- ABL: Chronic myeloid leukemia
- ALK: Large cell lymphoma, non–small cell lung cancer
- BRAF: Melanoma
- RAF is rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma
- BCL-2: [Non-Hodgkin lymphomas|Follicular lymphoma], Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- BCL-2 mutations are associated with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
- HER1: Squamous cell lung cancer
- HER2/neu: Breast cancer, ovarian cancer
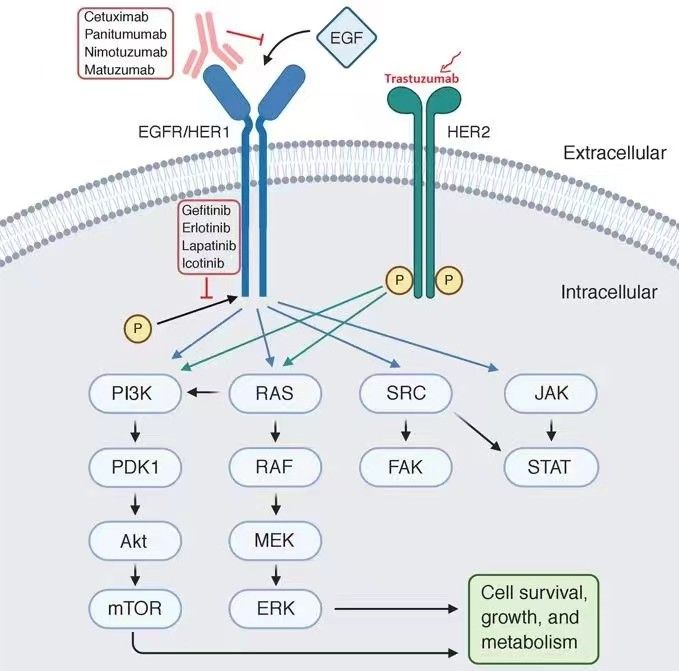
- JAK2: Chronic myeloproliferative disorders.
- Polycythemia Vera (PV) (~95% of cases).
- Essential Thrombocythemia (ET) (~50% of cases).
- Primary Myelofibrosis (MF) (~50% of cases).
- MYC: Neuroblastoma (NMYC), small cell lung cancer (LMYC), Burkitt lymphoma
- RET: Medullary thyroid cancer, pheochromocytoma
- Mutations are associated with MEN2
- KRAS: Colorectal, lung, pancreatic cancers
- EGFR leads to downstream activation of KRAS.
- Signal transducer in MAP-kinase pathway (Growth factors).
- Active = GTP-bound.
- Inactive = GDP-bound.
- Inactivation requires intrinsic GTPase activity (helped by GAPs).

- Defect: Point mutation disables GTPase activity → Ras stays GTP-bound (constitutively active).
Anti-oncogenes (tumor suppressors)

