Epidemiology
Etiology
- Idiopathic (most common cause of peripheral facial nerve palsy): Acute idiopathic peripheral facial palsy is also known as Bell palsy.
- Secondary
- Trauma (e.g., temporal bone fracture)
- Infection
- Herpes zoster (Ramsay Hunt syndrome)
- Borreliosis (Lyme disease)
- HSV reactivation
- HIV
- Malignant otitis externa
- Tumors (parotid gland tumors, acoustic neuroma)
- This nerve exits the skull through the stylomastoid foramen and courses within the substance of the parotid gland.
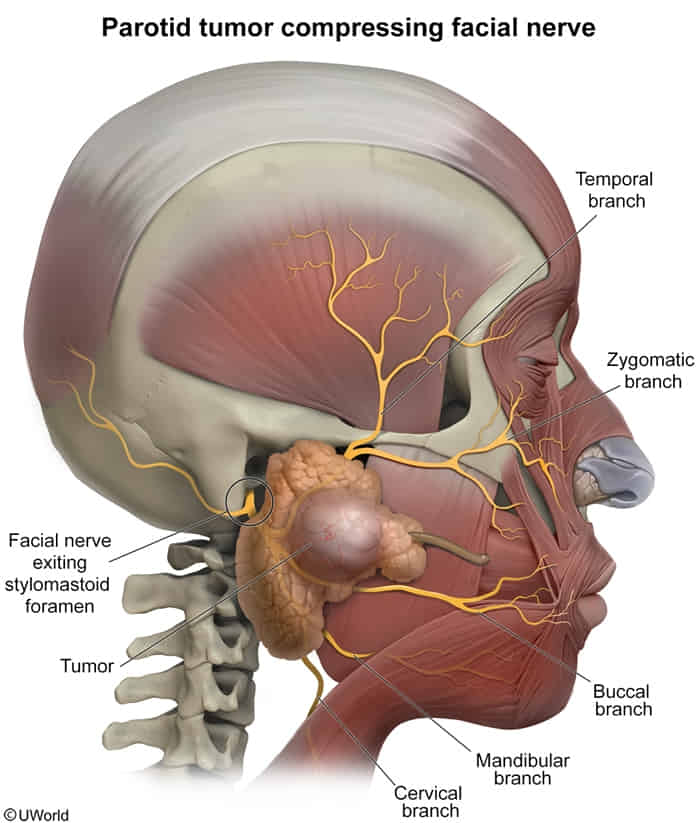
- Facial sensation won’t be affected, since CNV follows a deep course and is unlikely to be damaged by a tumor of the parotid gland.
- This nerve exits the skull through the stylomastoid foramen and courses within the substance of the parotid gland.
- Diabetes mellitus
- Sarcoidosis (Heerfordt syndrome)
Pathophysiology
Functions of facial nerve
- Sensory
- Taste: anterior ⅔ of the tongue (chorda tympani)
- Innervation of:
- Tympanic membrane (chorda tympani)
- Skin behind the ear (posterior auricular branch)
- Motor (somatic)
- Facial expression
- Eyelid closing: orbicularis oculi muscle
- Efferent limb of the corneal reflex (temporal branch, bilaterally)
- Jaw opening: posterior belly of the digastric muscle
- Hyoid elevation: stylohyoid muscle
- Efferent limb of the acoustic reflex (stapedius muscle) → auditory volume modulation
- The stapedius muscle dampens transmission of loud noises to the inner ear (acoustic or stapedial reflex). Stapedius weakness (e.g., due to Bell palsy) can result in hyperacusis (increased sensitivity to environmental sounds, which can also result from ear trauma or middle/inner ear infection)
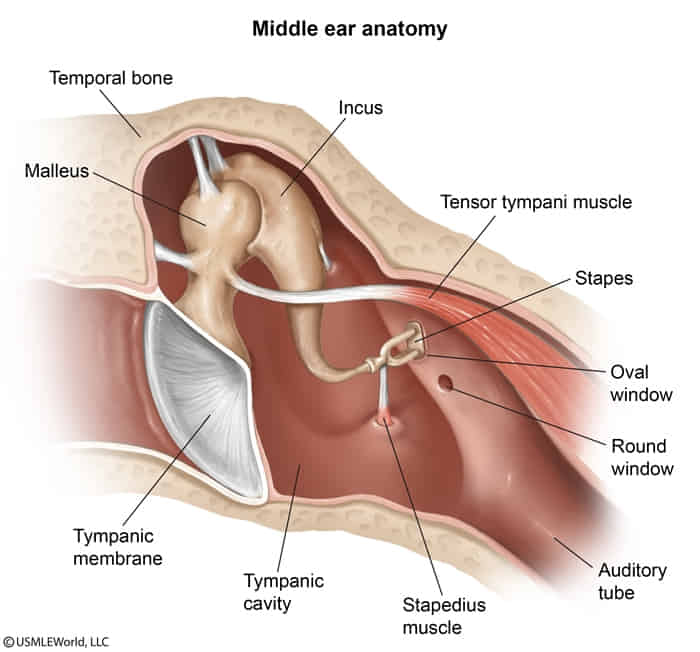
- The stapedius muscle dampens transmission of loud noises to the inner ear (acoustic or stapedial reflex). Stapedius weakness (e.g., due to Bell palsy) can result in hyperacusis (increased sensitivity to environmental sounds, which can also result from ear trauma or middle/inner ear infection)
- Motor (parasympathetic)
- Salivation: submandibular and sublingual glands
- Lacrimation: lacrimal gland
- Efferent limb of the lacrimation reflex
Clinical features
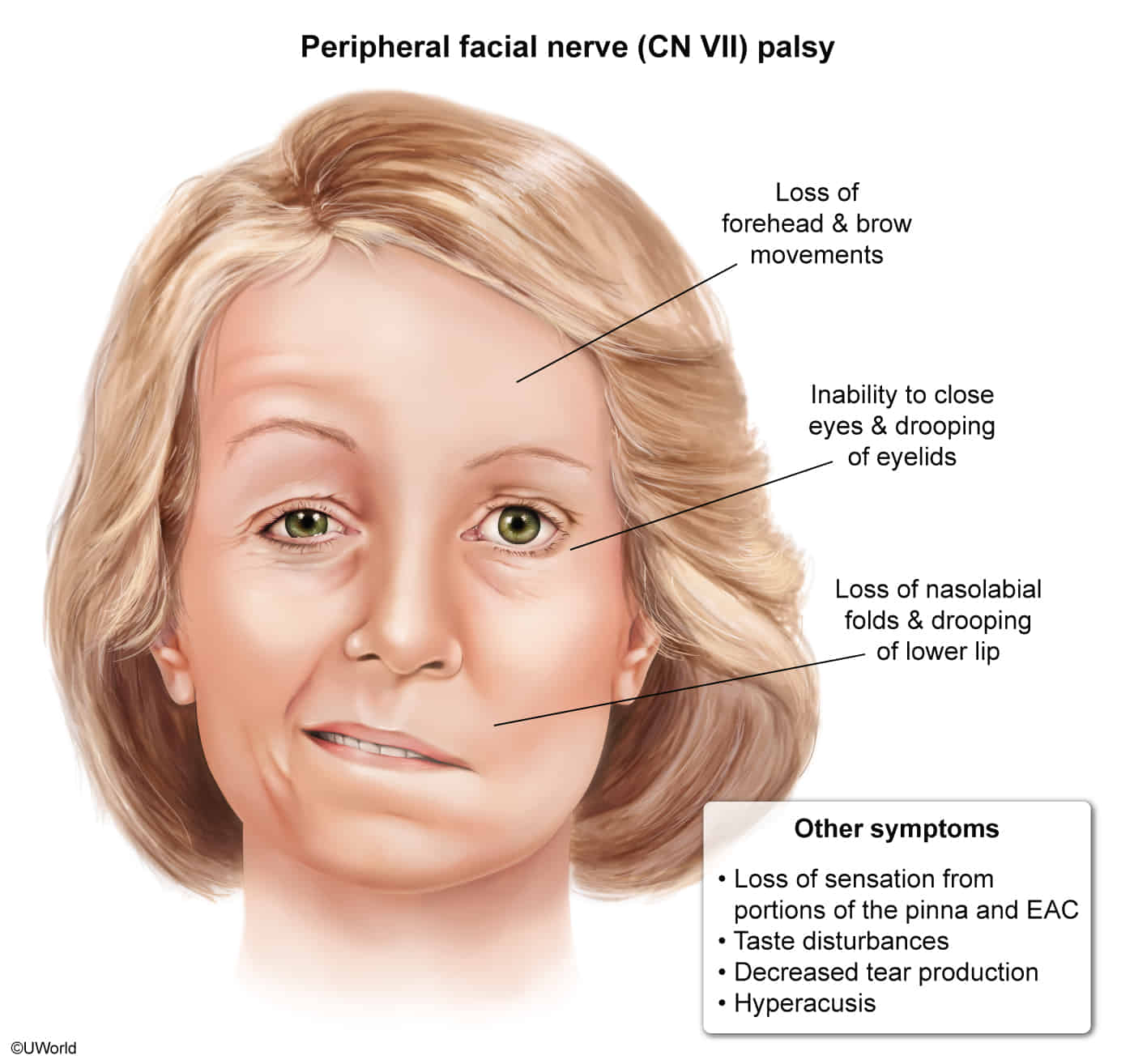
- Sensory disturbances
- Painful sensation around or behind the ear
- Impairment of taste in the anterior tongue
- Hyperacusis
- Dry mouth
- Ocular features
- Lagophthalmos
- Decreased lacrimation
- Corneal ulceration and keratitis
- Facial synkinesis; involuntary movements of the facial muscles; facial spasms while closing the eyes