Types
- Low-risk HPV types 6 and 11
- Anogenital warts (condylomata acuminata)
- Primarily transmitted through sexual contact
- High-risk HPV types 16, 18, 31, and 33
- Cervical cancer (responsible for 70% of cases)
- High risk of anogenital, oral, and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- Primarily transmitted through sexual contact
- HPV types 1, 2, and 4: cause skin warts, such as common warts (verruca vulgaris) and plantar warts (myrmecias)
- Primarily transmitted through non-sexual skin-to-skin contact or contact with contaminated surfaces
Etiology
Risk factors
- Immunodeficiency (e.g., due to HIV infection, chemotherapy)
- Additional risk factors for genital/mucosal HPV infections include:
- Unprotected sex
- Higher number of lifetime sexual partners
- Early age at first sexual activity
- Lack of circumcision in male individuals
Pathophysiology
- HPV expresses the following oncoproteins
- E6 → inhibition of p53 protein → inhibition of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway and inhibition of p21 protein t
- E7
- Inhibition of retinoblastoma protein (pRb) → increased activity of E2F-family of transcription factors
- Inhibits p21 and p27 (CDK inhibitors) → increased activity of cyclin-dependent kinase
Mnemonic
6 comes before 7 and P comes before R: E6 inhibits P53 and E7 inhibits pRb
Pathology
- HPV infect stratum basale, where epithelial cells are replicating
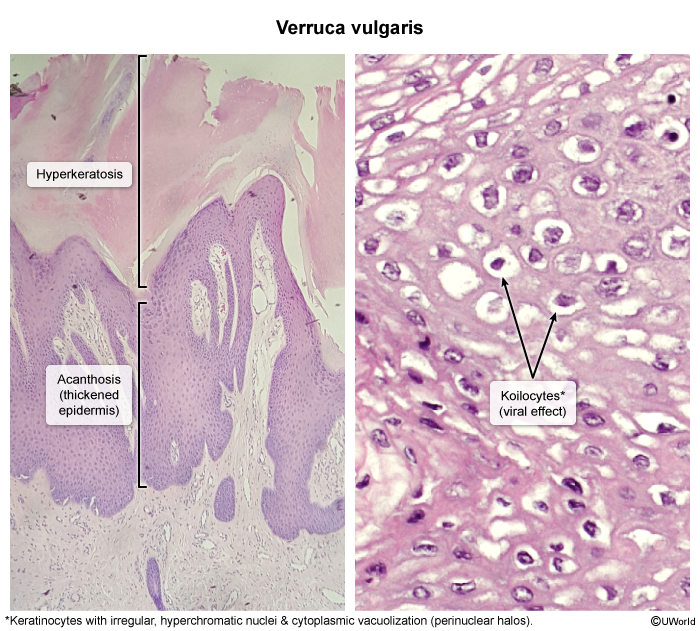
- Epidermal hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis
- Koilocytes
- Pathognomonic of an infection with HPV
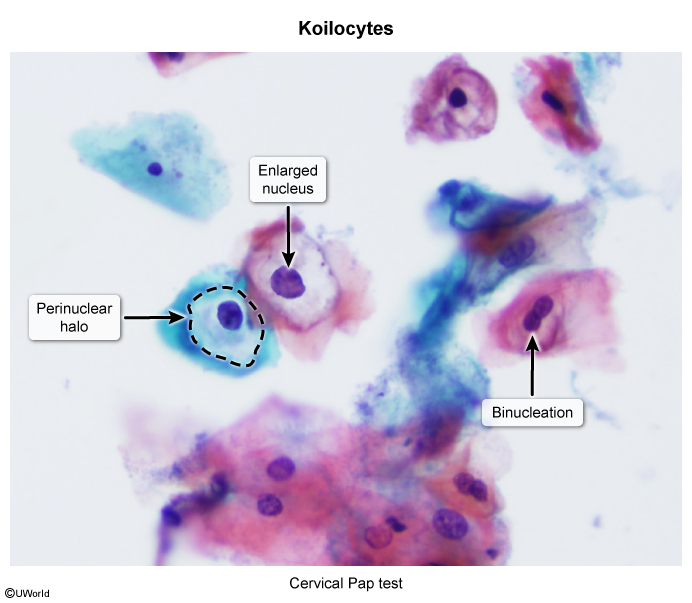
- Dysplastic squamous cells characterized by well-defined, clear, balloon-like, perinuclear halo and hyperchromasia
Nonanogenital manifestations
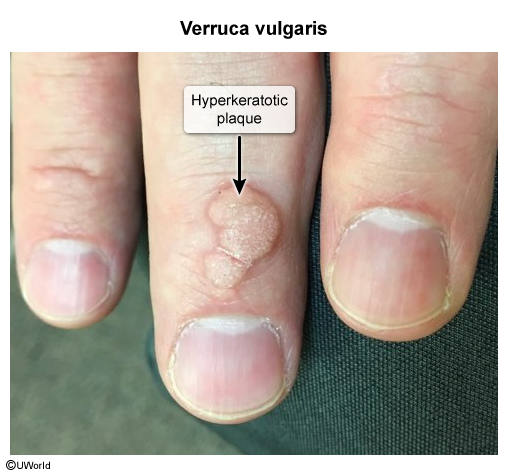
Common warts (verruca vulgaris)
- Pathogen: particularly low-risk HPV types 2 and 4
- Clinical features
- Location: Most common on sites of trauma like fingers, hands, elbows, and knees.
- Lesions are plaques or papules
- Skin-colored or whitish
- Usually firm, often with a rough and scaly surface
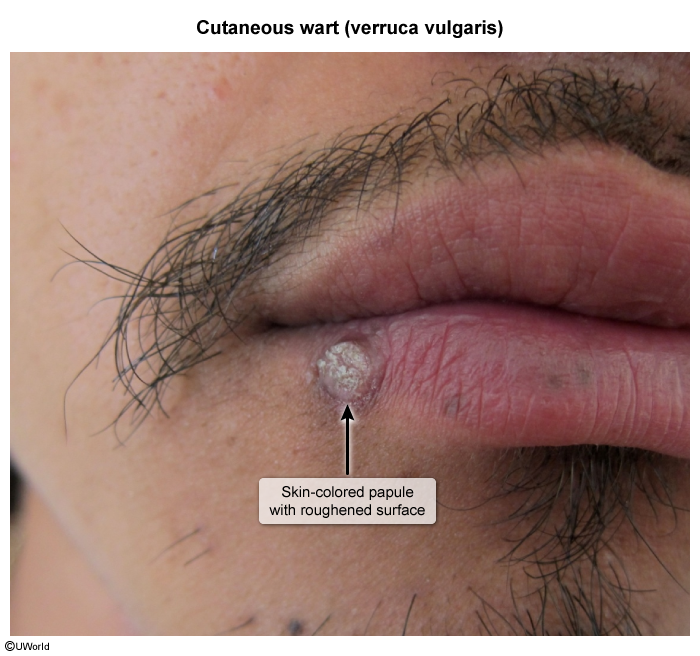
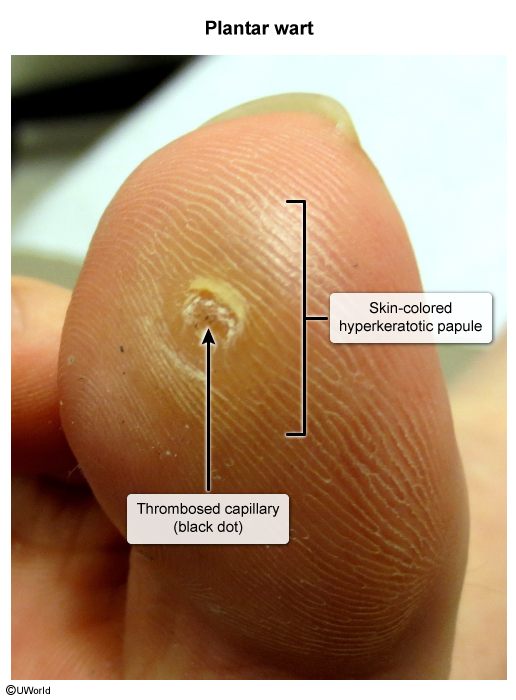
- Sometimes have a cauliflower-like appearance
Anogenital warts (Condylomata acuminata)
- Pathogen: HPV types that infect the mucosal epithelium (e.g., HPV types 6 and 11)
- Clinical features
- Flat, papular, or pedunculated exophytic, cauliflower-like lesions
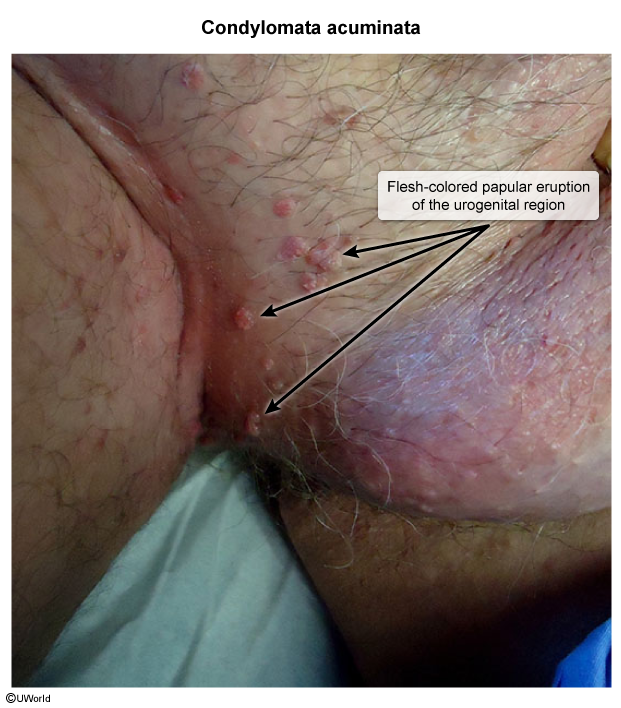
- Located on any part of the anogenital mucosa (e.g., glans penis, vagina, cervix, anal canal) and/or perineal skin
- Typically asymptomatic; occasionally cause pruritus or pain
- Flat, papular, or pedunculated exophytic, cauliflower-like lesions
- If transmit to children during birth: Laryngeal papillomatosis
Diagnostics
- Warts: Clinical diagnosis based on appearance.
- Cervical Cancer Screening:
- Pap Test (Cytology): Detects cellular abnormalities. Hallmark finding for HPV infection is koilocytes (raisin-like, wrinkled nucleus with a perinuclear halo).
- HPV DNA Test: Detects presence of high-risk HPV DNA. Can be done as a primary screen or co-testing with Pap smear.
- Colposcopy: Visualization of the cervix with magnification after acetic acid application (acetowhite changes). Used to guide biopsy for definitive diagnosis of dysplasia (CIN).
- The higher density of nuclear proteins in precancerous (CIN) and cancerous cells leads to a more significant coagulation effect, making these potentially dangerous areas visible as distinct white patches.
- Acetic acid test
- A dilute solution (3-5%) of acetic acid is applied to the cervical epithelium.
- Acetic acid causes temporary, reversible dehydration and coagulation of intracellular proteins.
- Dysplastic cells (e.g., CIN) and cancer cells have a higher nuclear density and more protein compared to normal superficial squamous cells. This high protein content causes them to turn white when exposed to acetic acid.
- Normal mature squamous epithelium has very little protein to coagulate, so its color remains largely unchanged.
Treatment
- Imiquimod
- Local treatment
- Mechanism of action: toll-like receptor 7 agonist → activates immune cells (i.e., macrophages, monocytes, dendritic cells)
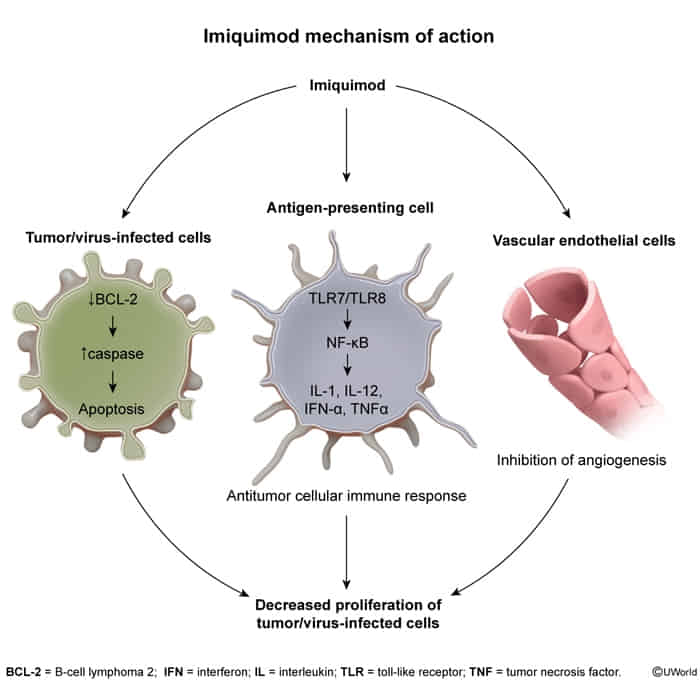
- Indication: actinic keratoses, superficial basal cell carcinomas, herpes simplex infections, and anogenital warts
- Adverse effects: burning pain at application site, dermal rash, pruritus