A genetic disorder that is characterized by decreased urinary calcium excretion and (usually asymptomatic) hypercalcemia. PTH levels are normal in most patients. Caused by an autosomal dominant mutation of a calcium-sensing receptor in the kidneys and parathyroid gland (CaSR gene).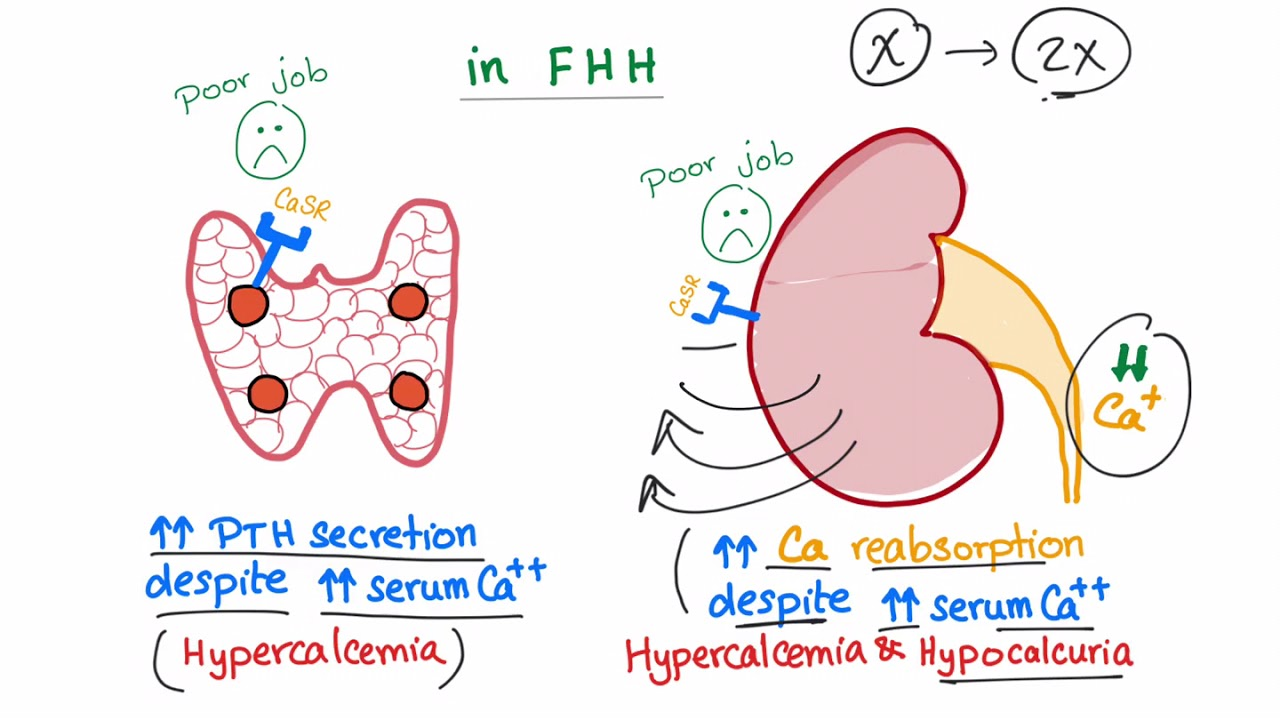
- Clinical features
- Usually asymptomatic
- Neonatal hypocalcemia in children of mothers with FHH (e.g., paresthesias, muscle spasms, seizures)
- Diagnosis
- Hypercalcemia and inappropriately normal or increased PTH
- Hypocalciuria
- Therapy
- No treatment necessary