GnRH agonists (antagonist in long term)
Agents
- Buserelin
- Leuprolide
- Nafarelin
- Histrelin
Mechanism of action
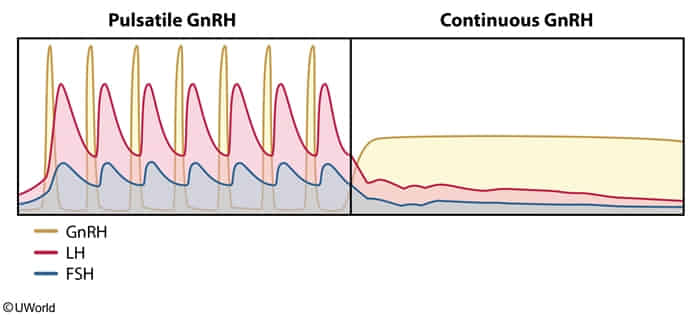
- Initially, the GnRH receptor agonist effect stimulates the HPO axis; this causes increased FSH and estrogen secretion without a significant change in GnRH levels.
- With prolonged use, leuprolide causes desensitization and downregulation of pituitary GnRH receptors, which eventually leads to low FSH and estrogen levels. Because leuprolide is an exogenous GnRH analogue, its prolonged use also decreases endogenous GnRH levels.
| Day 3 | Day 60 | |
|---|---|---|
| GnRH | Normal | Low |
| FSH | High | Low |
| Estrogen | High | Low |
Tip
Pulsatile GnRH won’t cause this problem
Indications
- Cancer (continuous administration)
- Uterine leiomyoma
- Infertility (pulsatile administration)
- Endometriosis
- Precocious puberty
Adverse effects
- Hypogonadism
- Decreased libido
- Vaginal dryness
- Hot flashes
- Nausea, vomiting
- Decreased bone mineral density