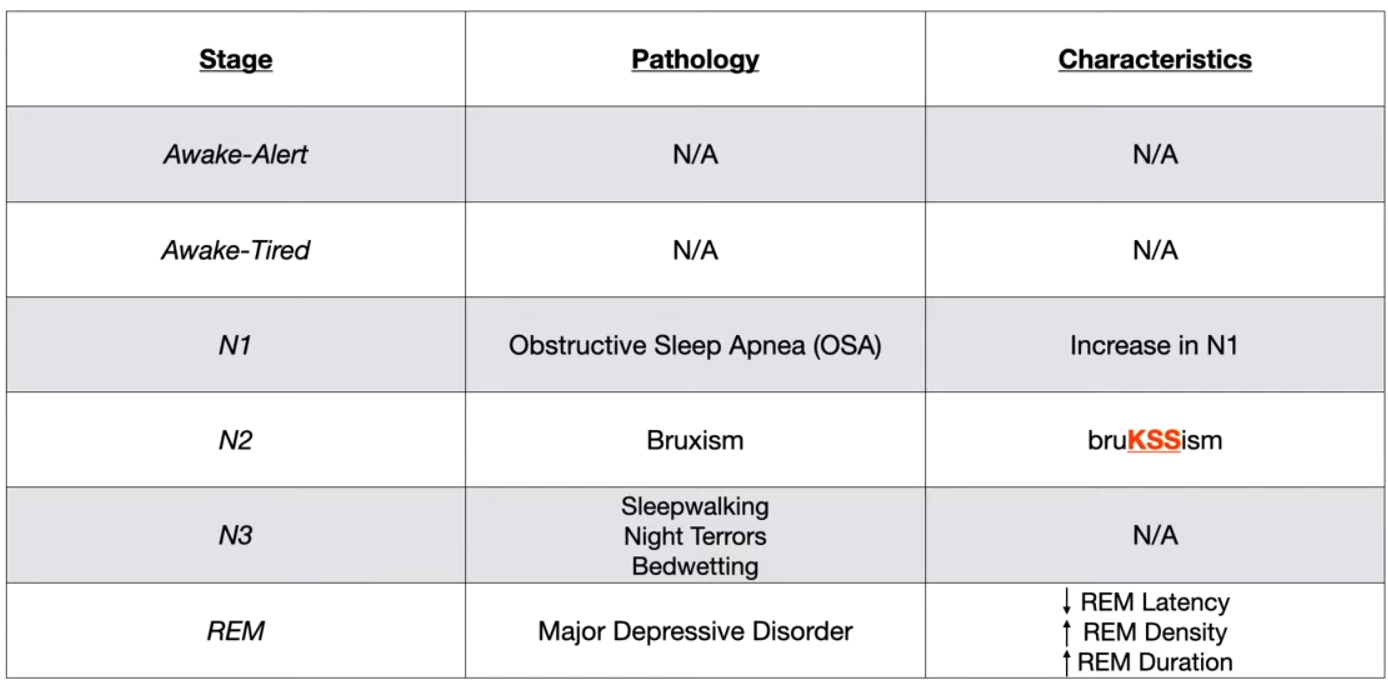
- N1: Obstructive Sleep ApN1a
- N3: All these things happen in deepest sleeping.
- REM: In MDD you have less fine, deep sleep (N3), more REM.
Parasomnias
Sleep terror disorder
- Definition: a non-REM-related parasomnia that occurs during the N3 sleep stage (slow-wave sleep), characterized by episodes of sleep terror
- Epidemiology: Discrete episodes of sleep terrors are relatively common in children (∼ 20% of children and ∼ 2% of adults), but the disorder is rare.
- Risk factors
- Stress or fatigue
- Fever
- Sleep deprivation
- Clinical features
- Screaming or crying suddenly upon awakening, usually in the first part of the night (rarely during daytime naps)
- Intense fear and agitation
- Tachypnea, diaphoresis, tachycardia during episodes
- Difficulty arousing patients during episodes
- Patients usually return to sleep after the episode.
- Typically no recollection of the arousal episode (unlike with nightmare disorder)
- Nightmare disorder
- a REM-related parasomnia characterized by recurrent nightmares
- Patient remembers the dream after awakening (REMember)
- Nightmare disorder
REM sleep behavior disorder
- Definition: a REM-related parasomnia characterized by dream enactment due to loss of REM sleep atonia
- Epidemiology
- Sex: ♂ > ♀
- Usually in older patients (> 50 years)
- Risk factors
- Narcolepsy
- Psychiatric medications (e.g., antidepressants)
- Neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Parkinson disease, Lewy body dementia)
- Clinical features
- Physically acting out dreams during sleep (e.g., yelling, moving limbs, walking, punching), sometimes leading to injury to self or others
- Patient is alert and orientated after awakening, and remembers the dream.
- Prognosis: Most patients with idiopathic RBD eventually develop a disorder of α-synuclein neurodegeneration, most commonly Parkinson disease.