Definition: inherited genetic disorder characterized by the impaired break down of branched-chain amino acids (BCAA)
Epidemiology
Etiology
autosomal recessive
Pathophysiology
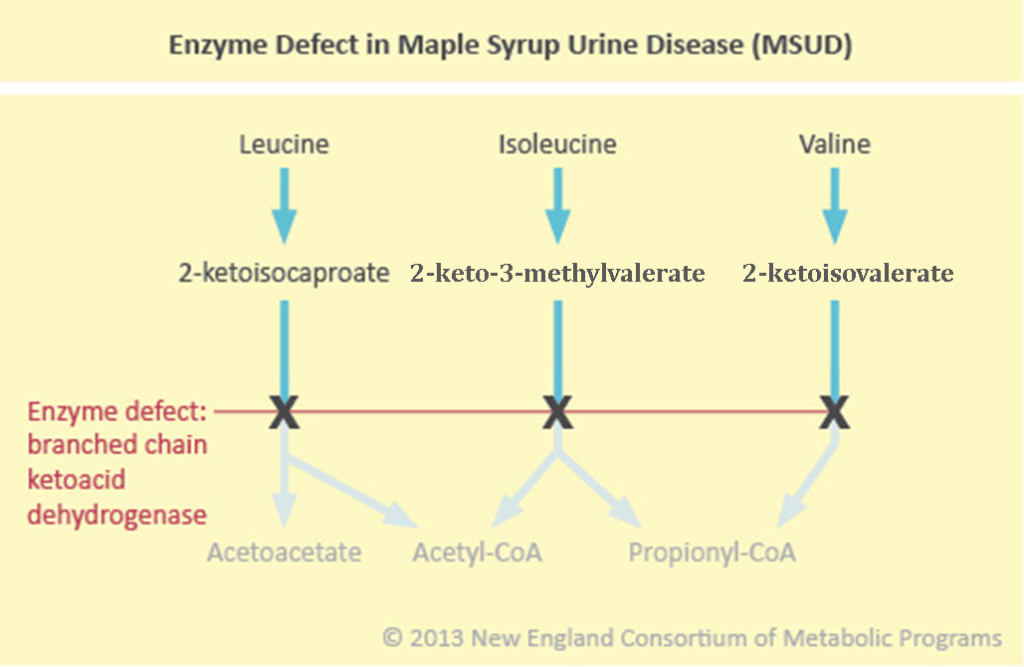
- Absent or deficient branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase → impaired degradation of BCAA (valine, leucine, isoleucine) → elevated α-ketoacid formation
Clinical features
- Symptom onset: early neonatal period
- Vomiting, lethargy, poor feeding
- Sweet-smelling urine (maple syrup or burnt sugar odor)
- Intellectual disability
- Dystonia
- Damage to the CNS can be severe (elevated leucine level leads to brain injury)
- Death may occur without appropriate treatment
Diagnostics
- Serum
- Increased levels of alpha-ketoacids (especially leucine alpha-ketoacids)
Treatment
- Avoid foods containing BCAA
- Supplementation of thiamine, a cofactor of branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase