Second-Degree AV Block
Mobitz Type I (Wenckebach)
- Pathophysiology: Progressive fatigue of the AV node.
- ECG Findings:
- Progressive lengthening of the PR interval until a beat (QRS) is dropped.
- “Going, going, gone.”
- The PR interval after the dropped beat is shorter than the one before the drop.
- R-R interval shortens as the PR interval lengthens.
- Location: Usually intranodal (AV node).
- Management:
- Asymptomatic: Observation.
- Symptomatic: Atropine, Isoproterenol.
Mobitz Type II
- Pathophysiology: Intermittent block, usually below the AV node (His-Purkinje system). Structural damage.
- ECG Findings:
- Constant PR interval in conducted beats.
- Intermittent dropped QRS complexes (e.g., 2:1 or 3:1 block).
- QRS complexes are often wide (bundle branch block).
- Significance: High risk of progression to 3rd-degree block.
- Management:
- Pacemaker is usually indicated.
- Contraindicated: Atropine (can worsen block/conduction ratio in distal blocks).
Description
Single or intermittent nonconducted P waves without QRS complexes The PR interval remains constant. The conduction of atrial impulses to the ventricles typically follows a regular pattern, e.g.:
- 3:2 block: regular AV block with 3 atrial depolarizations but only 2 atrial impulses that reach the ventricles (heart rate = ⅔ SA node rate)
- 4:3 block: regular AV block with 4 atrial depolarizations but only 3 atrial impulses that reach the ventricles (heart rate = ¾ SA node rate)
While 2:1 block follows a regular pattern, it cannot be classified as Mobitz type I or II and is classified separately (see “2:1 AV block”).
Risk of progression to complete heart block: high (> 50%), as it is typically due to infranodal block (usually in the His-Purkinje system)
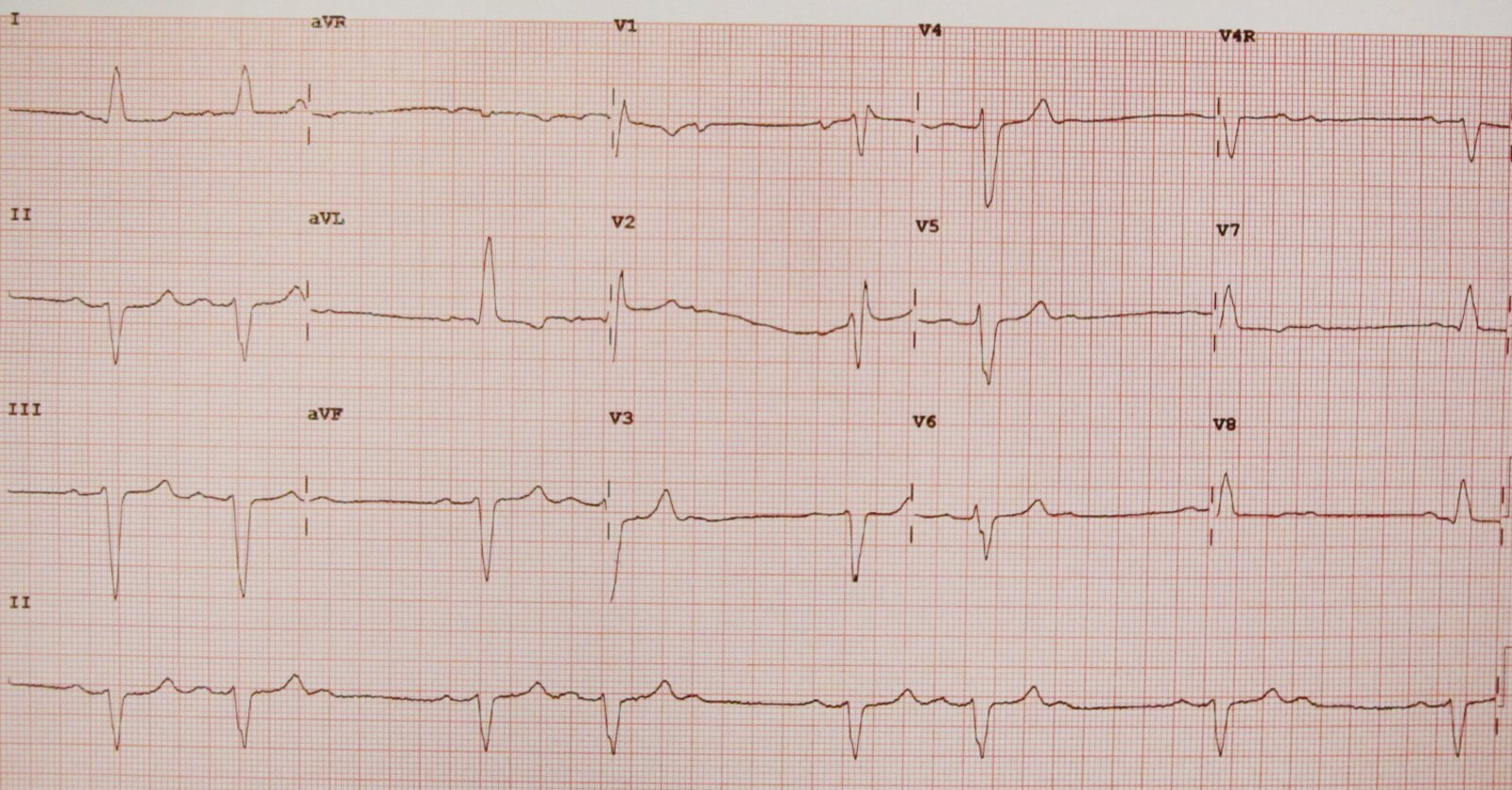
2:1 AV block
- Description
- Inhibited conduction of every second atrial depolarization (P wave) to the ventricles (heart rate = ½ SA node rate)
- Cannot be classified as Mobitz I or Mobitz II as only one PR interval is observed before the subsequent dropped complex (can fit into both types)
- Often a transient rhythm occurring on a baseline Mobitz I or Mobitz II rhythm
- Risk of progression to complete heart block: depends on level of block
- Block at the level of the AV node (more common): low
- Infranodal block (less common): high
Ventriculophasic sinus arrhythmia
Sinus rate variation of this type with complete heart block is called ventriculophasic sinus arrhythmia.