Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
Heavy ethanol consumption → intrahepatic oxidative damage → recruitment of neutrophils to the liver
Clinical features
- Acute hepatitis: tender hepatomegaly, acute jaundice, malaise, nausea, anorexia, fatigue, fever, weight loss, tachypnea
- Acute alcohol withdrawal: tremor, agitation, tachycardia, alcohol withdrawal seizures, alcohol withdrawal delirium
Diagnostics
LFTs
- AST: > 50 IU/L
- Both AST and ALT: < 400 IU/L
- AST:ALT ratio: > 1.5
- GGT: > 100 IU/L
- ALP: ↑
Mnemonic
AST > ALT in alcoholic hepatitis: Remember “make a toAST with alcohol!”
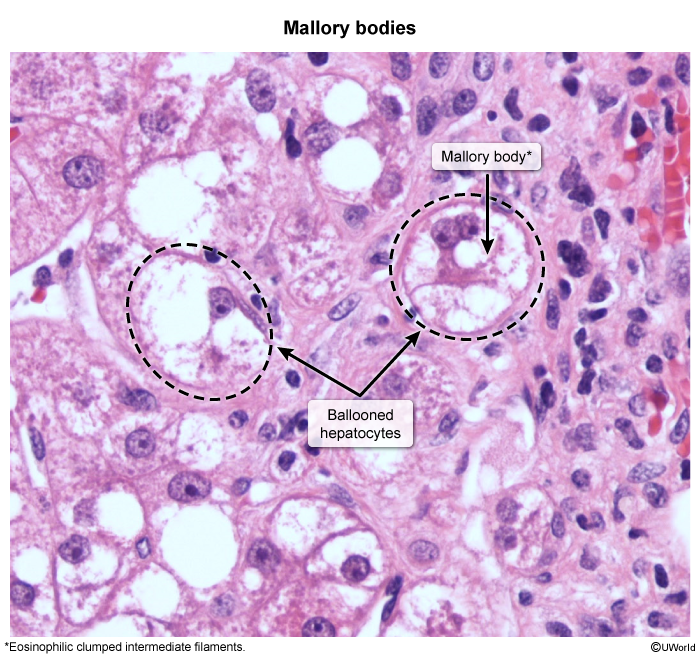
Liver biopsy
- Marked intrahepatic neutrophilic infiltration
- Hepatocellular ballooning
- Mallory bodies
- Steatosis