Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
- Neoplastic proliferation of plasma cells
- Bone marrow infiltration by malignant plasma cells → suppression of hematopoiesis → leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia
- Cell proliferation → pro-osteoclastogenic factors (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1, RANK-L) → osteolytic lesions → hypercalcemia
- Overproduction of monoclonal immunoglobulin and/or light chains → dysproteinemia (a state of pathologically increased synthesis of immunoglobulins and/or their subunits) → kidney damage (e.g., myeloma cast nephropathy) and/or paraprotein tissue deposition (may cause amyloidosis)
- Nonfunctioning antibodies → functional antibody deficiency
- ↑ Serum viscosity → hyperviscosity syndrome
Warning
Hypercalcemia in MM is nor related to PTHrP!
Clinical features
- Often asymptomatic
- Bone pain, especially back pain (most common symptom)
- Symptoms of hypercalcemia, e.g. constipation
- Foamy urine (caused by Bence Jones proteins in urine)
Diagnostics
- Calcium > 11 mg/dL or > 1 mg/dL above the ULN
- Renal insufficiency: GFR < 40 mL/min or serum creatinine > 2 mg/dL
- Anemia: Hb < 10 g/dL or more than 2 g/dL below the LLN
- Normocytic anemia
- Rouleaux formation
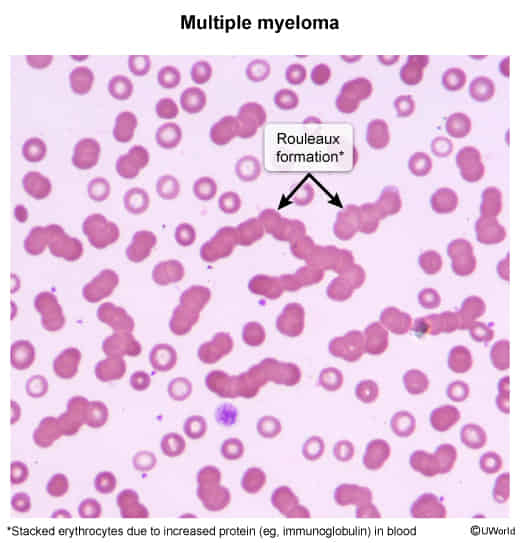
- Bone lesions: ≥ 1 osteolytic lesions on imaging
Bone marrow biopsy
- Cytology: clusters of plasma cells
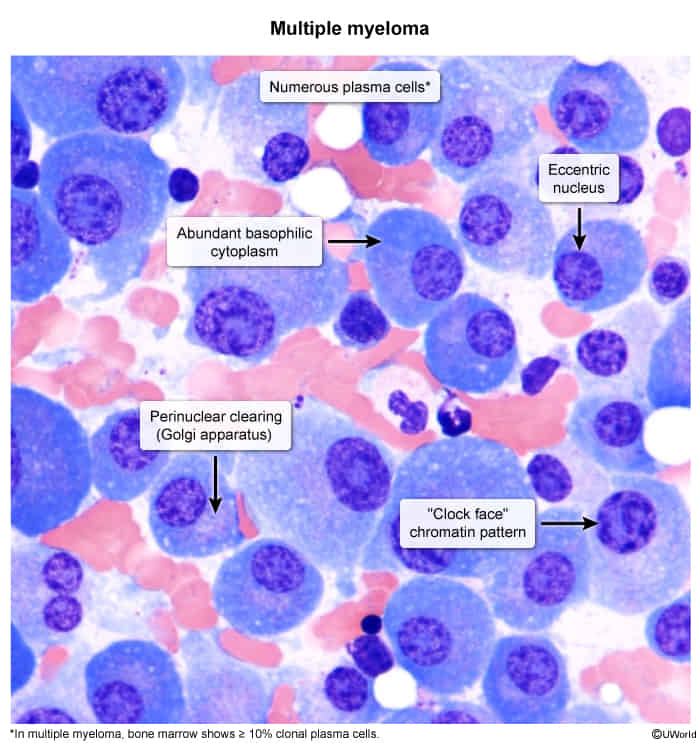
- Mildly organized monoclonal cells
- Perinuclear lucent zone
- Active Golgi apparatus
- Clockface nuclei: Chromatin in the periphery of the nucleus resembles a cartwheel or clock face arrangement.
- Intracytoplasmic crystalline inclusion bodies containing IgG
Treatment
Complications
- Myeloma cast nephropathy (i.e., myeloma kidney): most common cause of renal injury and renal failure in patients with multiple myeloma
- Clinical features: oliguria, peripheral edema, dyspnea
- Pathophysiology: excessive production and filtration of light chains into the urine → precipitation of light chains in renal tubules → tubular obstruction
- Diagnosis: markedly positive urine sulfosalicylic acid test and/or urine protein electrophoresis
- On light microscopy, numerous large, glassy eosinophilic casts are seen.
- May progress to end-stage renal disease (ESRD)
- AL amyloidosis: Light chains can accumulate as amyloids and may lead to restrictive cardiomyopathy, renal insufficiency, macroglossia, and malabsorption syndromes.
- Infections
- Secondary plasma cell leukemia