- Triad of iron deficiency anemia, postcricoid dysphagia, and upper esophageal webs
- Thin membranes of normal esophageal tissue protrude into the esophagus causing symptoms such as dysphagia, odynophagia, and food impaction.
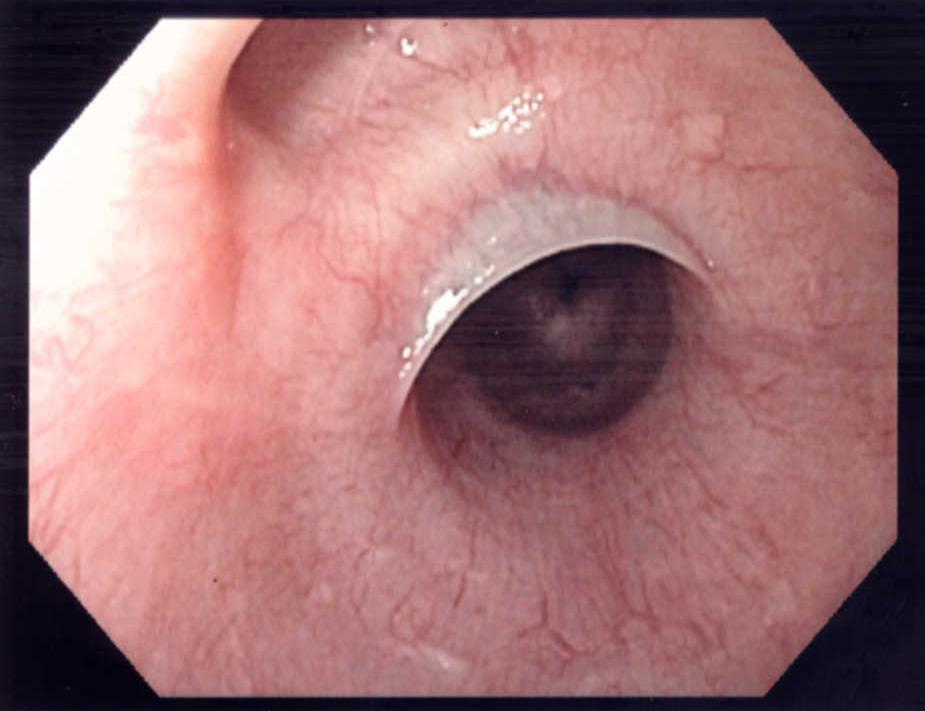
- Acquired esophageal webs are much more common than congenital webs and are mainly observed in Plummer–Vinson syndrome.
- Thin membranes of normal esophageal tissue protrude into the esophagus causing symptoms such as dysphagia, odynophagia, and food impaction.
- Associated with an increased risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and glossitis
- Etiopathogenesis unknown