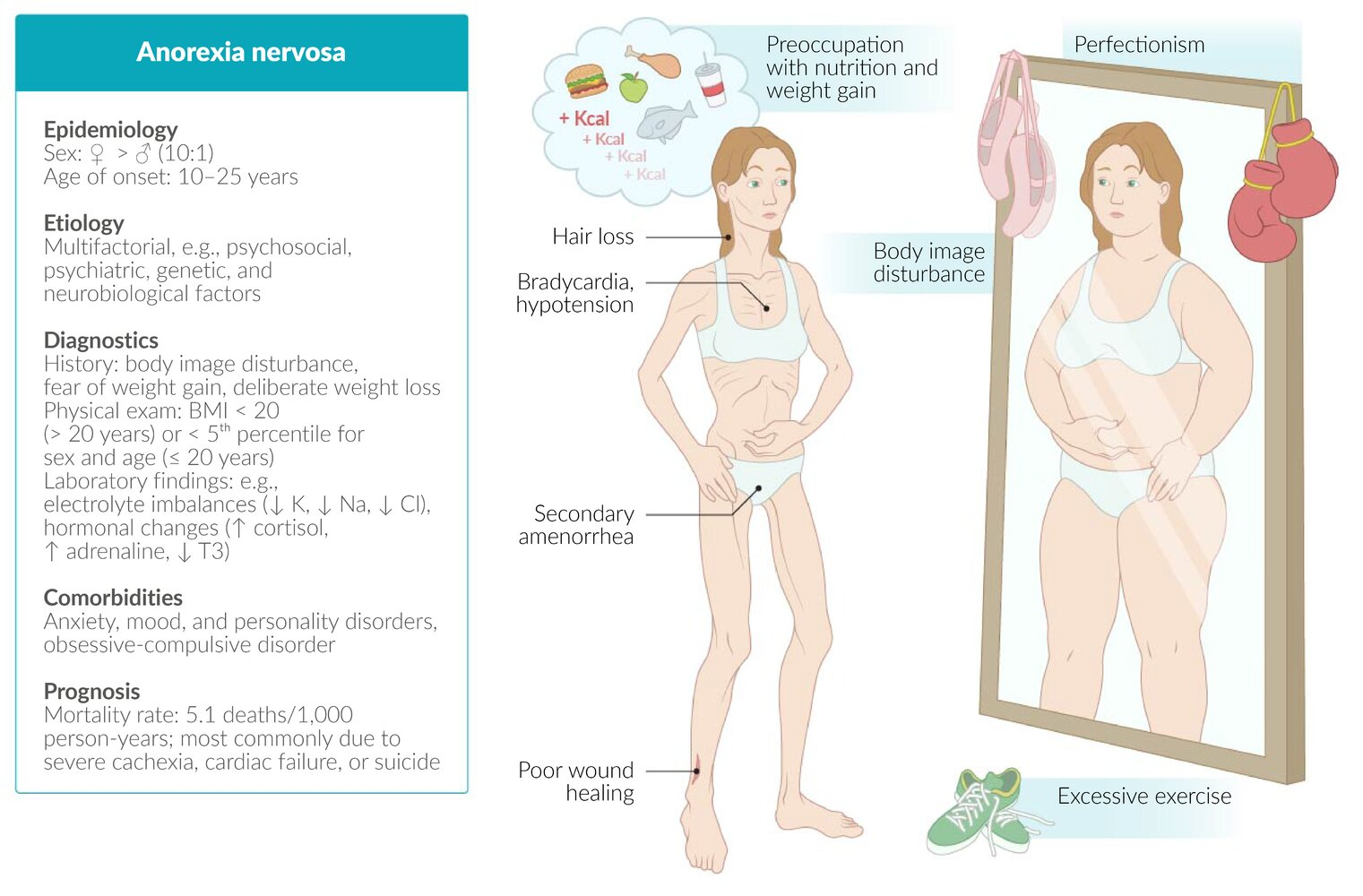
Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
- Most patients present with a low BMI.
Associated features of severe malnutrition
- CNS
- Hypothermia
- This is thought to be caused by a disorder of the hypothalamic thermoregulatory centers.
- Cortical atrophy with associated problems with concentration and reasoning
- Seizures
- As a result of dehydration and electrolyte imbalances
- Depressed mood, fatigue, and poor concentration
- Hypothermia
- Cardiac
- Hypotension
- Cardiac arrhythmia (bradycardia)
- Cardiac atrophy
- Mitral valve prolapse
- Endocrine
- Stress hormones: ↑ cortisol, ↑ adrenaline
- Thyroid: euthyroid sick syndrome
- Secondary amenorrhea (severe weight loss suppresses the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis → hypogonadotropic hypogonadism)
- Impaired glucose tolerance, hypoglycemia
- GI: Constipation, gastroparesis. t
- Musculoskeletal
- Muscle weakness
- Secondary osteoporosis
- Stress fractures
- Growth retardation in children and adolescents
- Skin and hair
- Dry skin
- Wound healing disorders
- Hair loss
- Lanugo body hair
Diagnostics
Tip
Consider screening the following individuals at increased risk:
- Preteens and adolescents
- At annual adolescent health visits
- Evaluation of weight loss
- Athletes (at annual preparticipation screens)
- Sexual minority, transgender, and gender diverse youth
- Patients with a:
- History of sexual abuse, childhood adversity, or trauma (including bullying)
- Chronic disease requiring dietary management
- Psychiatric disorder and those undergoing an initial psychiatric evaluation
Differential diagnostics
