Epidemiology
Etiology
- Compression of subclavian vessels and the lower trunk of the brachial plexus (mainly occurs within the scalene triangle) due to:
- Bones: anomalous cervical rib (an extra rib above the first rib)
- TOS most commonly occurs due to compression of the brachial plexus within the scalene triangle, which is formed by the anterior and middle scalene muscles and the first rib.
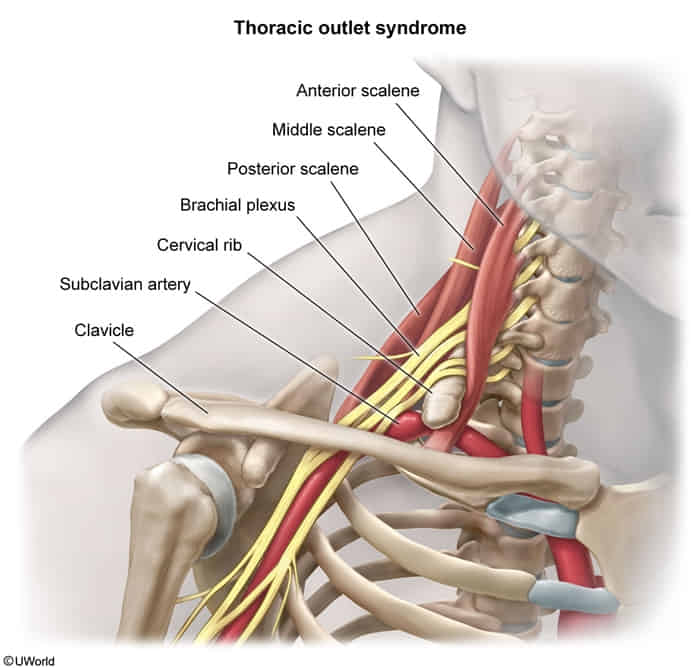
- TOS most commonly occurs due to compression of the brachial plexus within the scalene triangle, which is formed by the anterior and middle scalene muscles and the first rib.
- Soft tissue: hypertrophic muscles in athletes and weight lifters, poor posture and obesity, hematoma, tumors (e.g., Pancoast tumor)
- Bones: anomalous cervical rib (an extra rib above the first rib)
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Diagnostics
Treatment
<% tp.file.cursor() %>