Core Concepts
- Definition: An experimental study design where participants are randomly assigned to an experimental group (receives intervention) or a control group (receives placebo or standard of care).
- “Gold Standard”: Considered the highest level of evidence for determining the efficacy and causality of a therapeutic or preventive intervention.
- Objective: To minimize bias when testing the effectiveness and safety of a new intervention.
Key Features
- Randomization:
- Each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any group.
- Purpose: To minimize selection bias and control for confounding variables (both known and unknown) by distributing them evenly among the groups.
- Allocation Concealment: The process of hiding the next allocated group from the person enrolling the participant, which prevents selection bias during recruitment.
- Control Group:
- The group that receives a placebo, no treatment, or the current standard of care.
- Purpose: Provides a baseline to compare the effect of the new intervention against.
- Blinding (Masking):
- Concealing group allocation from individuals involved in the trial to prevent bias.
- Single-blind: Only the participant is unaware of their assigned group.
- Double-blind: Both the participant and the investigators/clinicians are unaware of the group assignments. This is the most common and preferred method.
- Triple-blind: Participants, investigators, and data analysts are all unaware of group assignments.
- Purpose: Reduces performance bias (systematic differences in care) and ascertainment/observer bias (distorted outcome assessment).
Trial Designs & Phases
- Common Designs:
- Parallel Group: Each group receives a different treatment simultaneously (most common design).
- Crossover: Each participant receives both treatments in a sequence, separated by a “washout” period. Participants serve as their own controls.
- Factorial: Tests two or more interventions simultaneously using various combinations.
Clinical trials
Mnemonic
Does the drug SWIM?
“Is it Safe?” Assesses safety, toxicity, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics
“Does it Work?” Assesses treatment efficacy, optimal dosing, and adverse effects.
“Is it as good or better?” Compares the new treatment to the current standard of care (any Improvement?).
“Can it stay?” Detects rare or long-term adverse effects (eg, black box warnings). Can result in treatment being withdrawn from Market.
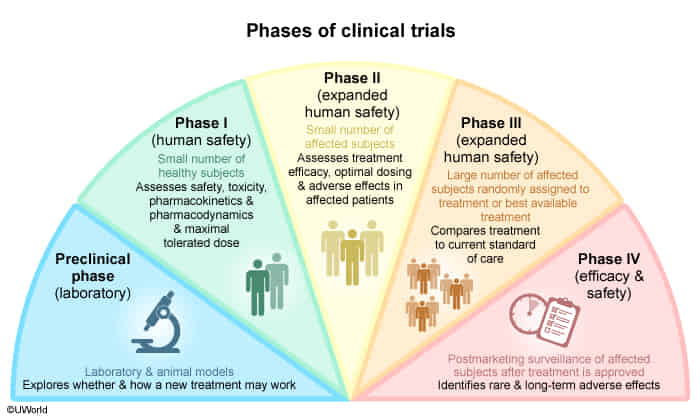
- Phase 0 trial
- Purpose: Exploratory phase with no therapeutic or diagnostic intent, aimed at gaining insight into pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.
- Only < 1% of the therapeutic dose is used.
- Safety and toxicity are not assessed.
- Study population: Small sample consisting of either healthy individuals or a population with a disease of interest (∼ 10–15).
- Study design: Open-label.
- Phase I trial
- Purpose: Evaluation of pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties of the drug, safety, and toxicity.
- Evaluation of the maximum tolerated dose.
- Study population: Small number of healthy individuals or patients with a specific disease (∼ 15–30).
- Study design: Open-label.
- Phase II trial
- Purpose: Evaluation of efficacy, optimal dose range, and side effects (especially common and short-term side effects).
- Study population: Moderate number of patients with a specific disease (∼ 10–100).
- Study design: Randomized, Controlled, Anonymized.
- Phase III trial
- Purpose: Final confirmation of safety and evaluation of efficacy against placebo or the current standard of care.
- Study population: Randomized control trial with a large number of patients with a specific disease (∼ 100–1000).
- Study design: Randomized Controlled Trial.
- Phase IV trial
- Purpose: Postmarketing surveillance, comparing real-life efficacy to that described in research studies. Safety studies following approval (especially evaluation of rare and long-term side effects).
- Study population: Large number of patients with a specific disease after drug approval.
- Study design: Open-label.
Analysis & Interpretation
- Intention-to-Treat (ITT) Analysis:
- All participants are analyzed in the groups to which they were originally randomized, regardless of whether they completed or adhered to the treatment protocol.
- Benefit: Preserves the benefits of randomization and gives a more realistic measure of the treatment’s effectiveness in a real-world setting. Minimizes bias from attrition.
- Per-Protocol Analysis:
- Only includes participants who strictly adhered to the protocol.
- Risk: Breaks randomization and is more susceptible to bias, but may provide a better measure of the treatment’s effect under ideal conditions.
Potential Biases & Limitations
- Selection Bias: Systematic differences between groups at baseline. Minimized by randomization and allocation concealment.
- Performance Bias: Systematic differences in the care provided to groups (apart from the intervention). Minimized by blinding.
- Detection/Ascertainment Bias: Systematic differences in how outcomes are assessed. Minimized by blinding of outcome assessors.
- Attrition Bias: Systematic differences in withdrawals or loss to follow-up between groups. Addressed by Intention-to-Treat analysis.
- Limitations of RCTs:
- Costly and time-consuming.
- Ethical concerns (e.g., withholding treatment, lack of clinical equipoise).
- Limited external validity (generalizability): Strict inclusion/exclusion criteria may result in a study population that is not representative of the general patient population.