- Etiology
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis (e.g., due to sinusitis and contiguous spread of infection)
- Carotid-cavernous fistula
- Cavernous sinus tumors
- Clinical features
- Swelling of the conjunctiva
- Proptosis
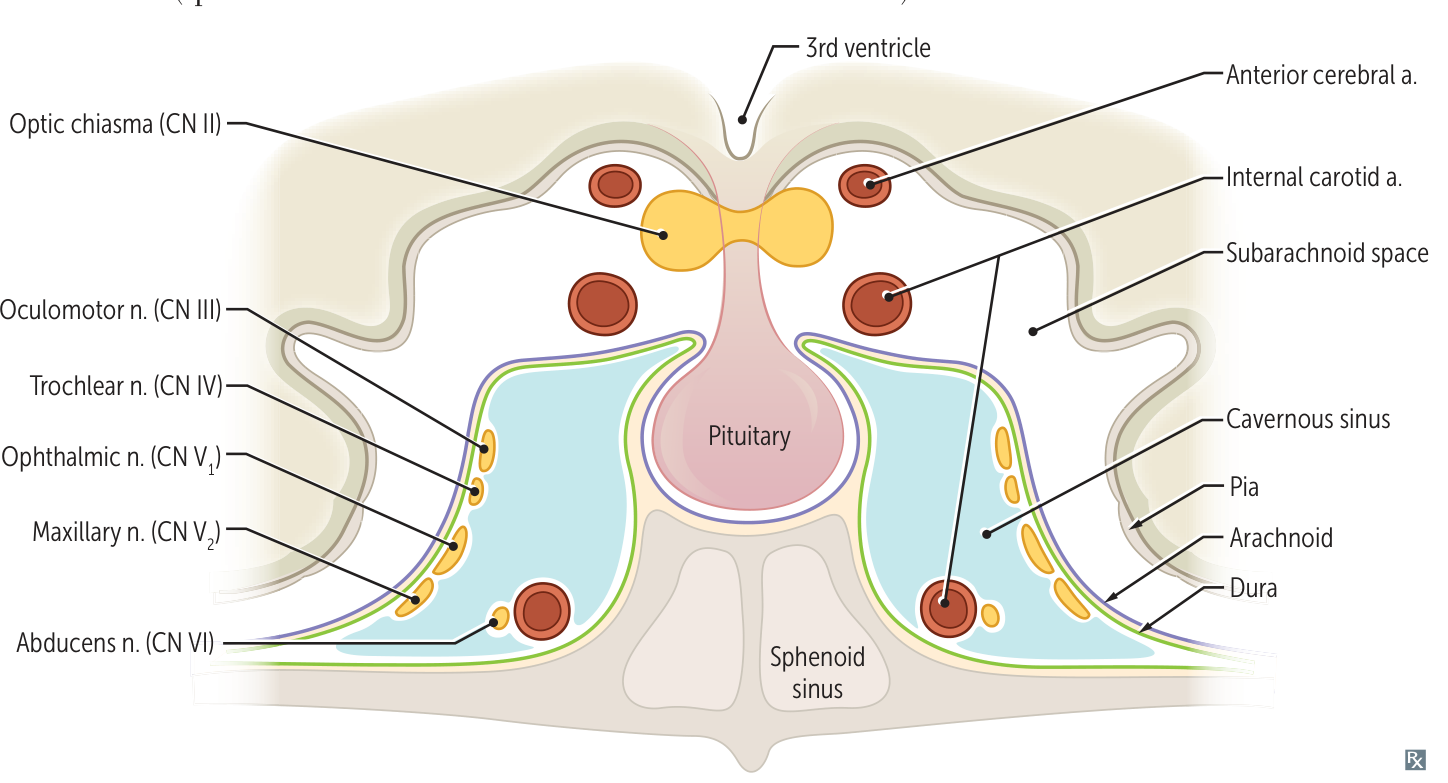
- Signs of CN palsy due to compression (CN III, IV, V-1, V-2, and VI pass through the cavernous sinus)
- Painful ophthalmoplegia: partial/complete paresis of oculomotor nerve (CN III), trochlear nerve (CN IV), and abducens nerve (CN VI)
- Absent corneal reflex: paresis of the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve (V1)
- Loss of upper facial and corneal sensation may occur due to damage to the trigeminal branches of V1 and V2 .
- Horner syndrome
