Epidemiology
Etiology
- Impaired development and/or fusion of embryonic structures (pleuroperitoneal membrane) → defect in the diaphragm persists during fetal development → displacement of abdominal contents into the pleural cavity → compression of lung tissue → pulmonary hypoplasia
- Failure of fusion of the septum transversum postero-laterally with the pleuroperitoneal membranes → Bochdalek hernia
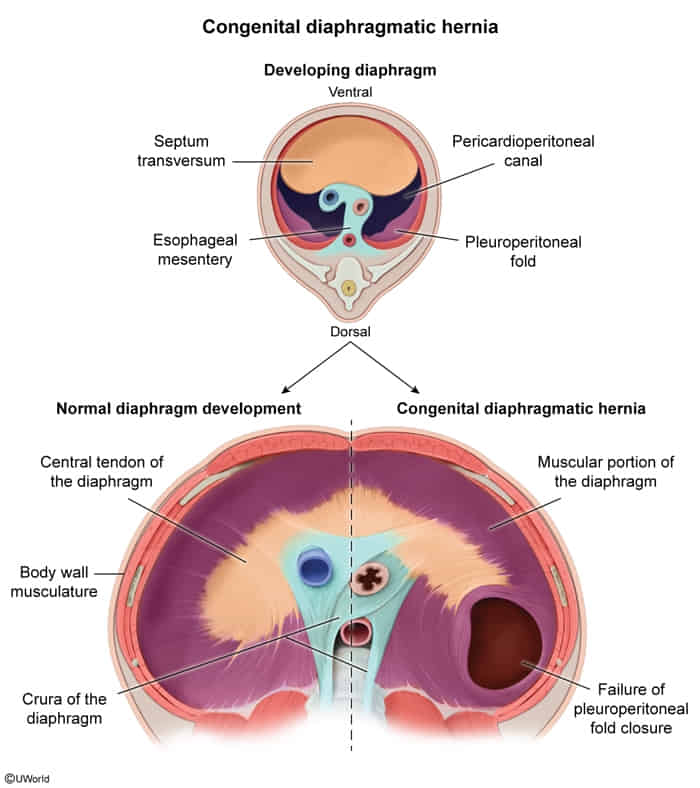
- Failure of fusion of the septum transversum postero-laterally with the pleuroperitoneal membranes → Bochdalek hernia
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
<% tp.file.cursor() %>
Diagnostics
<% tp.file.cursor() %>
Treatment
<% tp.file.cursor() %>