Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
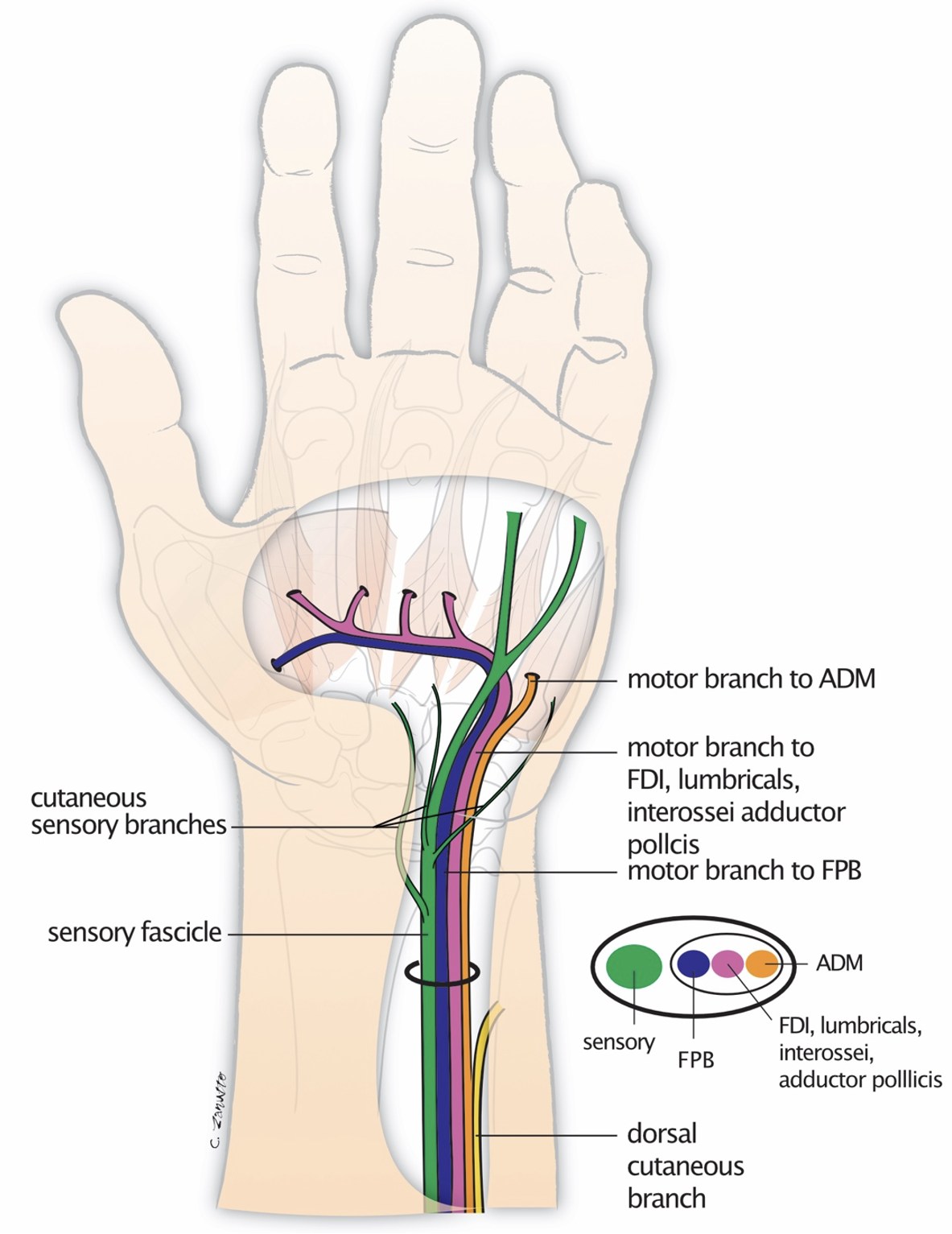
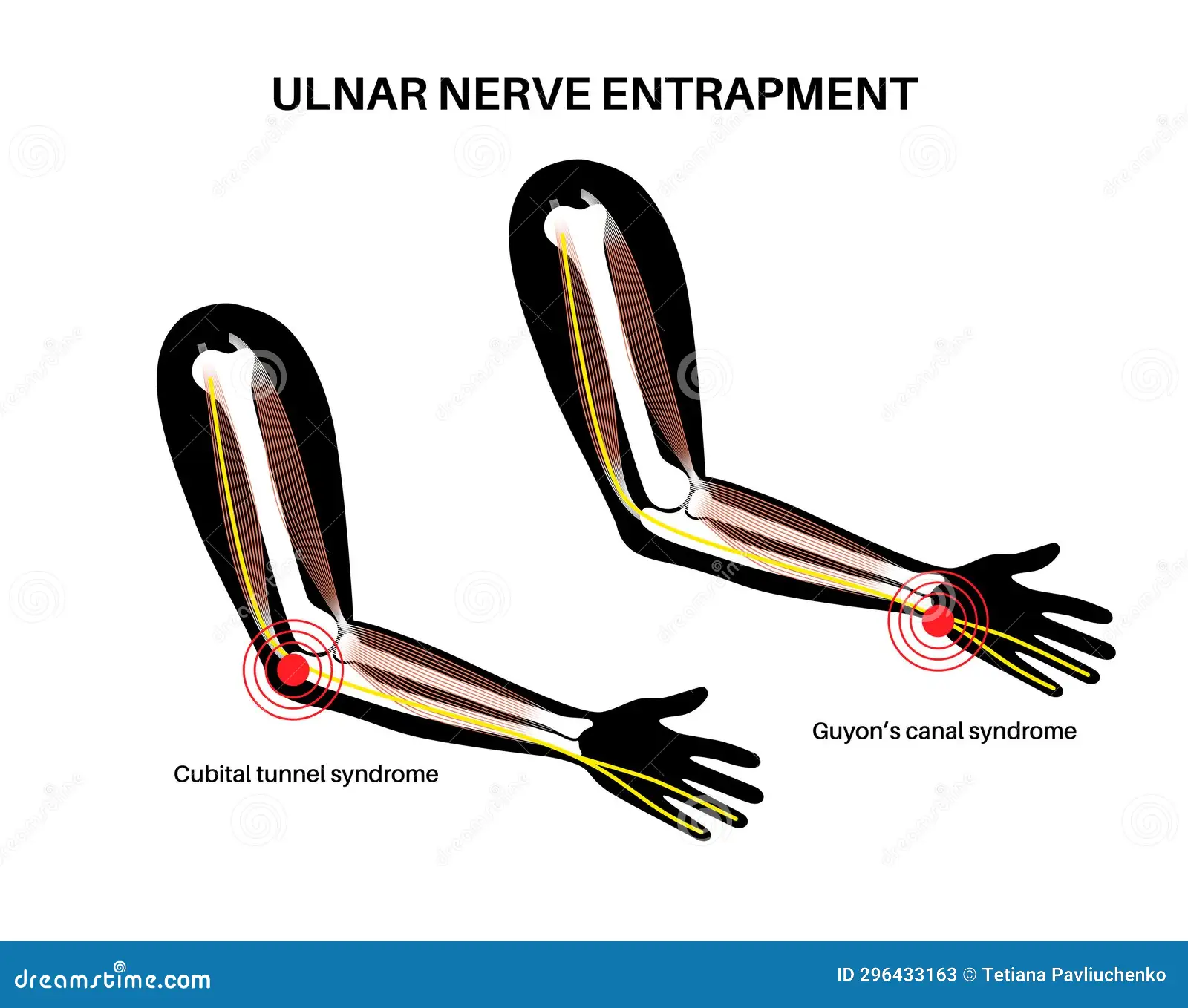
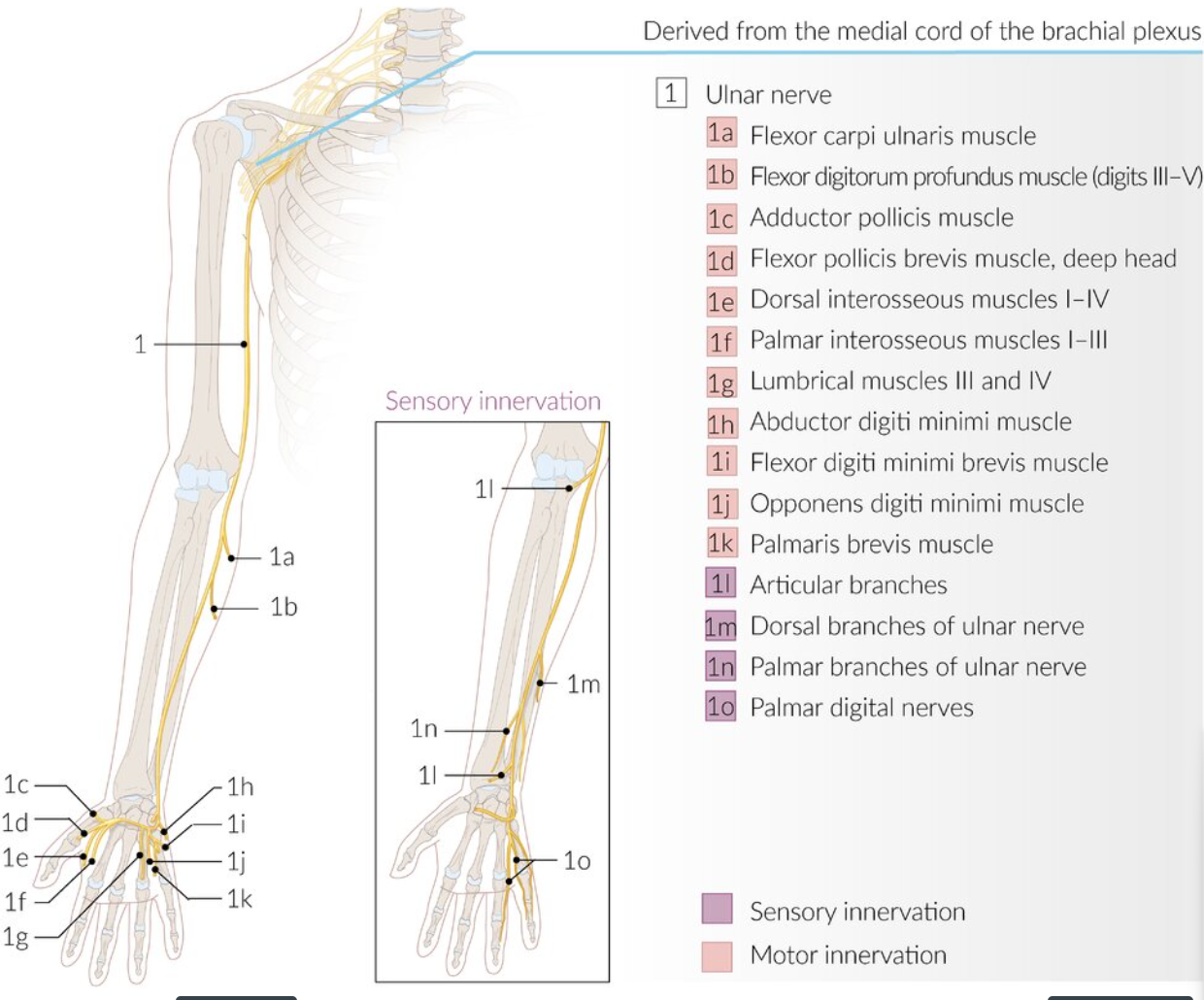
The ulnar nerve is most commonly compressed at or near the cubital tunnel of the elbow and Guyon canal of the wrist.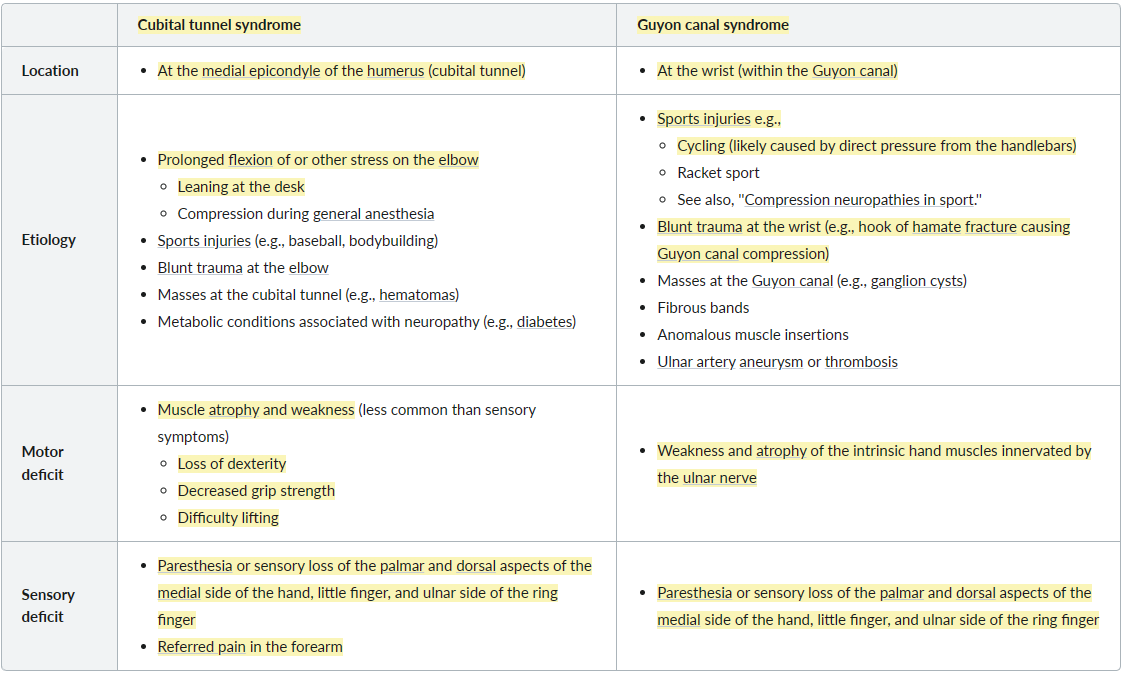
Clinical features
Motor symptoms
- Entrapment at the elbow
- Less common than sensory complaints and range from mild to severe weakness
- Muscle atrophy and weakness
- Loss of dexterity
- Decreased grip strength
- Difficulty lifting
- Entrapment at the wrist: weakness and atrophy of the intrinsic hand muscles innervated by the ulnar nerve
Sensory symptoms
- Entrapment at the elbow
- Paresthesia or sensory loss of palmar and dorsal aspects of the medial side of the hand, little finger, and ulnar side of the ring finger
- Referred pain in the forearm
- Entrapment at the wrist
- Variable paresthesia or sensory loss of the palmar and dorsal aspects of the medial side of the hand, little finger, and ulnar side of the ring finger
Warning
The dorsum of the medial half of the hand (ring and small fingers) is innervated by the dorsal cutaneous branch of the ulnar nerve, which arises in the forearm proximal to the passage of the ulnar nerve through Guyon canal. As this patient exhibits nerve compression at the level of Guyon canal, the sensory innervation to the medial half of the dorsum of the hand will remain intact.
Physical examination
- Ulnar claw
- Palsy of the 3rd and 4th lumbricals with preserved function of the extrinsic flexors (flexor digitorum profundus) → unopposed flexion
- Present at rest, increases when the patient is asked to extend the fingers
- Mainly seen in distal ulnar nerve injuries
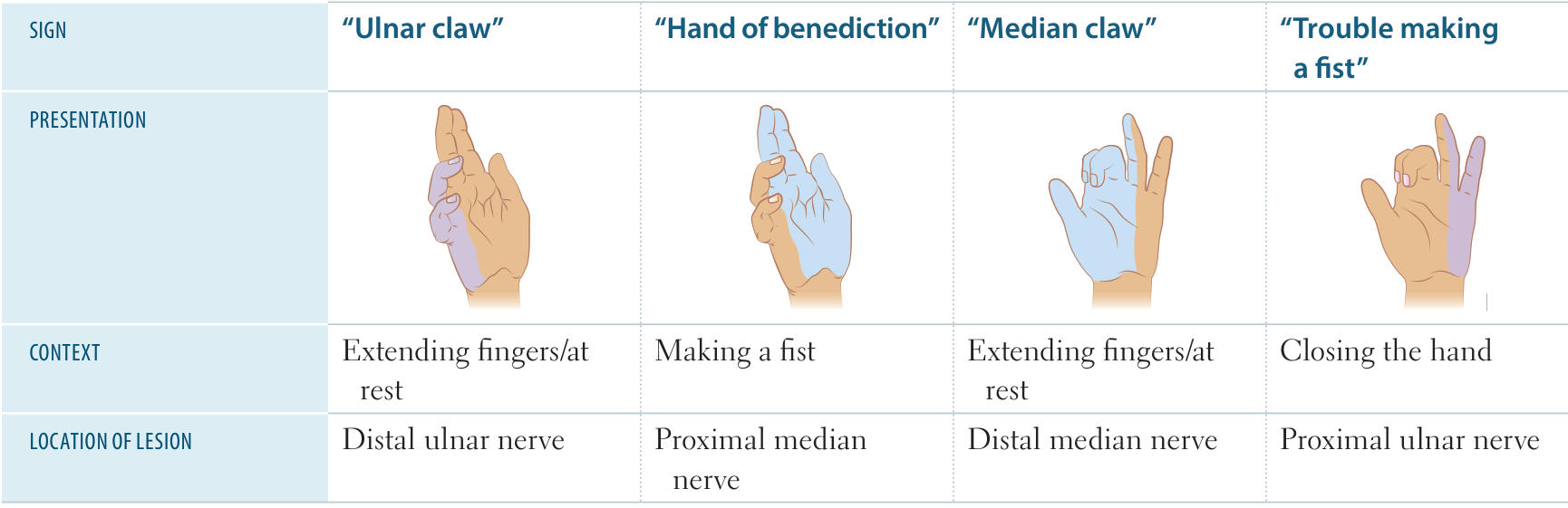
- The key is whether flexor digitorum profundus is damaged.
- Nerves controlling flexor digitorum profundus branches out below the elbow. So it’s spared in distal lesion, but included in proximal lesion. So the claw hand is more prominent in distal lesion.
- Froment sign
- Flexion of the thumb at the interphalangeal joint elicited when tightly pressing together the tips of the index finger and thumb, or when tightly adducting the thumb against the 2nd metacarpal (e.g., pinching a piece of paper using the thumb)
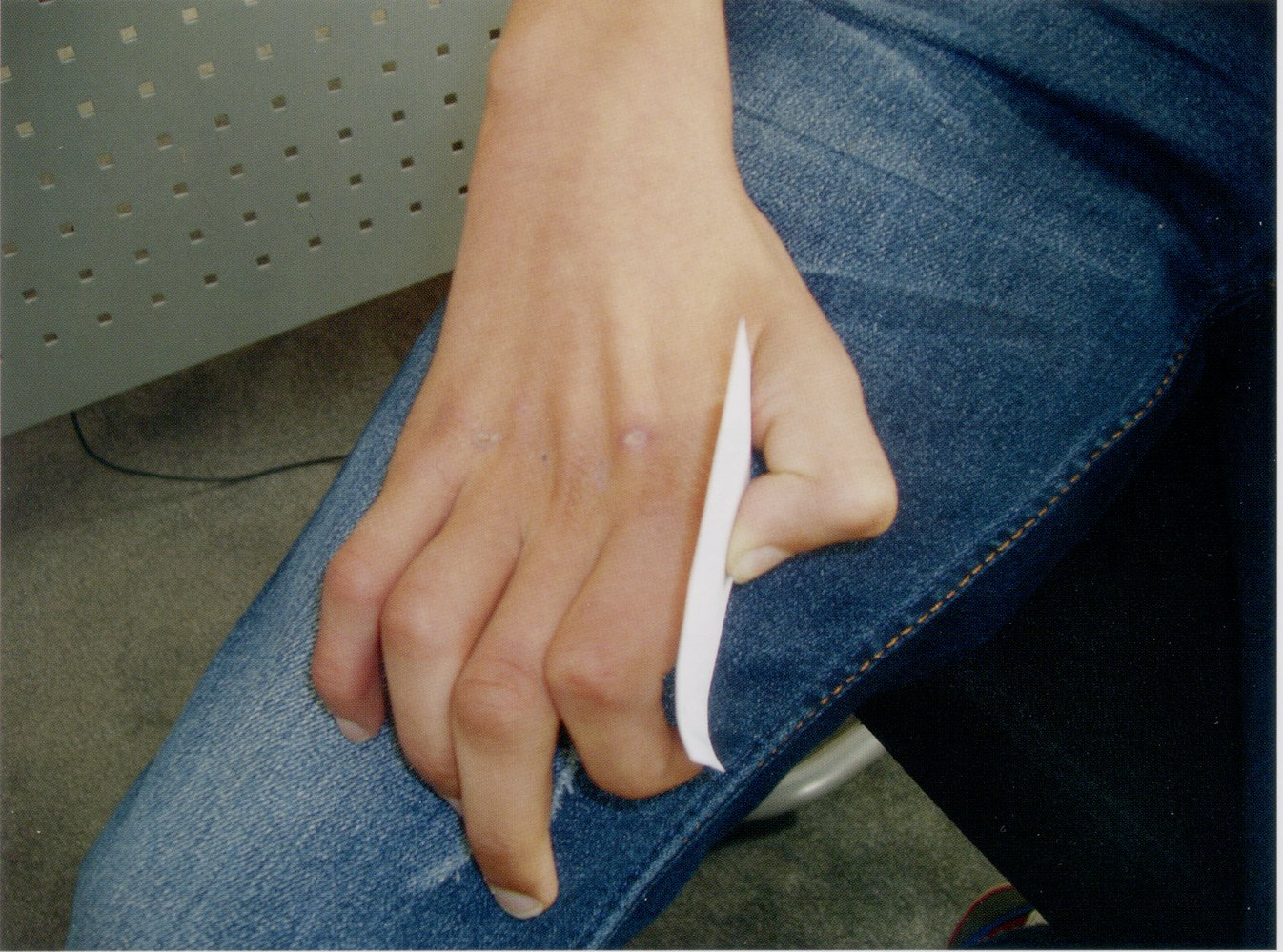
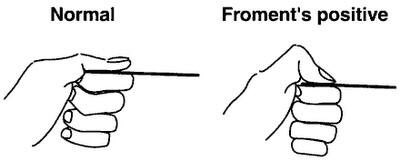

- Due to weakness of the adductor pollicis muscle and the unopposed action of flexor pollicis longus
- Flexion of the thumb at the interphalangeal joint elicited when tightly pressing together the tips of the index finger and thumb, or when tightly adducting the thumb against the 2nd metacarpal (e.g., pinching a piece of paper using the thumb)