Etiology
Tip
- The most common cause of nephritic syndrome is immune complex deposition, which leads to serum hypocomplementemia.
- IgA nephropathy is an exception, which is characterized by normal serum complement levels
- ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis (pauci-immune glomerulonephritis)
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
- Microscopic polyangiitis
- Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis
- Anti-glomerular basement membrane (GBM) associated glomerulonephritis
- Anti-GBM disease (Goodpasture disease)
- Anti-GBM glomerulonephritis (no lung involvement)
- Immune complex-mediated glomerulonephritis
- Low C3 levels
- Lupus nephritis
- Infection-related glomerulonephritis
- Normal C3 levels
- Low C3 levels
Classifications
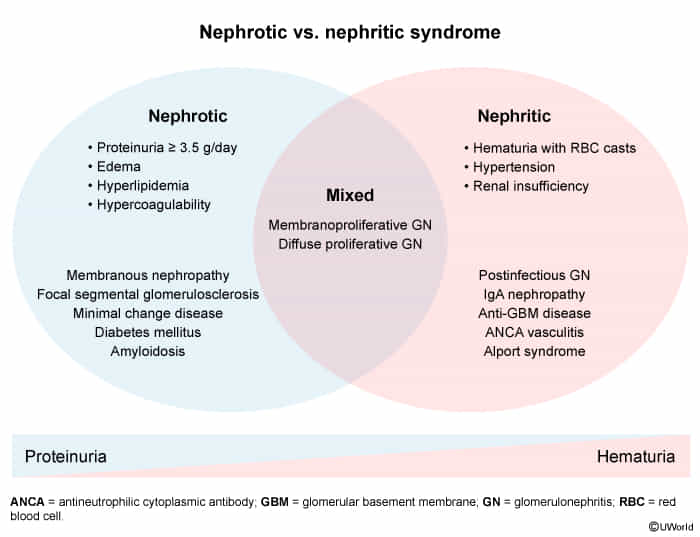
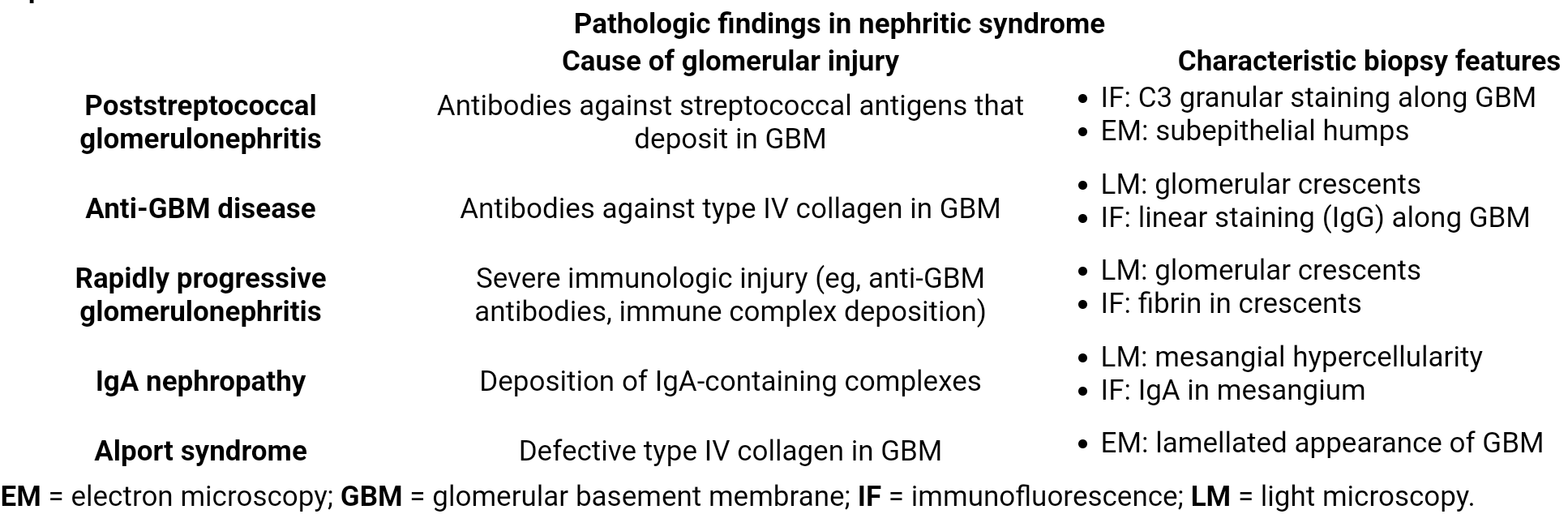
- Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis
- Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis
- Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis
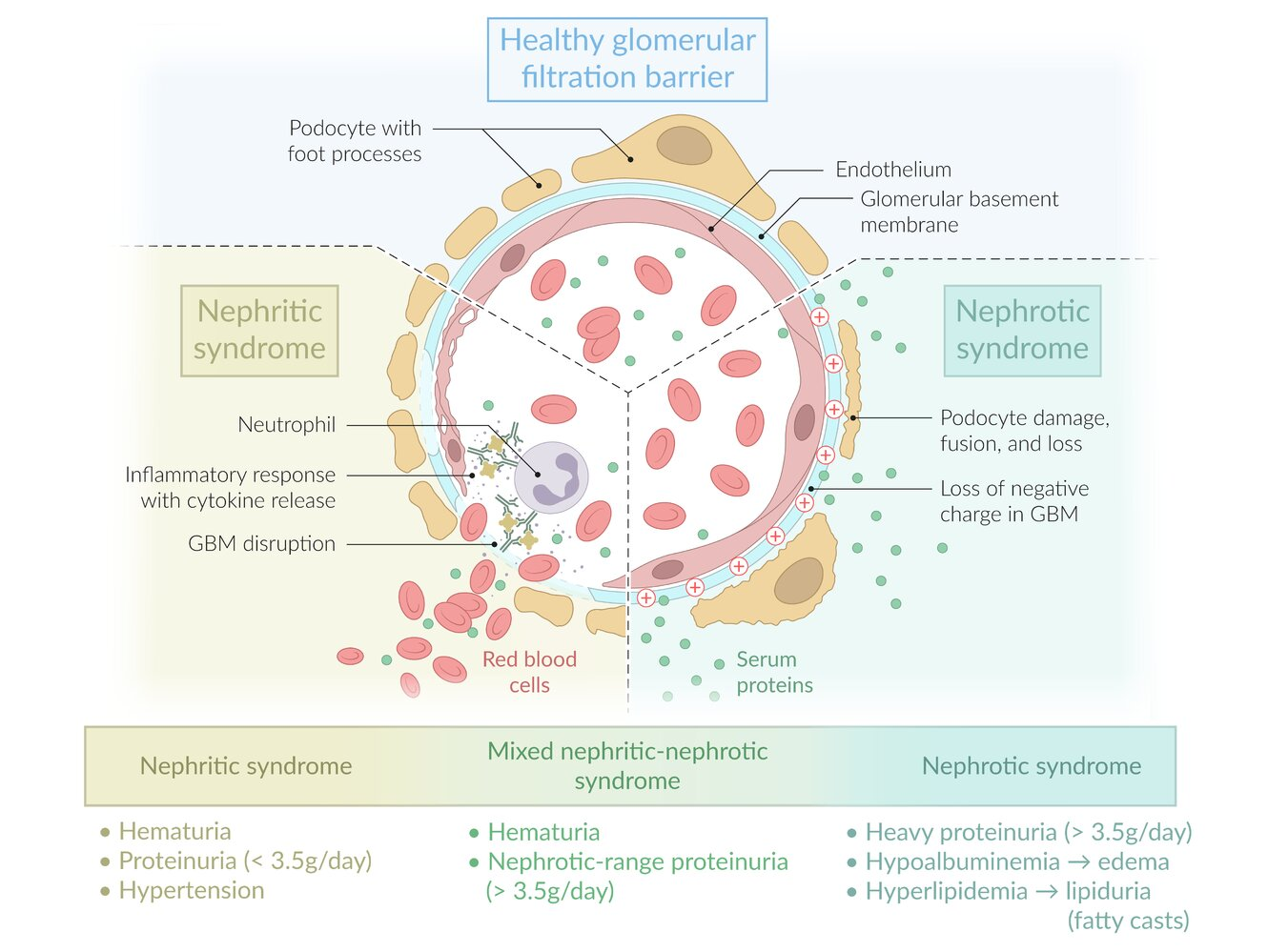
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Diagnostics
- Urinalysis: nephritic sediment
- Hematuria (either microhematuria or intermittent macrohematuria)
- Acanthocytes
- Red blood cell casts: RBC casts form through the congregation of proteins and RBCs inside the tubules.
- Mild to moderate proteinuria of > 150 mg/24 h but < 3.5 g/24 h (nonselective glomerular proteinuria)
- Sterile pyuria and sometimes WBC casts
- Blood tests
- ↑ Creatinine, ↓ GFR
- Azotemia with ↑ BUN
- Complement, ANA, ANCA, and anti-GBM antibodies