1. 简介
- Nextflow 是一款基于数据流(dataflow)的生物信息编程框架
- 简化在不同计算平台(本地、集群、云端)编写并行计算流程
- 支持多种编程语言
- 支持多种容器技术
- nf-core 是社区维护的高质量 Nextflow 流程的集合
- 在运行时,使用nextflow调用如nf-core/rnaseq等流程,可实现一行命令运行所有上游分析
2. 安装
Warning
Nextflow需要依赖Java > 17,目前系统安装的版本为JDK 1.8 = Java 8. 因此建议使用mamba创建一个Java环境,后面的所有命令在此环境中运行。
mamba create -n java-env openjdk=17 -y
Nextflow 可以通过以下命令安装:
curl -s https://get.nextflow.io | bash 这个命令会将 nextflow 的可执行文件下载到当前文件夹,然后可以将其移动到 PATH 路径中,如:
mv nextflow ~/bin/ 安装完成后,可以使用 nextflow -v 检查是否安装成功。
3. 使用
3.1 查找需要运行的流程
在Pipelines上可查看nf-core发布的所有流程
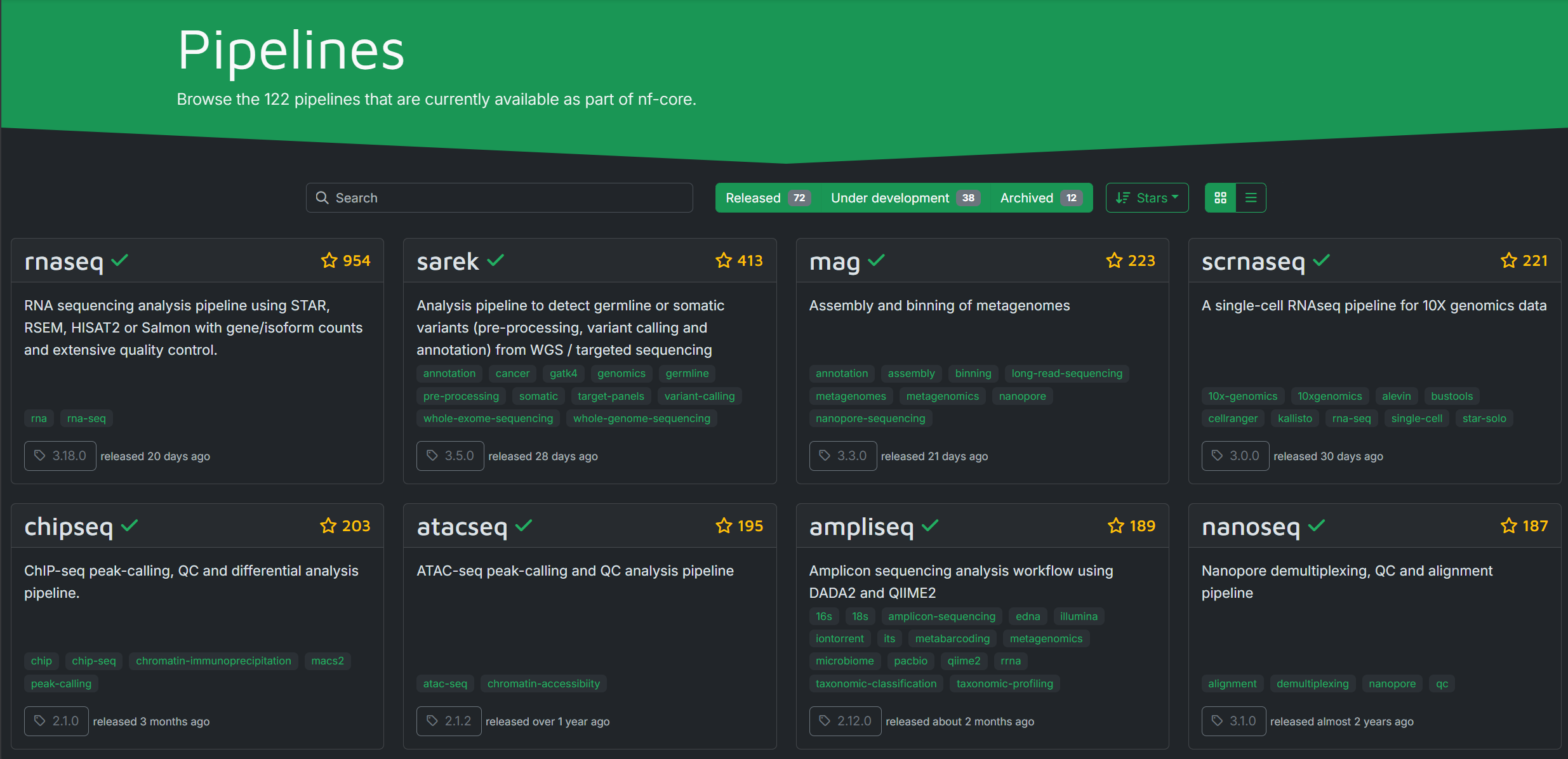 点击可查看该流程包含的步骤、配置和参数
点击可查看该流程包含的步骤、配置和参数
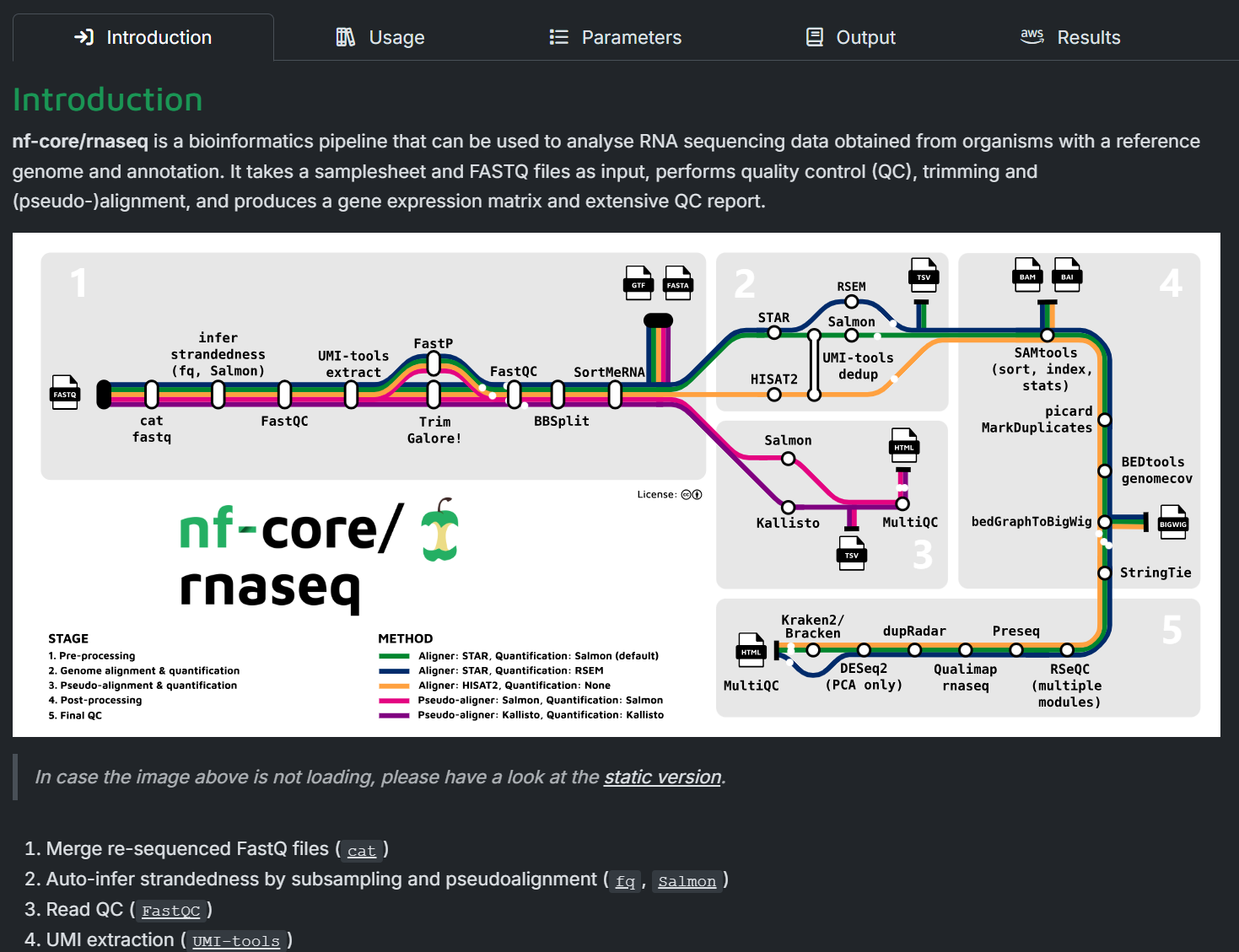 后文均以RNA-seq流程为例
后文均以RNA-seq流程为例
3.2 编写samplesheet.csv
在Usage页面可查看samplesheet.csv的格式,如
sample,fastq_1,fastq_2,strandedness
CONTROL_REP1,AEG588A1_S1_L002_R1_001.fastq.gz,AEG588A1_S1_L002_R2_001.fastq.gz,auto
CONTROL_REP1,AEG588A1_S1_L003_R1_001.fastq.gz,AEG588A1_S1_L003_R2_001.fastq.gz,auto
CONTROL_REP1,AEG588A1_S1_L004_R1_001.fastq.gz,AEG588A1_S1_L004_R2_001.fastq.gz,auto3.3 准备GTF与FASTA
建议使用Refgenie来管理参考基因组,参见refgenie:让基因组参考序列管理更简单高效
也可手动下载
3.4 编写自定义配置文件nf.config(可选)
一般来说,nf-core的默认配置文件可以满足我们的需求。若有额外的自定义需求,可以编写nf.config来完成。
workDir = "data/101.RNA_workflow/work"
process {
// 全局资源限制
resourceLimits = [ cpus: 50, memory: 400.GB]
}
executor {
// 'local' is default executor
name = 'local'
}
params {
// Default Resources
max_memory = 400.GB
max_cpus = 50
}
此处将nextflow运行时产生的临时文件的目录设置为data/101.RNA_workflow/work,将所有任务的最大资源限制设置为cpus: 50, memory: 400.GB,将运行方法设置为local,即只在当前节点运行流程。
若希望同时使用多个节点运行流程,参考下方的“使用Slurm调度作业”。
3.5 运行Nextflow
建议在Screen或tmux等终端复用器上运行此脚本,以防止断开终端造成的流程中断。
#!/bin/bash
nextflow run nf-core/rnaseq \
--input data/01.RawData/samplesheet.csv \
--outdir data/101.RNA_workflow \
--gtf data/reference_data/alias/mm10/gencode_gtf/default/mm10.gtf.gz \
--fasta data/reference_data/alias/mm10/fasta/default/mm10.fa \
--featurecounts_group_type gene_type \
--save_reference \
-profile docker \
-resume \
-c ./nf.config参数解释:
nextflow run nf-core/rnaseq: 运行名为nf-core/rnaseq的 Nextflow 流程。--input data/01.RawData/samplesheet.csv: 指定输入文件为data/01.RawData/samplesheet.csv,该文件包含了样本信息。--outdir data/101.RNA_workflow: 指定输出目录为data/101.RNA_workflow。--gtf data/reference_data/alias/mm10/gencode_gtf/default/mm10.gtf.gz: 指定基因注释文件 (GTF) 的路径。--fasta data/reference_data/alias/mm10/fasta/default/mm10.fa: 指定基因组序列文件 (FASTA) 的路径。--featurecounts_group_type gene_type: 指定 featureCounts 的group-type参数为gene_type。- 若使用gencode的GTF,则此项为
gene_type;若使用ensembl的GTF,则此项为gene_biotype.
- 若使用gencode的GTF,则此项为
--save_reference: 保存生成的index,这样重复运行流程时,会使用上次生成的index.-profile docker: 使用 Docker 运行流程。- 对于本服务器,可选的引擎为
docker或conda,但推荐使用docker.
- 对于本服务器,可选的引擎为
-resume: 断点续跑,继续之前未完成的任务。-c ./nf.config: 指定 Nextflow 的自定义配置文件为./nf.config(如果有的话)。
Tip
若运行时遇到网络问题(通常是GitHub连接不通导致的),参考下方的“解决GitHub连接失败的问题”。
3.6 Debug
若运行时遇到错误,可查看
- 命令行最后输出的错误信息
- 日志文件
.nextflow.log,一般在运行命令时所在的目录- 多次运行流程时,nextflow会产生多个日志。
.nextflow.log为最近一次运行的日志,.nextflow.log.1为上上次运行的日志,以此类推,最多可保存最近10次运行的日志。
- 多次运行流程时,nextflow会产生多个日志。
若遇到困难,可在官方社群的Slack上进行提问。响应很快,一般一天之内就有回复。
4. 其他
4.1 解决GitHub连接失败的问题
在GitHub连接失败的情况下,一般需要修改两个地方来解决问题。
- 修改
~/.nextflow/assets/local/rnaseq/nextflow.config中
custom_config_base = "https://github.com/nf-core/configs/${params.custom_config_version}"
为
custom_config_base = "https://fastly.jsdelivr.net/gh/nf-core/configs@${params.custom_config_version}"
- 将运行的流程clone到本地
git clone https://gitclone.com/github.com/nf-core/rnaseq.git tools/而后修改脚本中的命令为
nextflow run file:/data0/work/guozhonghao/HCC/tools/rnaseq.git \此处似乎只能用绝对路径,请修改上面路径为你的项目的路径。
4.2 使用Slurm调度作业
由于Slurm调度作业时需要耗费一定的时间,因此小样本量使用Slurm运行流程可能反而不如在单节点上快。因此建议只在**单节点的算力明显不足时(如样本量>50-100)**使用Slurm.
4.2.1 (管理员)升级Slurm和系统配置Slurm(建议)
Slurm默认的资源选择是以节点为粒度的资源分配(select/linear),在节点中如果作业申请资源不能全部占满全部核心,就会出现资源超额分配的问题。也就是在实际运行中,一个节点只能同时运行一项任务,无法做到一个节点同时运行多项任务。
独占模式调度策略的优势在于,作业可以获得所分配节点的全部资源,从而实现最佳的并行性能。其缺点是,作业可能会占用大量其自身并不使用的资源,而这些资源也无法与其他作业共享。
Slurm在19.05的版本中,增加了_cons_tres_ Select 插件,可以做到将单个的CPU核、内存、GPU及其它可追踪资源作为可消费资源(消费及分配)。也就是可以根据每项任务所需求的CPU核、内存、GPU数量,将其填充到节点中,做到一个节点中同时运行多个任务,最大化利用资源。
消耗型资源调度策略的优势在于可以显著提升作业吞吐量。集群的整体作业吞吐量和生产力得以提高,从而减少用户等待作业完成的时间,并提升集群的整体使用效率。其缺点是,默认情况下,用户无法独占整个节点来运行其作业。
目前服务器上Slurm版本为18.08.8,没有_cons_tres_ Select 插件,需要升级到新版本。(目前有_cons_res_ Select插件,但只能将单个的CPU核和内存作为可消费资源,无法细致管理GPU,并且不支持_cons_tres_的许多功能)
升级教程
参考
- 升级slurm,从18.08到23.02 - 花花今天没吃药 - 博客园
- Slurm Workload Manager - Upgrade Guide 注意升级时不能一次超过两个大版本,因此需要逐步升级。如上面教程的策略是18.08→20.02→21.08→23.02
修改slurm.conf
修改SelectType=SELECT/LINEAR为
SelectType=select/cons_tres
SelectTypeParameters=CR_Core_Memory
(可选但建议)增加DefMemPerCPU,即默认为每个线程配备的内存量,防止memory oversubscription
# Based on 256GB nodes
# 256GB * 0.95 = 243GB usable
# 243GB * 1024 / 64 ≈ 3,888MB
DefMemPerCPU=3888Tip
可在提交任务时使用
--mem-per-cpu=覆盖此参数
详细解释:
- Slurm Workload Manager - Consumable Resources in Slurm
- Slurm Workload Manager - Sharing Consumable Resources
4.2.2 (用户)在nf.config中配置使用Slurm运行
将nf.config的executor项修改为
executor {
name = 'slurm'
queueSize = 100
pollInterval = '10 sec'
clusterOptions = "--partition=compute,xu-gpu --exclude='xu_cu21,xu_cu23,xu_cu25'"
}
参数解释
name = 'slurm': 指定执行器的名称为slurm.queueSize = 100': 设置提交给 Slurm 调度器的最大作业队列大小为 100。这意味着 Nextflow 一次最多会向 Slurm 提交 100 个作业。如果流程中的任务数量超过 100,Nextflow 会等待直到有作业完成,才会继续提交新的作业。这样可以避免一次性向 Slurm 提交过多作业,导致调度器负载过高。pollInterval = '10 sec': 设置轮询 Slurm 调度器以获取作业状态更新的时间间隔为 10 秒。Nextflow 会每隔 10 秒查询一次 Slurm,检查已提交作业的状态(例如,运行中、已完成、失败等)。clusterOptions = "--partition=compute,xu-gpu --exclude='xu_cu21,xu_cu23,xu_cu25'": 设置传递给 Slurm 的额外选项。这些选项会在 Nextflow 通过sbatch提交作业时添加到命令行中。--partition=compute,xu-gpu: 指定作业提交到名为compute和xu-gpu的分区。--exclude='xu_cu21,xu_cu23,xu_cu25': 排除名为xu_cu21、xu_cu23和xu_cu25的节点。这些节点将不会被 Slurm 用于运行作业。
Warning
- 在使用Slurm运行流程时,参与工作的节点经常存在SSH莫名断开的问题(Connection closed by remote)。因此强烈建议在
--exclude=中增加自己平时工作用的节点。例如我设置的是xu_cu23。xu_cu21、xu_cu25似乎存在网络问题,会导致docker pull出现错误,因此也暂时排除。若后面修复网络问题可再加入这两个节点。