Etiology
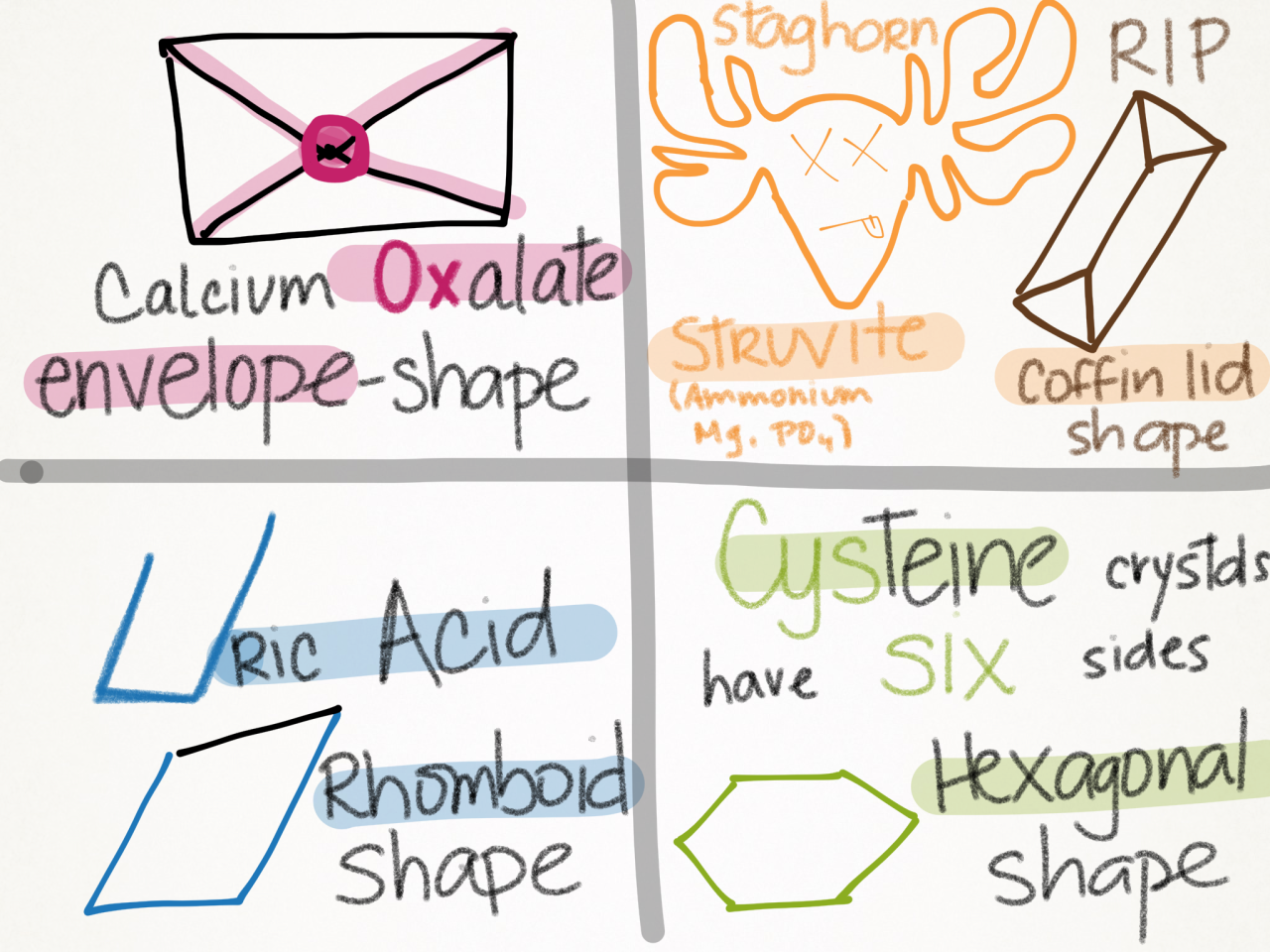
Classifications
Mnemonic
PH
Elevated: Struvite stones, Calcium phosphate stones Decreased: Else
Calcium stones
Calcium oxalate stones
Etiology
- Hypercalciuria
- Hyperoxaluria
- Increased intestinal absorption of oxalate, e.g., due to fatty acid malabsorption (e.g., Crohn disease, ulcerative colitis, short bowel syndrome)
- Calcium normally binds oxalate to form calcium oxalate, which is excreted via feces.
- In conditions associated with fatty acid malabsorption due to impaired bile acid reabsorption, calcium preferentially binds free fatty acids, leading to excess free oxalate and, therefore, to increased oxalate absorption.
- Vitamin C > Vitamin C toxicity
- Vitamin C is metabolized to oxalate
- Increased intestinal absorption of oxalate, e.g., due to fatty acid malabsorption (e.g., Crohn disease, ulcerative colitis, short bowel syndrome)
- Hypocitraturia
- Citrate inhibits stone formation by forming a soluble complex with calcium in the renal tubule, which reduces the amount of free calcium in the urine to bind with oxalate or phosphate. Citrate excretion in the kidney is strongly influenced by pH (systemic, tubular, and intracellular). Alkalosis increases renal citrate excretion, whereas acidosis decreases it.
Tip
Individuals with higher (but not excessive) calcium intake paradoxically have a lower risk of calcium oxalate stone formation. Dietary calcium binds oxalate in the gut to form insoluble calcium oxalate, which is eliminated in the feces. This reduces the amount of oxalate absorbed into the body and excreted in the urine, reducing stone formation.
Diagnosis
- Urine microscopy: dumbbell-shaped or octahedron-shaped crystals
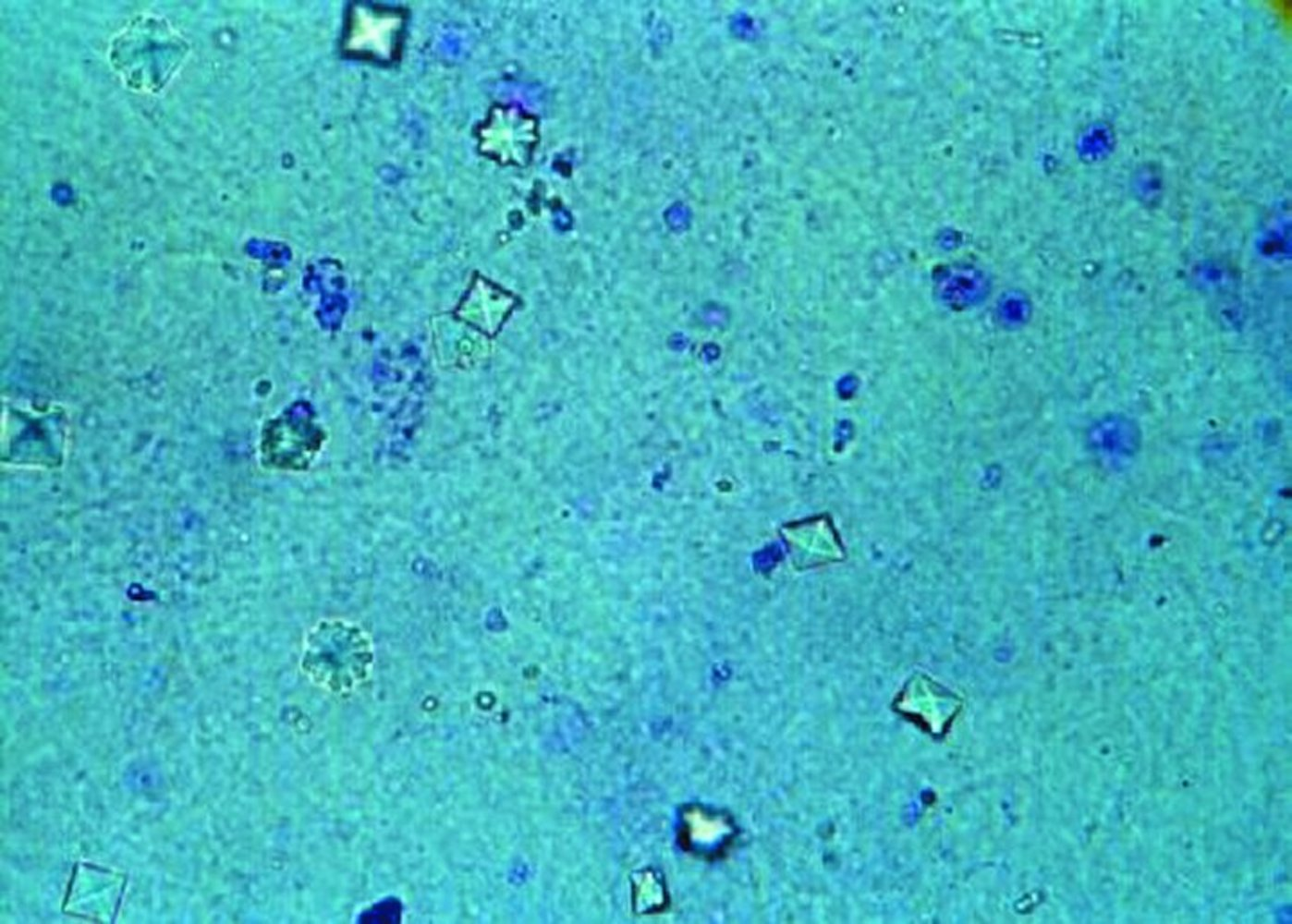
- The monohydrate calcium oxalate crystal is described as the “picket fence” form. These dumbbells shaped crystals are common in ethylene glycol toxicity. The dihydrate form is octahedral or “envelope” shaped.
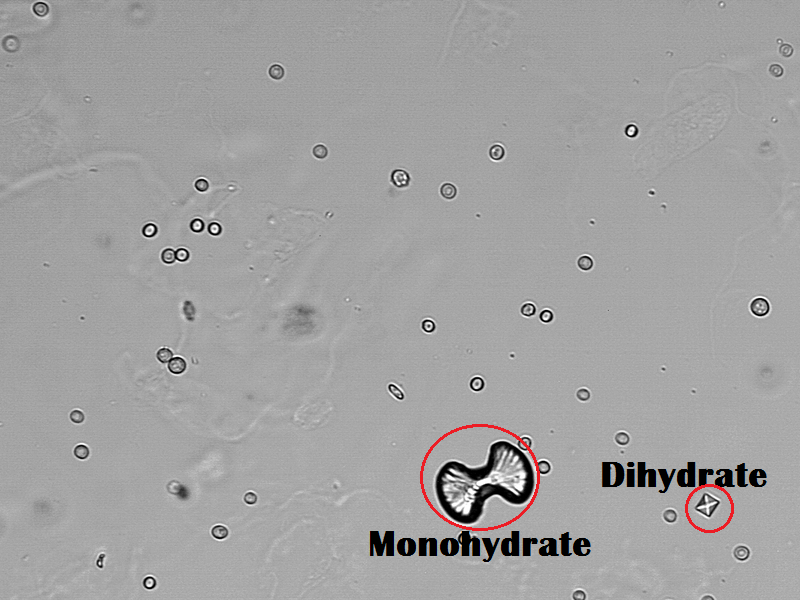
- The monohydrate calcium oxalate crystal is described as the “picket fence” form. These dumbbells shaped crystals are common in ethylene glycol toxicity. The dihydrate form is octahedral or “envelope” shaped.
- X-ray (or CT): radiopaque stones
Tip
Serum calcium can be normal or elevated.
Treatment
- Hydration
- Dietary modification
- Reduced intake of salt (mainly sodium) and animal protein (Low sodium enhances renal tubular reabsorption of sodium and calcium, decreasing urinary calcium levels. Animal protein consumption increases calcium excretion in urine.)
- Reduced intake of oxalate-rich foods and supplemental vitamin C
- Calcium intake should not be restricted (restriction increases risk of hyperoxaluria, and thereby, the risk for osteoporosis)
- Thiazide diuretics for recurrent calcium-containing stones with idiopathic hypercalciuria (i.e., no hypercalcemia)
- Urine alkalinization (e.g., with potassium citrate)
- Possibly citrate supplementation
Calcium phosphate stones
Etiology
- Hyperparathyroidism (brushite)
- Type 1 renal tubular acidosis (brushite)
- Develop in persistently alkalic urine
Diagnosis
- Urine microscopy: wedge-shaped crystals
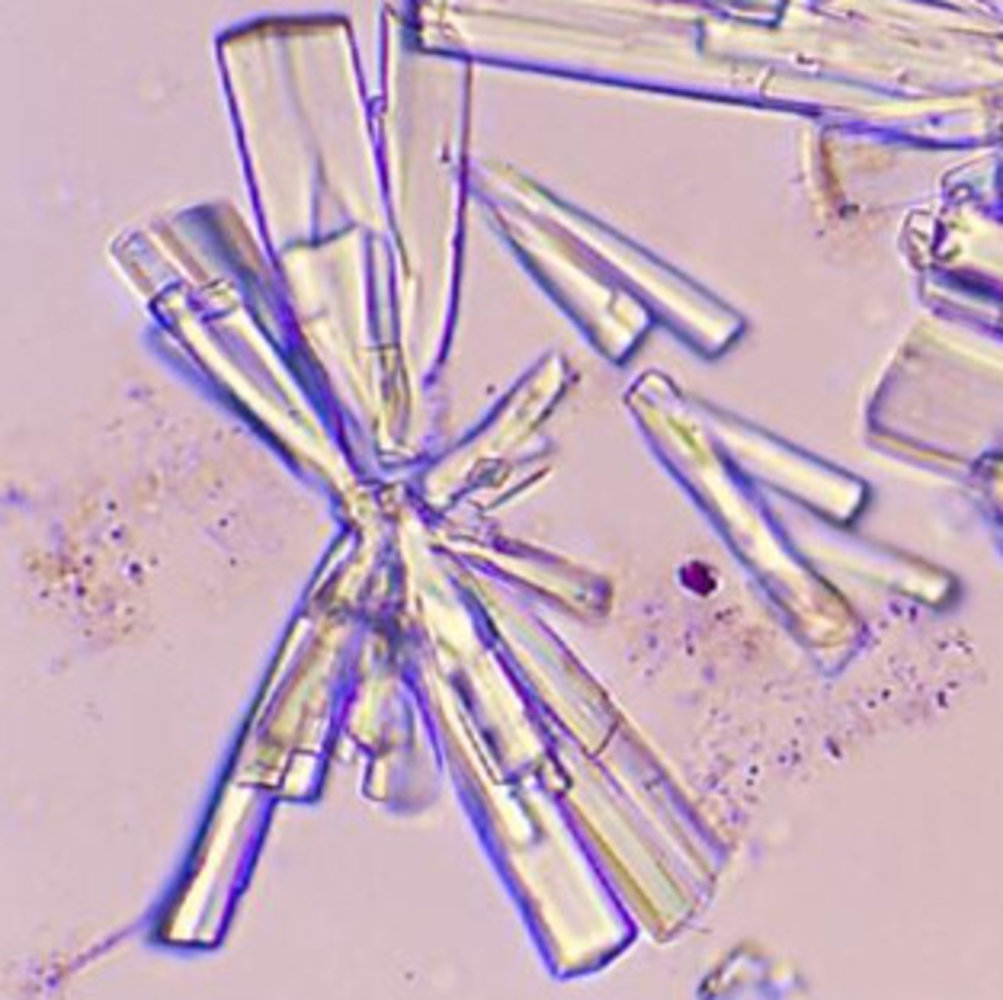

- X-ray (or CT): radiopaque stones
Prevention
- Hydration
- Thiazide diuretics
- Diet low in sodium
Uric acid stones
Etiology
- Hyperuricemia and hyperuricosuria
- Gout
- High cell turnover (e.g., tumor lysis syndrome, myelodysplastic syndrome)
- Diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome
- Chronic diarrhea
Diagnosis
- Urine microscopy: rhomboid/needle-shaped crystals
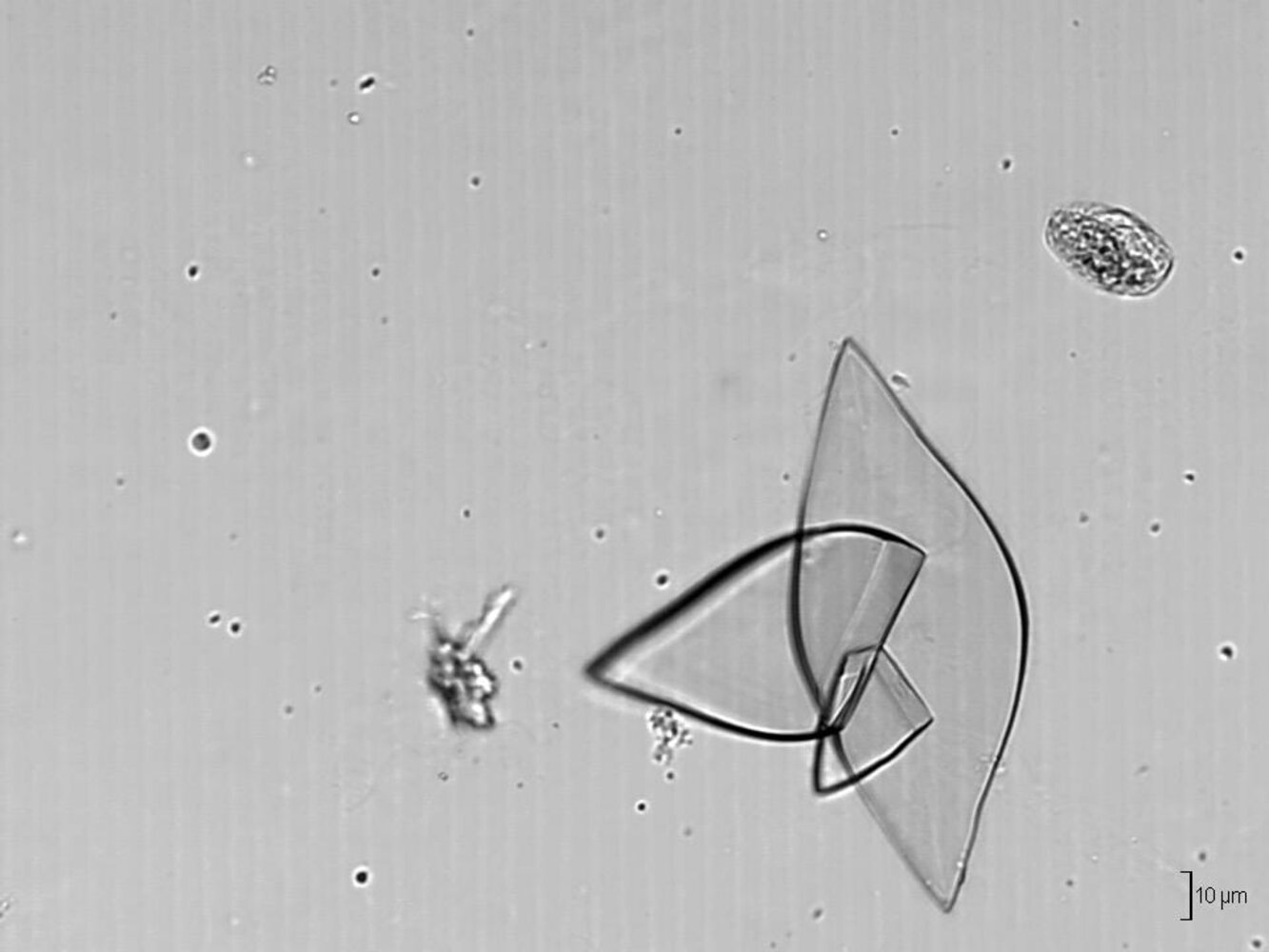
- X-ray: radiolucent stones
- CT: can be visible but are usually only minimally visible (not as visible as calcium stones)
Treatment
- Hydration
- Oral chemolitholysis (e.g., potassium citrate) via urine alkalinization
- Uric acid (pKa = 5.4) is soluble at physiologic pH, but precipitates in an acidic environment. The lowest pH along the nephron is found in the distal tubules and collecting ducts; so these are the segments of the nephron that become obstructed by uric acid crystals. Obstructive uropathy and acute renal failure follow.
- Uric acid stones are unique in that they can usually be dissolved by alkalizing the urine. In other stones, urine alkalinization is used for prophylaxis rather than treatment.
- Low-purine diet
- Allopurinol
Mnemonic
Uric acid stones are radiolUcent (x-ray negative).
Warning
Uricosuric agents (e.g., probenecid) increase the excretion of uric acid, which can accelerate the formation of stones.
Cystine stones
Etiology
- Autosomal recessive defect in cystine-reabsorbing PCT transporter → impaired proximal renal tubular absorption of dibasic amino acids → Cystinuria → cystine stone formation (as cystine is poorly soluble)
- Develop in persistently acidic urine
Clinical features
Recurrent kidney stones (manifesting with e.g., flank pain) starting in childhood
Diagnosis
- Urine microscopy: hexagonal crystals
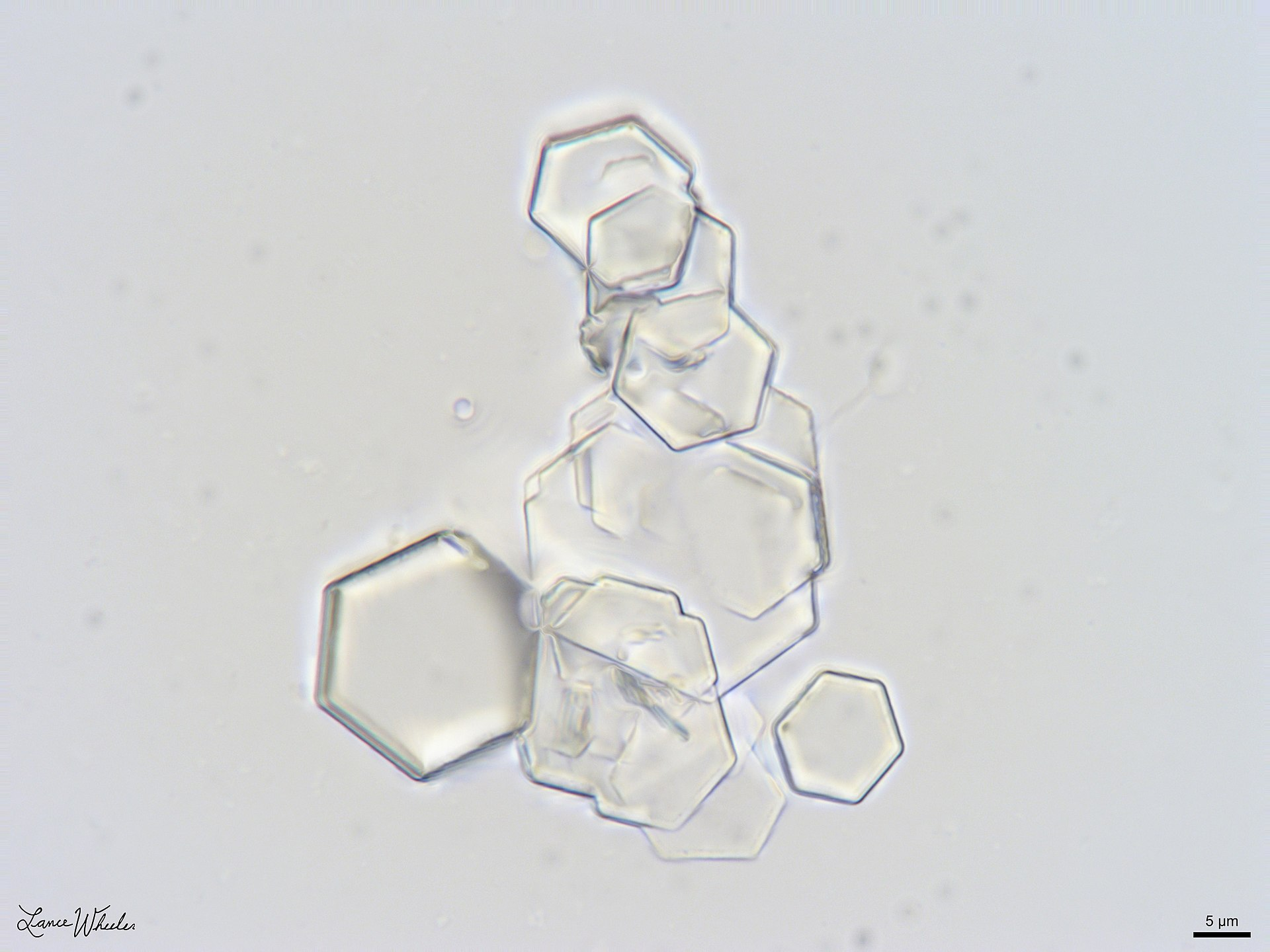
- X-ray (or CT)
- Weakly radiopaque stones
- Possibly staghorn calculi
- Positive cyanide nitroprusside test
Struvite stones (magnesium ammonium phosphate stones)
Etiology
- Upper UTI with urease-producing bacteria such as Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, and/or Pseudomonas
- These bacteria convert urea to ammonia → elevated ammonia causing alkaline urine → precipitation of the ammonium magnesium phosphate salt → crystal and stone formation
- Urea → 2 NH3 + CO2
- NH3 + H2O → NH4+ + OH−
- Grow rapidly into a branched staghorn calculus that fills the renal calyces and pelvis.
- Over time, the affected kidney can atrophy due to recurrent infection and chronic obstructive nephropathy.
- These bacteria convert urea to ammonia → elevated ammonia causing alkaline urine → precipitation of the ammonium magnesium phosphate salt → crystal and stone formation
Treatment
- Antibiotic treatment of urinary tract infections
- Hydration
- Urine acidification
- Usually require surgical stone removal