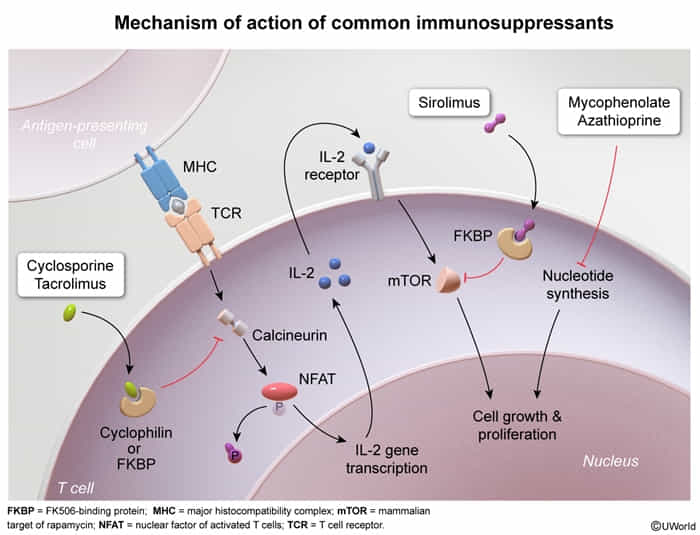
Mycophenolate mofetil
- Reversible inhibition of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase → blockade of purine synthesis → selective inhibition of lymphocyte proliferation
- Indications
- Lupus nephritis
- Used in combination with cyclosporin or tacrolimus as transplant rejection prophylaxis
- Rheumatic diseases (glucocorticoid sparing)
- Adverse effects
- Infection (especially with CMV)
- Vomiting and diarrhea
- Hyperglycemia
- Hypertension
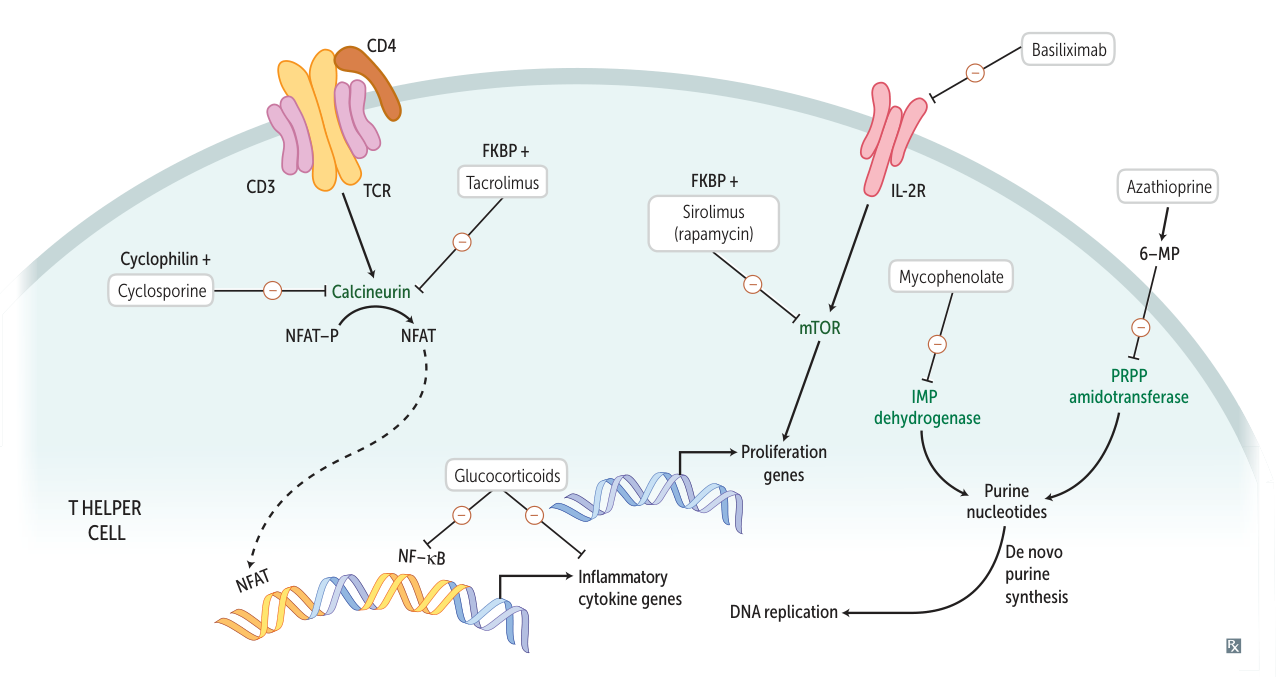
Calcineurin inhibitors
calcineurin = calcium- and calmodulin-dependent serine-threonine phosphatase
- Drugs: Cyclosporine, Tacrolimus (FK506)
- MOA: Inhibit calcineurin → ↓ transcription of IL-2 → ↓ T-cell activation.
- Cyclosporine binds to Cyclophilin.
- Tacrolimus binds to FKBP (FK506 binding protein).
- Clinical Use:
- Solid organ transplant rejection prophylaxis.
- Autoimmune disorders (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis).
- Adverse Effects (AE):
- Nephrotoxicity: Most important, dose-limiting toxicity. Causes afferent arteriolar constriction → ↓ RBF and GFR.
- Hypertension.
- Neurotoxicity (tremor, paresthesias).
- Hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia.
- Gingival hyperplasia and hirsutism (specific to Cyclosporine).
mTOR inhibitors
- Drugs: Sirolimus (Rapamycin) t
- MOA: Binds to FKBP but does not inhibit calcineurin. The Sirolimus-FKBP complex inhibits mTOR → blocks T-cell activation and B-cell differentiation by preventing response to IL-2.
- Clinical Use:
- Solid organ transplant rejection prophylaxis (often used with calcineurin inhibitors).
- Drug-eluting stents (prevents intimal hyperplasia).
- AE:
- Pancytopenia (thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, anemia).
- Insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia.
- NOT nephrotoxic (key distinction from calcineurin inhibitors).
Glucocorticoids
- Mechanism of action
- Inhibition of intracellular NF-κB → inhibition of multiple inflammatory and immune mediators (e.g., cytokines) → suppression of B cells and T cells function
- Long-term effects (in hours) → direct influence on gene expression
- Increased apoptosis of eosinophils, T cells, and monocytes, perhaps by decreasing Bcl-2 expression
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
A medication that inhibits the action of regulatory proteins, known as checkpoint proteins, on the immune response. Checkpoint inhibitors are used in the treatment of cancers which produce checkpoint proteins that reduce a patient’s intrinsic antineoplastic T-cell activity.
Biological agents used in immunotherapy
- Nomenclature
- Suffixes are key to identifying the type of biologic agent:
- -mab: Monoclonal Antibody
- -omab: Murine (mouse)
- -ximab: Chimeric
- -zumab: Humanized
- -umab: Fully Human
- -cept: Receptor fusion protein (acts as a “decoy receptor”)
- -nib: Kinase Inhibitor (small molecule)
- -kinra: Interleukin receptor antagonist
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
- Mechanism: Block inhibitory signals on T-cells, unleashing a potent anti-tumor response. They “take the brakes off” the immune system.
- PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors
- Drugs: Pembrolizumab, Nivolumab (target PD-1); Atezolizumab, Durvalumab (target PD-L1)
- Uses: Melanoma, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC), Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC), bladder cancer, Hodgkin lymphoma.
- CTLA-4 Inhibitors
- Drug: Ipilimumab
- Uses: Primarily melanoma.
- Toxicity (Immune-Related Adverse Events - irAEs)
- Common theme: Autoimmune inflammation in various organs.
- Dermatitis: Rash, pruritus (most common).
- Colitis: Diarrhea, abdominal pain.
- Hepatitis: ↑ LFTs (AST, ALT).
- Endocrinopathies: Hypophysitis (can present with headache, fatigue, ↓ libido), thyroiditis, adrenal insufficiency, type 1 diabetes.
- Pneumonitis: Cough, dyspnea.
- Tx for irAEs: Corticosteroids; may need to discontinue immunotherapy.
TNF-α Inhibitors
- Mechanism: Bind to and neutralize TNF-α, a pro-inflammatory cytokine.
- Drugs:
- Infliximab, Adalimumab, Golimumab: Monoclonal antibodies against TNF-α.
- Etanercept: A fusion protein of the human TNF receptor linked to the Fc portion of IgG1 (acts as a decoy receptor).
- Etanercept intercepts TNF.
- Uses: Chronic inflammatory conditions.
- Rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s, ulcerative colitis).
- Toxicity:
- Immunosuppression: ↑ Risk of infection.
- Reactivation of latent TB: Screening with PPD or IGRA is mandatory before starting therapy. TNF-α is crucial for granuloma formation and maintenance.
- Can worsen heart failure.
- Drug-induced lupus.
Other Monoclonal Antibodies (Oncology)
- Rituximab
- Target: CD20 antigen on B-cells.
- Uses: B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL), rheumatoid arthritis, ITP.
- Toxicity: ↑ Risk of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML) reactivation.
- Trastuzumab (Herceptin)
- Target: HER2 (Human Epidermal growth factor Receptor 2), a tyrosine kinase.
- Uses: HER2-positive breast cancer and gastric cancer.
- Toxicity: Cardiotoxicity (reversible myocardial dysfunction).
- Bevacizumab
- Target: VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor). Inhibits angiogenesis.
- Uses: Solid tumors (colorectal cancer, RCC).
- Toxicity: Hemorrhage, blood clots, impaired wound healing, GI perforation.
Interleukin (IL) Inhibitors
- Anakinra
- Mechanism: IL-1 receptor antagonist.
- Uses: Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Ustekinumab
- Mechanism: Targets IL-12 and IL-23.
- Uses: Psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis.
- Secukinumab
- Mechanism: Targets IL-17A.
- Uses: Psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis.
- Tocilizumab
- Mechanism: Targets IL-6 receptor.
- Uses: Rheumatoid arthritis, cytokine release syndrome (CRS).
CAR-T Cell Therapy
- Mechanism: Patient’s own T-cells are genetically engineered ex vivo to express a Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) that targets a tumor antigen (e.g., CD19 on B-cell malignancies). These modified cells are then re-infused.
- Uses: Relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies (e.g., ALL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma).
- Toxicity:
- Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS): Massive, rapid release of cytokines leading to systemic inflammation (fever, hypotension, hypoxia). Can be life-threatening. Tx with Tocilizumab (IL-6R inhibitor).
- Immune effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome (ICANS): Confusion, aphasia, seizures, cerebral edema. Tx with corticosteroids.
- B-cell aplasia: On-target, off-tumor effect leading to hypogammaglobulinemia and ↑ risk of infection.