Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Mnemonic
诱发三高和溃疡,伤口感染不好长,骨松眼青人发狂 三高 is related to Permissive action of corticosteroids
- ↑ Hematocrit
- Steroids, particularly anabolic steroids, stimulate the production of erythropoietin
Diagnostics
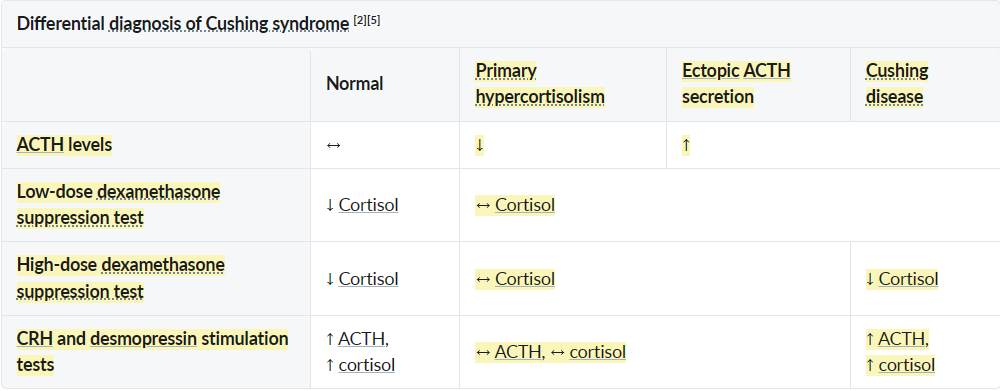
- High-dose dexamethasone suppression test
- Used to differ ectopic ACTH secretion vs Cushing disease
- This test is similar to the low-dose dexamethasone suppression test but uses 8 mg of dexamethasone. Most pituitary adenomas retain partial sensitivity to feedback inhibition in response to high doses of glucocorticoids, while ectopic tumors are resistant even to high doses.
Treatment
Bilateral adrenalectomy
- Indications
- Primary hypercortisolism caused by bilateral adrenal disease (recommended curative treatment)
- Emergency treatment in severe ACTH-dependent hypercortisolism that cannot be controlled pharmacologically
- Symptomatic treatment for metastatic or occult ectopic tumors
- Complication: Nelson syndrome (post adrenalectomy syndrome)
- Etiology: bilateral adrenalectomy in patients with a previously undetected pituitary adenoma
- Pathophysiology: bilateral adrenalectomy → no endogenous cortisol production → no negative feedback from cortisol on the hypothalamus → ↑ CRH production → uncontrolled enlargement of preexisting but undetected ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma → ↑ secretion of ACTH and MSH → manifestation of symptoms due to pituitary adenoma and ↑ MSH
- Clinical features: headache, bitemporal hemianopia (mass effect), cutaneous hyperpigmentation
- Diagnostics
- High levels of β-MSH and ACTH
- Pituitary adenoma on MRI confirms the diagnosis.
- Treatment: surgery (e.g., transsphenoidal resection) and/or pituitary radiation therapy (e.g., if the tumor cannot be fully resected)