Familial dyslipidemias
| Dyslipidemia | Protein defect | Elevated lipoproteins | Major manifestations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Familial chylomicronemia syndrome (type I) | Lipoprotein lipase, ApoC-2 | Chylomicrons (composed of TG, large) | Acute pancreatitis, Lipemia retinalis, Eruptive xanthomas |
| Familial hypercholesterolemia (type II A) | LDL receptor, ApoB-100 | LDL (small and can enter vessel wall) | Premature atherosclerosis, Tendon xanthomas, Xanthelasmas |
| Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia (type III) | ApoE | Chylomicron & VLDL remnants | Premature atherosclerosis, Tuboeruptive & palmar xanthomas |
| Familial hypertriglyceridemia (type IV) | Polygenic | VLDL | Associated with coronary disease, pancreatitis & diabetes |
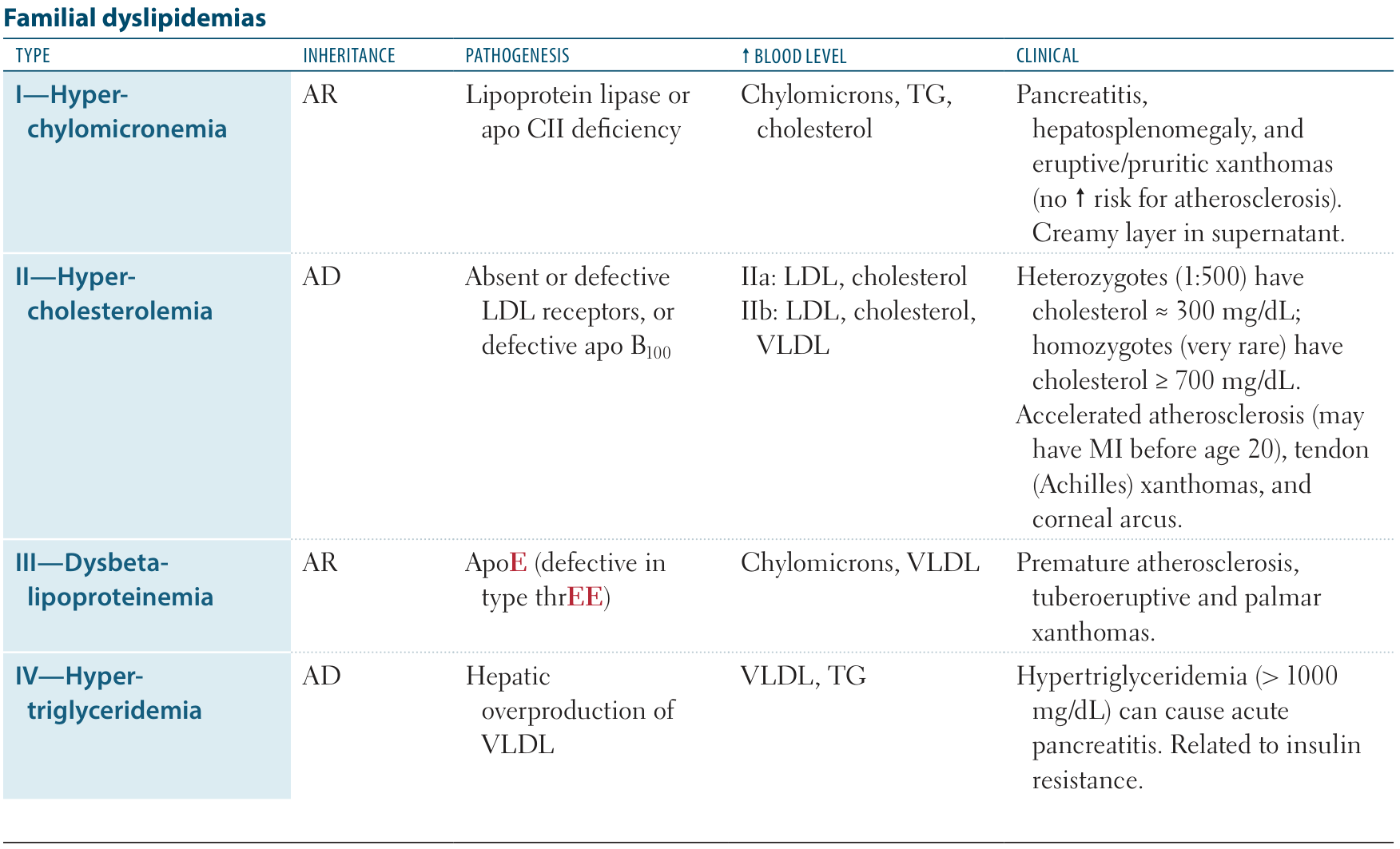

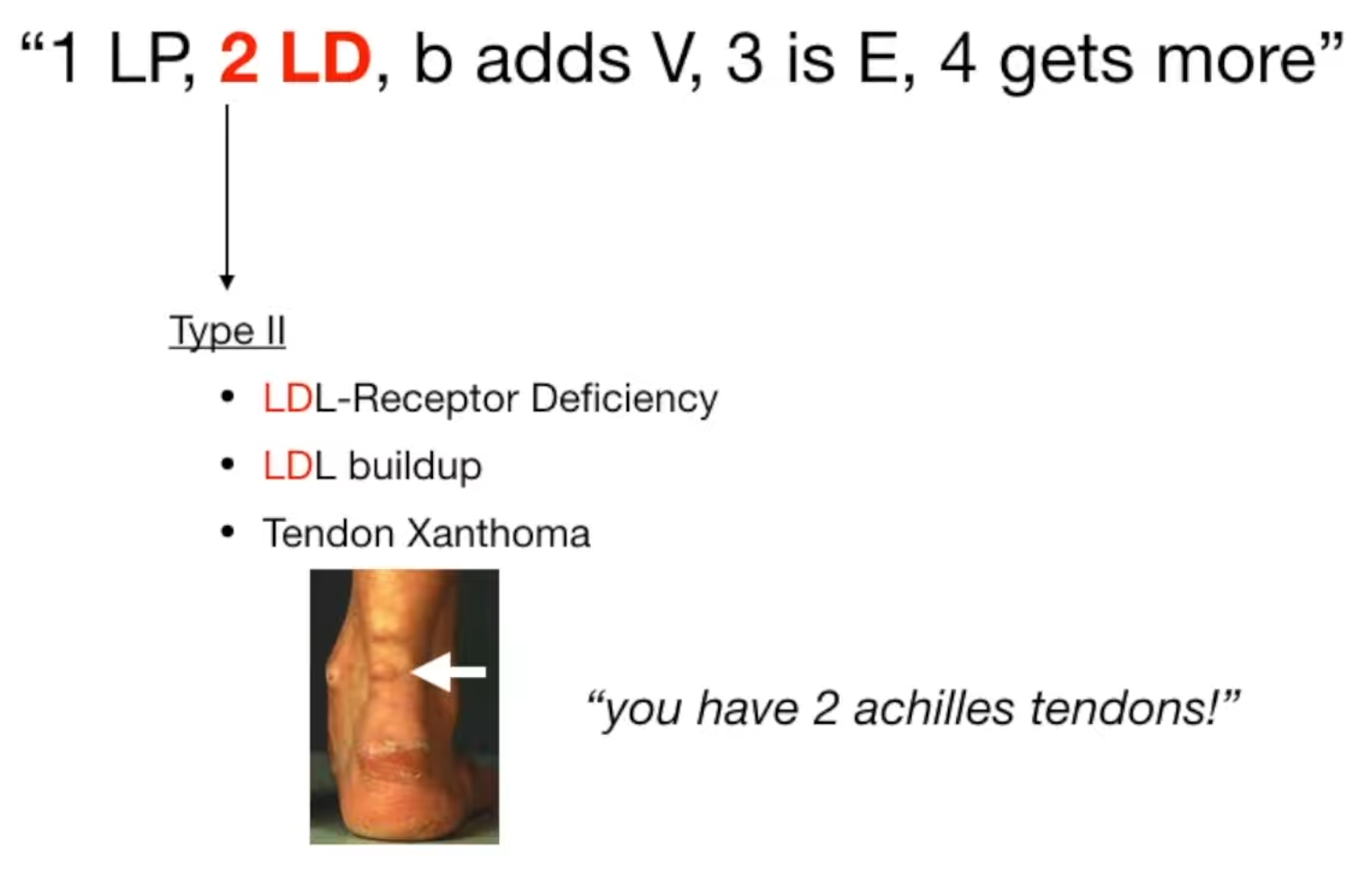
- Type II
- Premature atherosclerosis, may lead to myocardial infarction at a very young age (< 20 years)
- Arcus lipoides corneae
- Tuberous/tendon xanthomas (especially the Achilles tendon) in type IIa



Abetalipoproteinemia
- Etiology
- Deficiency of apolipoproteins (ApoB-48, ApoB-100) t
- Due to a mutation in the microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTTP) gene
- Pathophysiology
- Autosomal recessive disease
- Deficiency of chylomicrons, VLDL, and LDL (hypolipoproteinemia)
- Clinical features
- Early
- Steatorrhea
- Failure to thrive
- Fat malabsorption → fat-soluble vitamin deficiency
- Early
- Diagnostics
- Intestinal biopsy: Histology may reveal lipid-laden enterocytes.
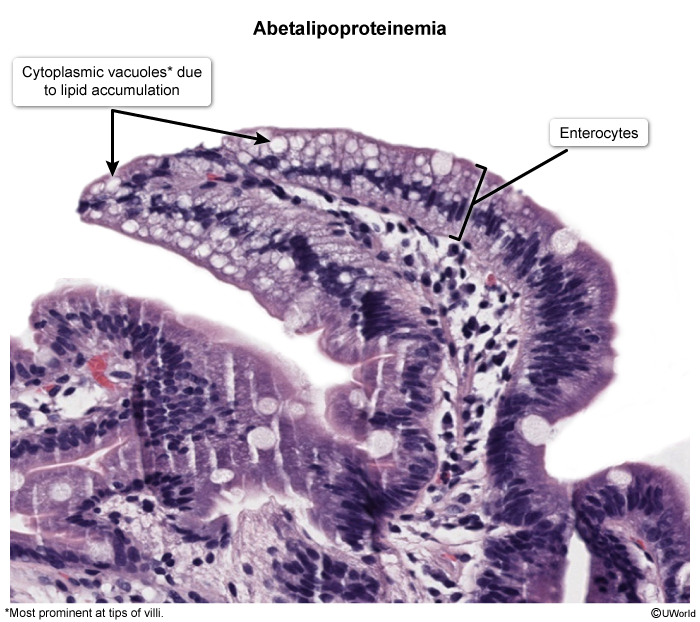
- Intestinal biopsy: Histology may reveal lipid-laden enterocytes.