Overview
- Definition: genetic syndromes caused by microdeletion (at 15q11-q13) in combination with genomic imprinting or uniparental disomy.
- Genomic inprinting: an epigenetic phenomenon that results in silencing of one of the alleles of a gene depending on whether the allele was paternally or maternally inherited.
- The mechanism of silencing is DNA methylation. Affects only a specific subset of genes (estimated to be around 100-200, which is <1% of all human genes).
- Uniparental disomy: a chromosomal abnormality in which offspring receive two copies of one chromosome from one parent and no copies from the other parent
- Genomic inprinting: an epigenetic phenomenon that results in silencing of one of the alleles of a gene depending on whether the allele was paternally or maternally inherited.
- Etiology: The resulting condition depends on the affected gene copy.
- Angelman syndrome
- Deletion or mutation of maternal UBE3A (chromosome 15) gene copy and paternal gene methylation (silencing)
- In ∼ 5% of cases, it results from paternal uniparental disomy (i.e. both copies of chromosome 15 are inherited from the father).
- Prader-Willi syndrome
- Deletion or mutation of paternal gene copy and maternal gene methylation (silencing)
- Caused by maternal uniparental disomy in about 20–35% of cases
- Angelman syndrome
- Diagnosis: genetic tests
- Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
Both syndromes are caused by a loss of gene function in the same region of chromosome 15 (15q11-q13). The resulting phenotype depends on which parental chromosome carries the defect.
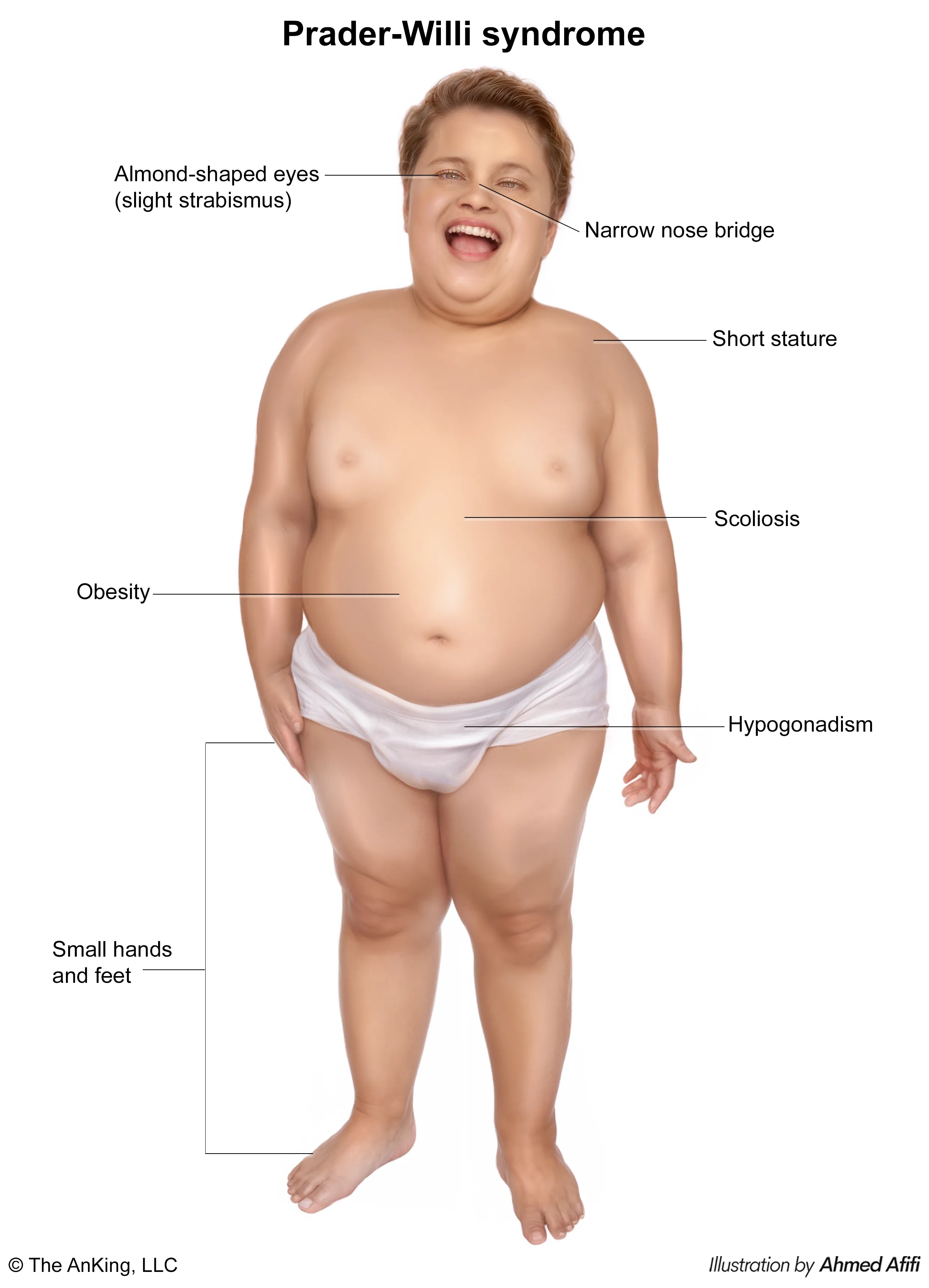
Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS)
- Patho/Etiology
- Prader-Willi = Paternal gene deletion/defect.
- Due to a loss of function of genes that are normally expressed only on the chromosome inherited from the father. This occurs via:
- Deletion of the paternal 15q11-q13 region (~70% of cases).
- Maternal Uniparental Disomy (UPD): The individual inherits two copies of the maternal chromosome 15 and no paternal copy (~25% of cases).
- Clinical Presentation
- Infancy: Severe hypotonia (“floppy baby”), poor suck, and feeding difficulties leading to failure to thrive.
- Childhood: Onset of hyperphagia (insatiable hunger) leading to morbid obesity. This is the most common genetic cause of life-threatening childhood obesity.
- Common Features:
- Mild to moderate intellectual disability.
- Behavioral problems (temper tantrums, skin picking).
- Hypogonadism (underdeveloped genitals, delayed puberty).
- Distinctive facies: narrow forehead, almond-shaped eyes, thin upper lip.
- Small hands and feet.
- Short stature, often due to growth hormone deficiency.
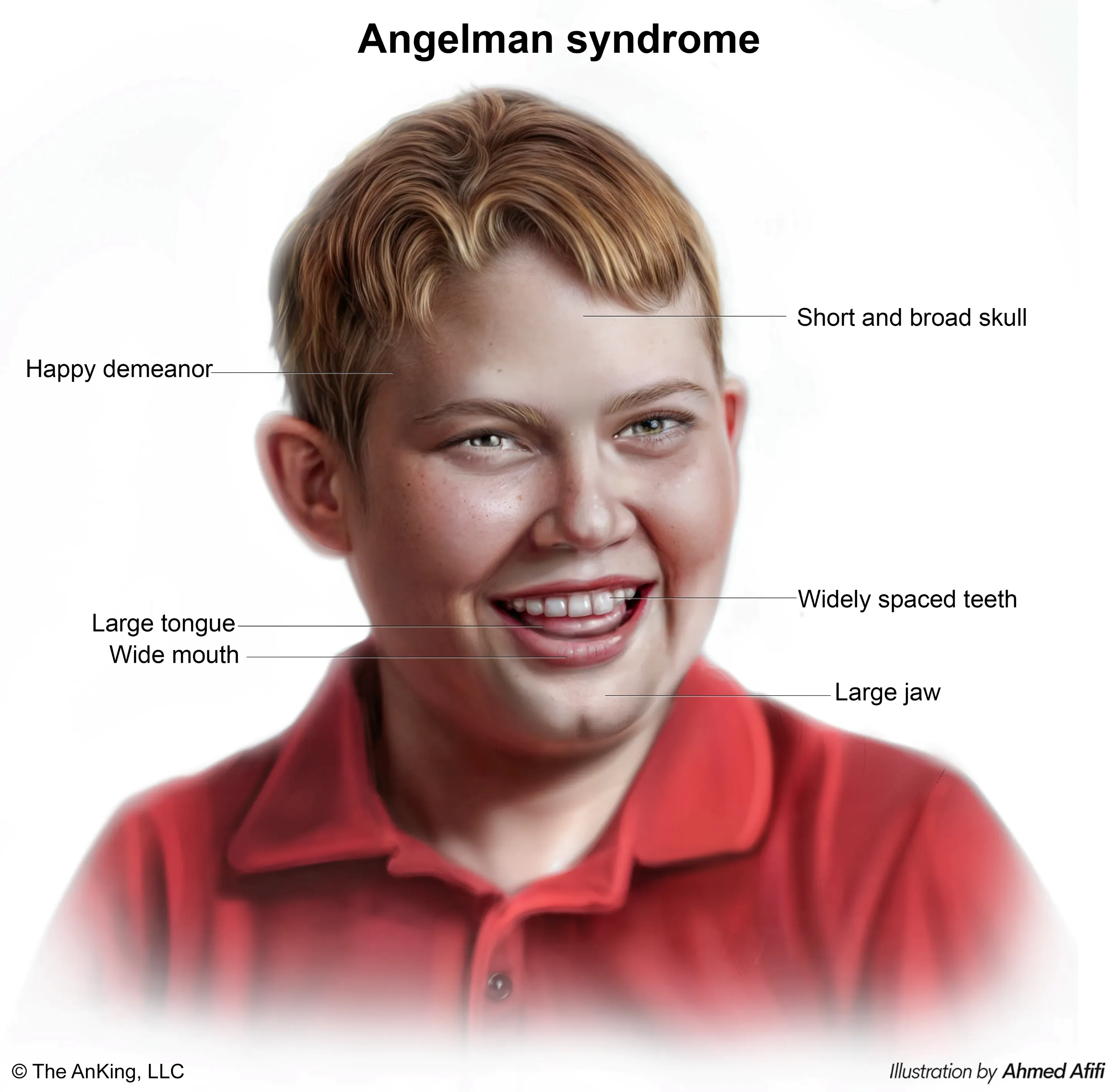
Angelman Syndrome (AS)
- Patho/Etiology
- Angelman = Maternal gene deletion/defect (A and M in the name).
- Due to a loss of function of the UBE3A gene, which is normally expressed only on the chromosome inherited from the mother. This occurs via:
- Deletion of the maternal 15q11-q13 region (~70% of cases).
- Paternal Uniparental Disomy (UPD): The individual inherits two paternal chromosome 15s and no maternal copy.
- Mutation in the maternal UBE3A gene (~11% of cases).
- Clinical Presentation
- “Happy Puppet” is the classic description.
- Common Features:
- Severe intellectual disability.
- Minimal to no speech.
- Seizures are very common.
- Ataxic gait and jerky arm movements (hence “puppet-like”).
- Inappropriate, frequent laughter and a happy demeanor.
- Microcephaly and a flat back of the head.
- Hyperactivity and a short attention span.