Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
- Chronic Th2 cell–mediated disorder triggered by food antigens
- Eosinophilic infiltration of the esophageal mucosa
Clinical features
- Dysphagia, food bolus impaction
- Symptoms can be worsened by ingestion of food containing allergens.
- Associated features: atopy (e.g., asthma, rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, alimentary allergies)
Diagnostics
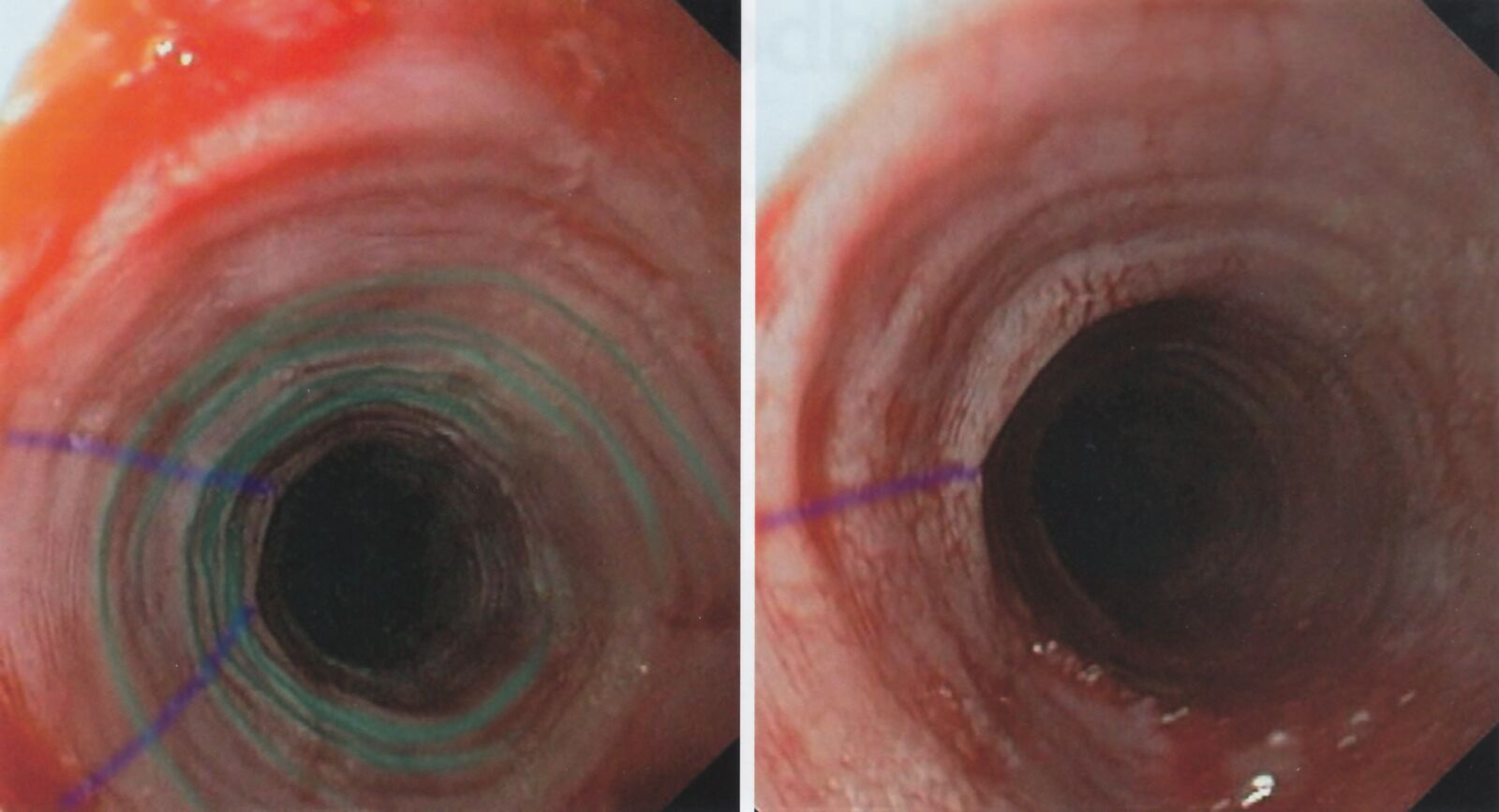
Endoscopic findings
- Circumferential mucosal lesions (e.g., rings, corrugations), with possible esophageal trachealization (presence of multiple rings in the esophagus, which results in a furrowed or corrugated appearance similar to the trachea)
- Longitudinal furrows
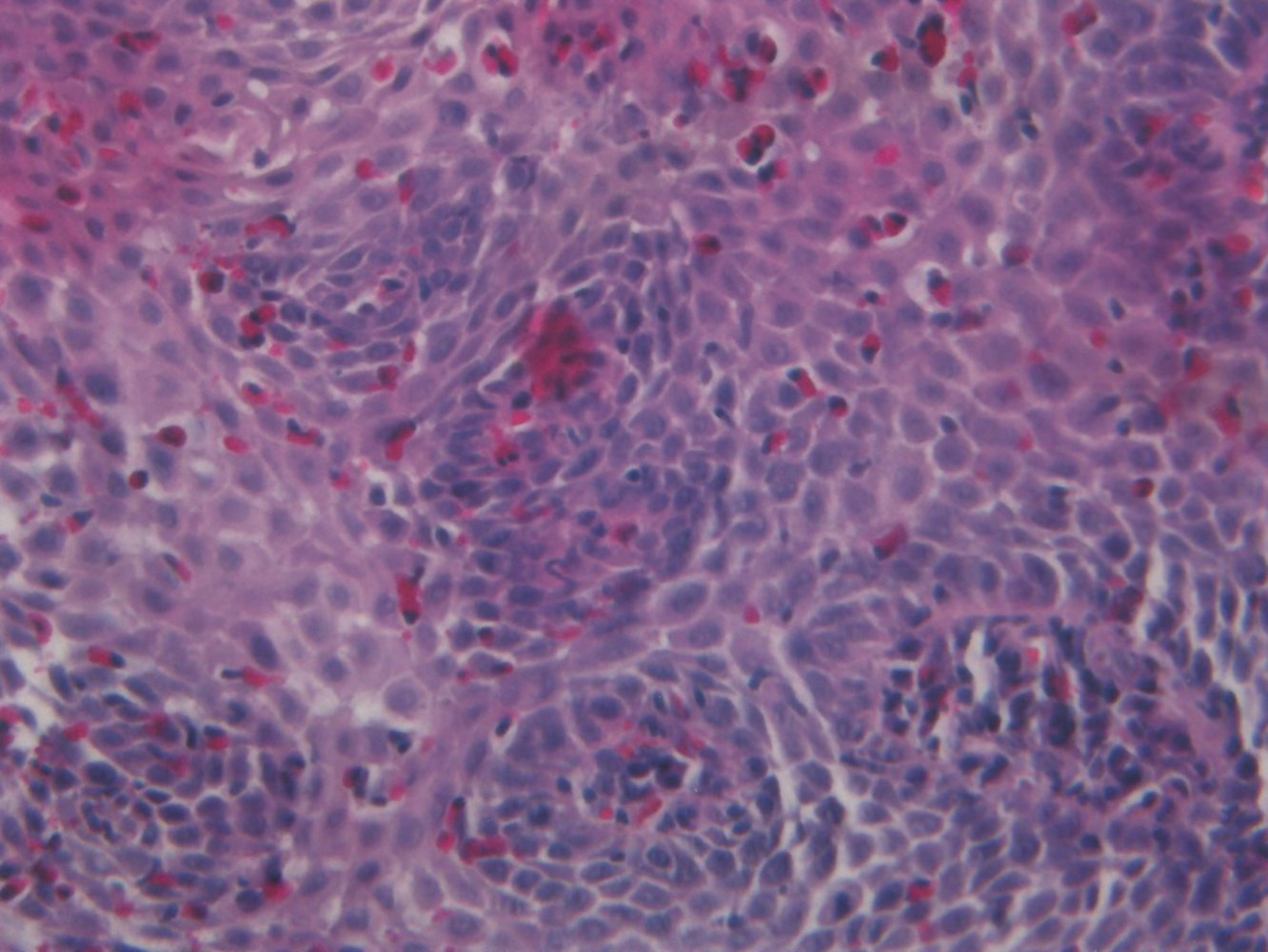
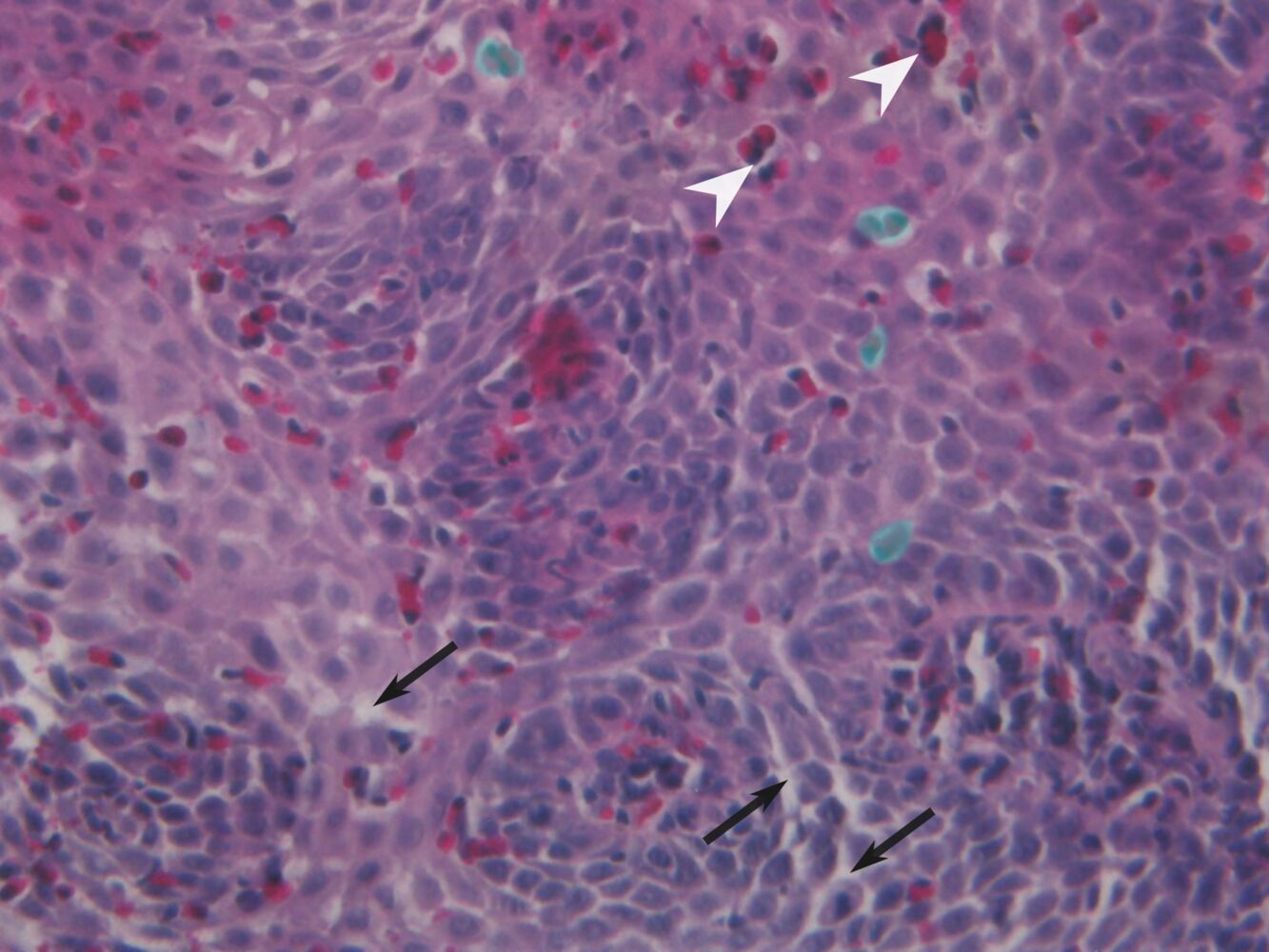
Histopathologic findings
- Intraepithelial accumulation of eosinophils
Treatment
- First-line: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)