Epidemiology
- Peak incidence: 10–19 years of age
Etiology
- Pathogenesis: Obstruction of the appendiceal lumen.
- Adults: Fecalith (most common)
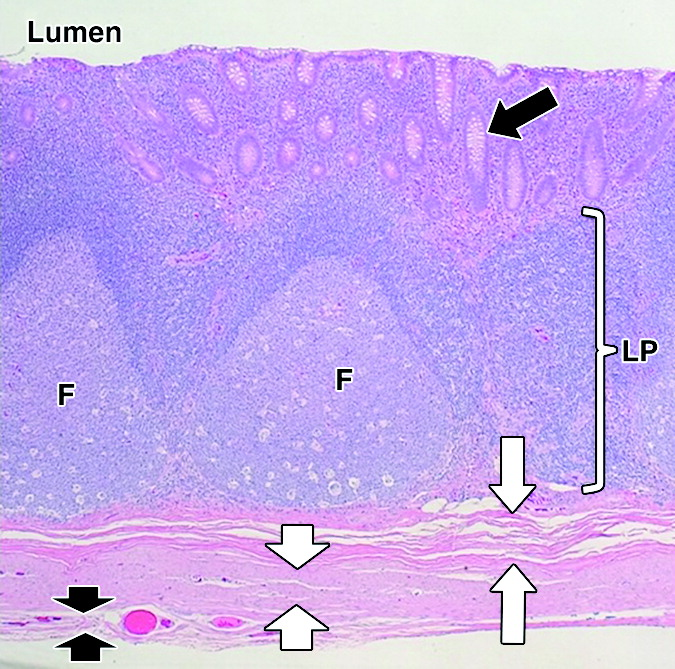
- Children/Adolescents: Lymphoid hyperplasia (often post-viral infection)
- Less common: tumor (carcinoid), foreign body, parasites
- Obstruction → ↑ intraluminal pressure → venous congestion → ischemia → bacterial invasion → necrosis/perforation.
- Common organisms: E. coli, Bacteroides fragilis