- Hemorrhagic necrotizing inflammation of the intestinal wall
- Most commonly affects the distal ileum and proximal colon
Epidemiology
NEC is the most common cause of acute abdomen in premature infants.
Etiology
- Defective or underdeveloped immune system
- Formula feeding
- Upon initiation of enteral feeding, bacteria are introduced into the bowel where they proliferate excessively due to compromised immune clearance.
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Bloody stool, abdominal distention, vomiting, lethargy, prematurity, afebrile
Diagnostics
- Abdominal radiography
- Pneumatosis intestinalis: bubbles of gas within the wall of the intestine (“tram tracking”)
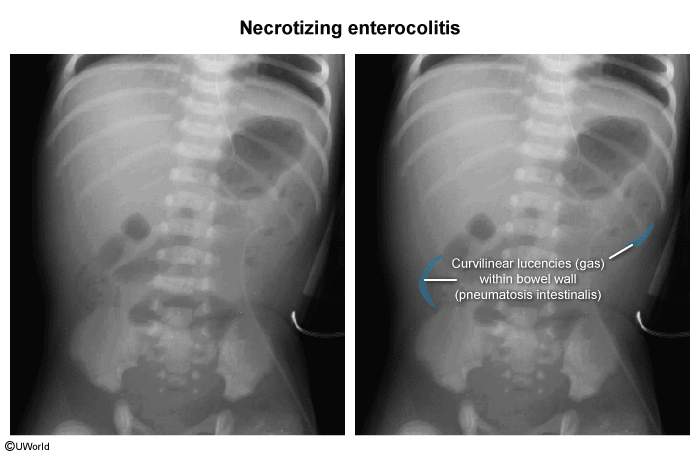
- Portal venous gas (pneumatosis hepatis)
- Increased intestinal wall thickness
- Pneumatosis intestinalis: bubbles of gas within the wall of the intestine (“tram tracking”)