Left part is for HIV, right part is for other virus.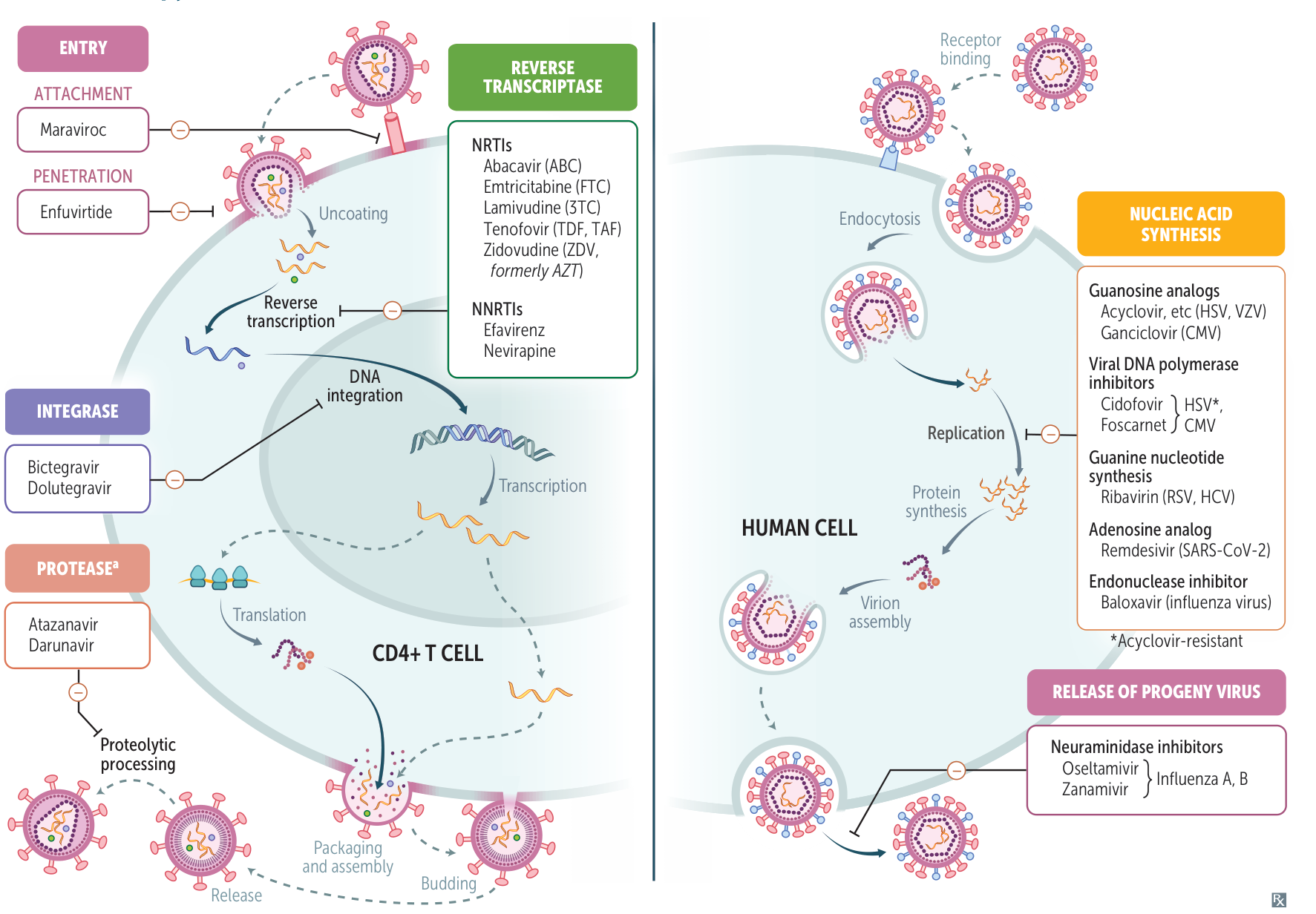
Tip
See HIV therapy for NRTIs and NNRTIs…
Oseltamivir, zanamivir
- Inhibit influenza neuraminidase → ↓ release of progeny virus.
- A viral enzyme that cleaves neuraminic acid residues from glycoprotein, which results in viral release from the host cell. Found in influenza virus.

Guanosine analogue
Acyclovir, famciclovir, valacyclovir
- Guanosine analogs.
- HSV/VZV-coded thymidine kinase monophosphorylates the guanosine analogue to an active intermediate → phosphorylation by cellular kinases → acyclovir triphosphate (ACV-TP)
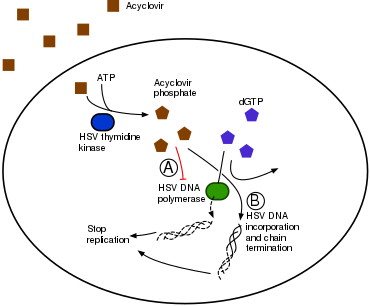
- The phosphorylated drug is incorporated into the replicating viral DNA strand → inhibition of viral DNA polymerase via chain termination

- Mechanism of antiviral resistance: Mutation of viral thymidine kinase
Ganciclovir, Valganciclovir
- Phosphorylation to 5’ monophosphate by the CMV-coded UL97 kinase → further phosphorylation to triphosphate by cellular kinases
Foscarnet, Cidofovir
- Direct inhibition of viral DNA polymerases
- Does not require activation by viral kinase
- Foscarnet already has phosphate in name

- Foscarnet already has phosphate in name
- Indications
- Adverse effects
- Common: nephrotoxicity
- Foscarnet: hypocalcemia, hypokalemia
- Foscarnet can chelate calcium.